Page 1157 - TNFlipTest
P. 1157
Toronto Notes 2019
Breast
Plastic Surgery PL35
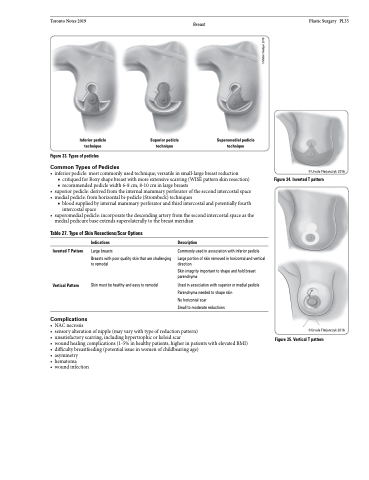
Inferior pedicle technique
Figure 33. Types of pedicles
Common Types of Pedicles
Superior pedicle technique
Superomedial pedicle technique
• inferiorpedicle:mostcommonlyusedtechnique;versatileinsmall-largebreastreduction
■ critiquedforBoxyshapebreastwithmoreextensivescarring(WISEpatternskinresection) ■ recommended pedicle width 6-8 cm, 8-10 cm in large breasts
• superiorpedicle:derivedfromtheinternalmammaryperforatorofthesecondintercostalspace
• medialpedicle:fromhorizontalbi-pedicle(Strombeck)techniques
■ blood supplied by internal mammary perforator and third intercostal and potentially fourth intercostal space
• superomedialpedicle:incorporatethedescendingarteryfromthesecondintercostalspaceasthe medial pedicure base extends superolaterally to the breast meridian
©Ursula Florjanczyk 2016
Figure34.InvertedTpattern
©Ursula Florjanczyk 2016
Figure 35. Vertical T pattern
Table 27. Type of Skin Resections/Scar Options
Inverted T Pattern
Vertical Pattern
Complications
Indications
Large breasts
Breasts with poor quality skin that are challenging to remodel
Skin must be healthy and easy to remodel
Description
Commonly used in association with inferior pedicle
Large portion of skin removed in horizontal and vertical direction
Skin integrity important to shape and hold breast parenchyma
Used in association with superior or medial pedicle Parenchyma needed to shape skin
No horizontal scar
Small to moderate reductions
• NACnecrosis
• sensoryalterationofnipple(mayvarywithtypeofreductionpattern)
• unsatisfactoryscarring,includinghypertrophicorkeloidscar
• woundhealingcomplications(1-5%inhealthypatients,higherinpatientswithelevatedBMI) • difficultybreastfeeding(potentialissueinwomenofchildbearingage)
• asymmetry
• hematoma
• woundinfection
©Midori Nediger 2016