Page 116 - TNFlipTest
P. 116
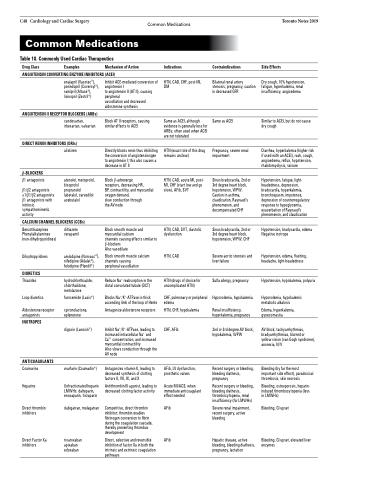
C48 Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery Common Medications Common Medications
Toronto Notes 2019
Dry cough, 10% hypotension, fatigue, hyperkalemia, renal insufficiency, angioedema
Similar to ACEI, but do not cause dry cough
Diarrhea, hyperkalemia (higher risk if used with an ACEI), rash, cough, angioedema, reflux, hypotension, rhabdomyolysis, seizure
Hypotension, fatigue, light- headedness, depression, bradycardia, hyperkalemia, bronchospasm, impotence, depression of counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia, exacerbation of Raynaud’s phenomenon, and claudication
Hypotension, bradycardia, edema Negative inotrope
Hypotension, edema, flushing, headache, light-headedness
Hypotension, hypokalemia, polyuria
Hypovolemia, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis
Edema, hyperkalemia, gynecomastia
AV block, tachyarrhythmias, bradyarrhythmias, blurred or yellow vision (van Gogh syndrome), anorexia, N/V
Bleeding (by far the most important side effect), paradoxical thrombosis, skin necrosis
Bleeding, osteoporosis, heparin- induced thrombocytopenia (less in LMWHs)
Bleeding, GI upset
Bleeding, GI upset, elevated liver enzymes
Table 18. Commonly Used Cardiac Therapeutics
Drug Class Examples Mechanism of Action
ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS (ACEI)
Indications
HTN, CAD, CHF, post-MI, DM
Same as ACEI, although evidence is generally less for ARBs; often used when ACEI are not tolerated
HTN (exact role of this drug remains unclear)
HTN, CAD, acute MI, post- MI, CHF (start low and go slow), AFib, SVT
HTN, CAD, SVT, diastolic dysfunction
HTN, CAD
HTN (drugs of choice for uncomplicated HTN)
CHF, pulmonary or peripheral edema
HTN, CHF, hypokalemia
CHF, AFib
AFib, LV dysfunction, prosthetic valves
Acute MI/ACS; when immediate anticoagulant effect needed
AFib
AFib
Contraindications
Bilateral renal artery stenosis, pregnancy, caution in decreased GFR
Same as ACEI
Pregnancy, severe renal impairment
Sinus bradycardia, 2nd or 3rd degree heart block, hypotension, WPW. Caution in asthma, claudication, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and decompensated CHF
Sinus bradycardia, 2nd or 3rd degree heart block, hypotension, WPW, CHF
Severe aortic stenosis and liver failure
Sulfa allergy, pregnancy
Hypovolemia, hypokalemia
Renal insufficiency, hyperkalemia, pregnancy
2nd or 3rd degree AV block, hypokalemia, WPW
Recent surgery or bleeding, bleeding diathesis, pregnancy
Recent surgery or bleeding, bleeding diathesis, thrombocytopenia, renal insufficiency (for LMWHs)
Severe renal impairment, recent surgery, active bleeding
Hepatic disease, active bleeding, bleeding diathesis, pregnancy, lactation
Side Effects
enalapril (Vasotec®), perindopril (Coversyl®), ramipril (Altace®), lisinopril (Zestril®)
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS (ARBs)
candesartan, irbesartan, valsartan
DIRECT RENIN INHIBITORS (DRIs)
Inhibit ACE-mediated conversion of angiotensin I
to angiotensin II (AT II), causing peripheral
vasodilation and decreased aldosterone synthesis
Block AT II receptors, causing similar effects to ACEI
Directly blocks renin thus inhibiting the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I; this also causes a decrease in AT II
Block β-adrenergic
receptors, decreasing HR,
BP, contractility, and myocardial oxygen demand,
slow conduction through
the AV node
Block smooth muscle and myocardial calcium
channels causing effects similar to β-blockers
Also vasodilate
Block smooth muscle calcium channels causing
peripheral vasodilation
Reduce Na+ reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Blocks Na+/K+-ATPase in thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle
Antagonize aldosterone receptors
Inhibit Na+/K+-ATPase, leading to increased intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ concentration, and increased myocardial contractility
Also slows conduction through the AV node
Antagonizes vitamin K, leading to decreased synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X
Antithrombin III agonist, leading to decreased clotting factor activity
Competitive, direct thrombin inhibitor; thrombin enables fibrinogen conversion to fibrin during the coagulation cascade, thereby preventing thrombus development
Direct, selective and reversible inhibition of factor Xa in both the intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation pathways
β-BLOCKERS
β1 antagonists β1/β2 antagonists
α1/β1/β2 antagonists β1 antagonists with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity
aliskiren
atenolol, metoprolol, bisoprolol propranolol labetalol, carvedilol acebutalol
CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS (CCBs)
Benzothiazepines Phenylalkylamines (non-dihydropyridines)
Dihydropyridines
DIURETICS
Thiazides
Loop diuretics
Aldosterone receptor antagonists
INOTROPES
ANTICOAGULANTS
Coumarins Heparins
Direct thrombin inhibitors
Direct Factor Xa inhibitors
diltiazem verapamil
amlodipine (Norvasc®), nifedipine (Adalat®), felodipine (Plendil®)
hydrochlorthiazide, chlorthalidone, metolazone
furosemide (Lasix®)
spironolactone, eplenerone
digoxin (Lanoxin®)
warfarin (Coumadin®)
Unfractionated heparin LMWHs: dalteparin, enoxaparin, tinzaparin
dabigatran, melagatran
rivaroxaban apixaban edoxaban