Page 1022 - TNFlipTest
P. 1022
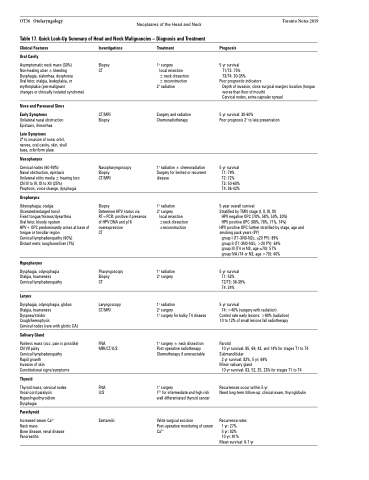
OT36 Otolaryngology Neoplasms of the Head and Neck Table 17. Quick Look-Up Summary of Head and Neck Malignancies – Diagnosis and Treatment
Toronto Notes 2019
Clinical Features
Oral Cavity
Asymptomatic neck mass (30%) Non-healing ulcer ± bleeding Dysphagia, sialorrhea, dysphonia
Oral fetor, otalgia, leukoplakia, or erythroplakia (pre-malignant
changes or clinically isolated syndrome)
Nose and Paranasal Sinus Early Symptoms
Unilateral nasal obstruction Epistaxis, rhinorrhea
Late Symptoms
2o to invasion of nose, orbit, nerves, oral cavity, skin, skull base, cribriform plate
Nasopharynx
Cervical nodes (60-90%)
Nasal obstruction, epistaxis Unilateral otitis media ± hearing loss CN III to VI, IX to XII (25%)
Proptosis, voice change, dysphagia
Oropharynx
Odynophagia, otalgia
Ulcerated/enlarged tonsil
Fixed tongue/trismus/dysarthria
Oral fetor, bloody sputum
HPV+ OPC predominantly arises at base of tongue or tonsillar region
Cervical lymphadenopathy (60%)
Distant mets: lung/bone/liver (7%)
Hypopharynx
Dysphagia, odynophagia Otalgia, hoarseness Cervical lymphadenopathy
Larynx
Dysphagia, odynophagia, globus Otalgia, hoarseness Dyspnea/stridor Cough/hemoptysis
Cervical nodes (rare with glottic CA)
Salivary Gland
Painless mass (occ. pain is possible) CN VII palsy
Cervical lymphadenopathy
Rapid growth
Invasion of skin
Constitutional signs/symptoms
Thyroid
Thyroid mass, cervical nodes Vocal cord paralysis Hyper/hypothyroidism Dysphagia
Parathyroid
Increased serum Ca2+
Neck mass
Bone disease, renal disease Pancreatitis
Investigations
Biopsy CT
CT/MRI Biopsy
Nasopharyngoscopy Biopsy
CT/MRI
Biopsy
Determine HPV status via RT=PCR: positive if presence of HPV DNA and p16 overexpression
CT
Pharyngoscopy Biopsy
CT
Laryngoscopy CT/MRI
FNA MRI/CT/U/S
FNA U/S
Sestamibi
Treatment
1o surgery
local resection
± neck dissection ± reconstruction
2o radiation
Surgery and radiation Chemoradiotherapy
1o radiation ± chemoradiation Surgery for limited or recurrent disease
1o radiation 2o surgery
local resection ±neck dissection ±reconstruction
1o radiation 2o surgery
1o radiation
2o surgery
1o surgery for bulky T4 disease
1o surgery ± neck dissection Post-operative radiotherapy Chemotherapy if unresectable
1o surgery
I131 for intermediate and high risk well differentiated thyroid cancer
Wide surgical excision Post-operative monitoring of serum Ca2+
Prognosis
5 yr survival T1/T2: 75% T3/T4: 30-35%
Poor prognostic indicators
Depth of invasion, close surgical margins location (tongue worse than floor of mouth)
Cervical nodes, extra-capsular spread
5 yr survival: 30-60%
Poor prognosis 2o to late presentation
5 yr survival T1: 79% T2: 72% T3: 50-60% T4: 36-42%
5 year overall survival
Stratified by TMN stage (I, II, III, IV)
HPV negative OPC (70%, 58%, 50%, 30%)
HPV positive OPC (88%, 78%, 71%, 74%)
HPV positive OPC further stratified by stage, age and smoking pack years (PY)
group I (T1-3N0-N2c, ≤20 PY): 89% group II (T1-3N0-N2c, >20 PY): 64% group III (T4 or N3, age ≤70): 57% group IVA (T4 or N3, age >70): 40%
5 yr survival T1: 53% T2/T3: 36-39% T4: 24%
5 yr survival
T4: >40% (surgery with radiation)
Control rate early lesions: >90% (radiation) 10 to 12% of small lesions fail radiotherapy
Parotid
10 yr survival: 85, 69, 43, and 14% for stages T1 to T4
Submandibular
2 yr survival: 82%, 5 yr: 69%
Minor salivary gland
10 yr survival: 83, 52, 25, 23% for stages T1 to T4
Recurrences occur within 5 yr
Need long-term follow-up: clinical exam, thyroglobulin
Recurrence rates 1 yr: 27%
5 yr: 82%
10 yr: 91%
Mean survival: 6-7 yr