Page 1065 - TNFlipTest
P. 1065
Toronto Notes 2019
Endocrinology
Pediatrics P31
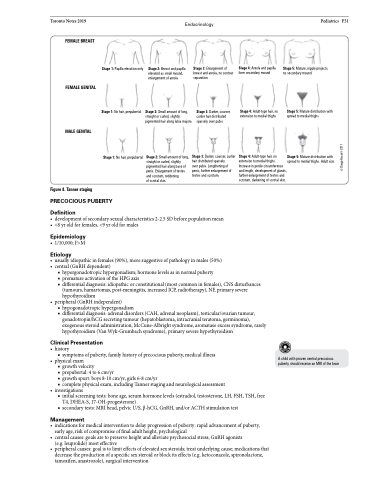
FEMALE BREAST
FEMALE GENITAL
MALE GENITAL
Figure 8. Tanner staging
Stage 3: Enlargement of breast and areola, no contour separation
Stage 3: Darker, coarser, curlier hair distributed sparsely over pubis
Stage 3: Darker, coarser, curlier hair distributed sparsely
over pubis. Lengthening of penis, further enlargement of testes and scrotum.
Stage 4: Areola and papilla form secondary mound
Stage 4: Adult-type hair, no extension to medial thighs
Stage 4: Adult-type hair, no extension to medial thighs. Increase in penile circumference and length, development of glands, further enlargement of testes and scrotum, darkening of scrotal skin.
Stage 1: Papilla elevation only
Stage 1: No hair, prepubertal
Stage 1: No hair, prepubertal
Stage 2: Breast and papilla elevated as small mound, enlargement of areola
Stage 2: Small amount of long, straight or curled, slightly pigmented hair along labia majora
Stage 2: Small amount of long, straight or curled, slightly pigmented hair along base of penis. Enlargement of testes and scrotum, reddening
of scrotal skin.
Stage 5: Mature, nipple projects, no secondary mound
Stage 5: Mature distribution with spread to medial thighs
Stage 5: Mature distribution with spread to medial thighs. Adult size.
PRECOCIOUS PUBERTY
Definition
• developmentofsecondarysexualcharacteristics2-2.5SDbeforepopulationmean • <8yroldforfemales,<9yroldformales
Epidemiology
• 1/10,000; F>M
Etiology
• usuallyidiopathicinfemales(90%),moresuggestiveofpathologyinmales(50%) • central(GnRHdependent)
■ hypergonadotropic hypergonadism; hormone levels as in normal puberty
■ premature activation of the HPG axis
■ differential diagnosis: idiopathic or constitutional (most common in females), CNS disturbances
(tumours, hamartomas, post-meningitis, increased ICP, radiotherapy), NF, primary severe
hypothyroidism
• peripheral(GnRHindependent)
■ hypogonadotropic hypergonadism
■ differential diagnosis: adrenal disorders (CAH, adrenal neoplasm), testicular/ovarian tumour,
gonadotropin/hCG secreting tumour (hepatoblastoma, intracranial teratoma, germinoma), exogenous steroid administration, McCune-Albright syndrome, aromatase excess syndrome, rarely hypothyroidism (Van Wyk-Grumbach syndrome), primary severe hypothyroidism
Clinical Presentation
• history
■ symptoms of puberty, family history of precocious puberty, medical illness
• physicalexam
■ growth velocity
■ prepubertal: 4 to 6 cm/yr
■ growth spurt: boys 8-10 cm/yr, girls 6-8 cm/yr
■ complete physical exam, including Tanner staging and neurological assessment
• investigations
■ initial screening tests: bone age, serum hormone levels (estradiol, testosterone, LH, FSH, TSH, free
T4, DHEA-S, 17-OH-progesterone)
■ secondary tests: MRI head, pelvic U/S, β-hCG, GnRH, and/or ACTH stimulation test
Management
• indicationsformedicalinterventiontodelayprogressionofpuberty:rapidadvancementofpuberty, early age, risk of compromise of final adult height, psychological
• centralcauses:goalsaretopreserveheightandalleviatepsychosocialstress;GnRHagonists (e.g. leuprolide) most effective
• peripheralcauses:goalistolimiteffectsofelevatedsexsteroids;treatunderlyingcause;medicationsthat decrease the production of a specific sex steroid or block its effects (e.g. ketoconazole, spironolactone, tamoxifen, anastrozole), surgical intervention
A child with proven central precocious puberty should receive an MRI of the brain
© Diego Accorsi 2011