Page 1294 - TNFlipTest
P. 1294
RH8 Rheumatology
Connective Tissue Disorders
Toronto Notes 2019
Connective Tissue Disorders
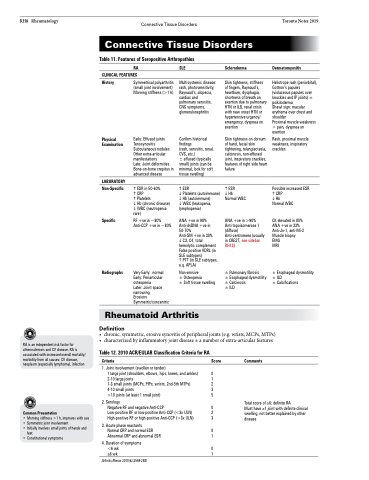
Table 11. Features of Seropositive Arthropathies
RA
CLINICAL FEATURES
SLE
Multisystemic disease: rash, photosensitivity, Raynaud’s, alopecia, cardiac and
pulmonary serositis, CNS symptoms, glomerulonephritis
Confirm historical findings
(rash, serositis, renal, CVS, etc.)
± effused (typically small) joints (can be minimal, look for soft tissue swelling)
ESR
Platelets (autoimmune) Hb (autoimmune) WBC (leukopenia, lymphopenia)
ANA +ve in 98% Anti-dsDNA +ve in 50-70%
Anti-SM +ve in 30% C3, C4, total hemolytic complement False positive VDRL (in SLE subtypes)
PTT (in SLE subtypes, e.g. APLA)
Non-erosive
± Osteopenia
± Soft tissue swelling
Scleroderma
Skin tightness, stiffness of fingers, Raynaud’s, heartburn, dysphagia, shortness of breath on exertion due to pulmonary HTN or ILD, renal crisis with new onset HTN or hypertensive urgency/ emergency, dyspnea on exertion
Skin tightness on dorsum of hand, facial skin tightening, telangiectasia, calcinosis, non-effused joint, inspiratory crackles, features of right side heart failure
ESR
Hb
Normal WBC
ANA +ve in >90% Anti-topoisomerase 1 (diffuse) Anti-centromere (usually in CREST, see sidebar RH13)
± Pulmonary fibrosis
± Esophageal dysmotility ± Calcinosis
± ILD
Dermatomyositis
Heliotrope rash (periorbital), Gottron’s papules (violaceous papules over knuckles and IP joints) ± poikiloderma
Shawl sign: macular erythema over chest and shoulder
Proximal muscle weakness > pain, dyspnea on exertion
Rash, proximal muscle weakness, inspiratory crackles
Possible increased ESR CRP
Hb
Normal WBC
CK elevated in 80% ANA +ve in 33% Anti-Jo-1, anti-Mi-2 Muscle biopsy EMG
MRI
± Esophageal dysmotility ± ILD
± Calcifications
History
Physical Examination
LABORATORY
Non-Specific
Specific
Radiographs
Symmetrical polyarthritis (small joint involvement) Morning stiffness (>1 h)
Early: Effused joints Tenosynovitis Subcutaneous nodules Other extra-articular manifestations
Late: Joint deformities Bone-on-bone crepitus in advanced disease
ESR in 50-60%
CRP
Platelets
Hb (chronic disease) WBC (neutropenia rare)
RF +ve in ~80% Anti-CCP +ve in ~80%
Very Early: normal Early: Periarticular osteopenia
Later: Joint space narrowing
Erosions Symmetric/concentric
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Definition
RA is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis and CV disease. RA is associated with increased overall mortality/ morbidity from all causes: CV disease, neoplasm (especially lymphoma), infection
Common Presentation
• Morning stiffness >1 h, improves with use
• Symmetric joint involvement
• Initially involves small joints of hands and
feet
• Constitutional symptoms
• chronic,symmetric,erosivesynovitisofperipheraljoints(e.g.wrists,MCPs,MTPs) • characterizedbyinflammatoryjointdisease±anumberofextra-articularfeatures
Table 12. 2010 ACR/EULAR Classification Criteria for RA
Criteria Score
1. Joint involvement (swollen or tender)
1 large joint (shoulders, elbows, hips, knees, and ankles) 0 2-10 large joints 1 1-3 small joints (MCPs, PIPs, wrists, 2nd-5th MTPs) 2 4-10 small joints 3 >10 joints (at least 1 small joint) 5
2. Serology
Negative RF and negative Anti-CCP 0 Low-positive RF or low-positive Anti-CCP (<3x ULN) 2 High-positive RF or high-positive Anti-CCP (>3x ULN) 3
3. Acute phase reactants
Normal CRP and normal ESR 0 Abnormal CRP and abnormal ESR 1
4. Duration of symptoms
<6 wk 0 ≥6 wk 1
Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:2569-2581
Comments
Total score of ≥6: definite RA
Must have ≥1 joint with definite clinical swelling, not better explained by other disease