Page 1315 - TNFlipTest
P. 1315
Toronto Notes 2019 Common Medications
Treatment
• non-pharmacologicaltherapy
■ education
■ exercise program (walking, aquatic exercises), physical therapy (good posture, stretching, muscle
strengthening, massage)
■ stress reduction, CBT
■ no evidence for alternative medicine such as biofeedback, meditation, acupuncture
• pharmacologicaltherapy
■ low dose tricyclic antidepressant (e.g. amitriptyline) ◆ for sleep restoration
◆ select those with lower anticholinergic side effects
■ for sleep restoration
■ select those with lower anticholinergic side effects
■ SNRI: duloxetine, milnacipran
■ anticonvulsant: pregabalin, gabapentin
■ analgesics may be beneficial for pain that interferes with sleep (NSAIDs, not narcotics)
Prognosis
• variable;usuallychronic,unlessdiagnosedandtreatedearly
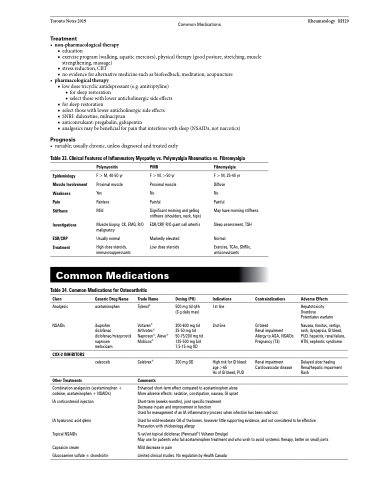
Table 33. Clinical Features of Inflammatory Myopathy vs. Polymyalgia Rheumatica vs. Fibromyalgia
Rheumatology RH29
Epidemiology Muscle Involvement Weakness
Pain
Stiffness
Investigations
ESR/CRP Treatment
Polymyositis
F > M, 40-50 yr Proximal muscle Yes
Painless
Mild
Muscle biopsy, CK, EMG, R/O malignancy
Usually normal
High dose steroids, immunosuppressants
PMR
F > M, >50 yr
Proximal muscle
No
Painful
Significant morning and gelling stiffness (shoulders, neck, hips)
ESR/CRP, R/O giant cell arteritis
Markedly elevated Low dose steroids
Fibromyalgia
F > M, 25-45 yr Diffuse
No
Painful
May have morning stiffness Sleep assessment, TSH
Common Medications
Table 34. Common Medications for Osteoarthritis
Normal
Exercise, TCAs, SNRIs, anticonvulsants
Indications
1st line 2nd line
High risk for GI bleed: age >65
Hx of GI bleed, PUD
Class
Analgesic NSAIDs
COX-2 INHIBITORS
Other Treatments
Generic Drug Name
acetaminophen
ibuprofen
diclofenac diclofenac/misoprostol naproxen
meloxicam
celecoxib
Trade Name
Tylenol®
Voltaren® Arthrotec® Naprosyn®, Aleve® Mobicox®
Celebrex®
Comments
Dosing (PO)
500 mg tid q4h (3 g daily max)
200-600 mg tid 25-50 mg tid 50-75/200 mg tid 125-500 mg bid 7.5-15 mg OD
200 mg OD
Contraindications
GI bleed
Renal impairment Allergy to ASA, NSAIDs Pregnancy (T3)
Renal impairment Cardiovascular disease
Adverse Effects
Hepatotoxicity Overdose Potentiates warfarin
Nausea, tinnitus, vertigo, rash, dyspepsia, GI bleed, PUD, hepatitis, renal failure, HTN, nephrotic syndrome
Delayed ulcer healing Renal/hepatic impairment Rash
Combination analgesics (acetaminophen + codeine, acetaminophen + NSAIDs)
IA corticosteroid injection
IA hyaluronic acid q6mo Topical NSAIDs
Capsaicin cream
Glucosamine sulfate ± chondroitin
Enhanced short-term effect compared to acetaminophen alone More adverse effects: sedation, constipation, nausea, GI upset
Short-term (weeks-months), joint specific treatment
Decrease in pain and improvement in function
Used for management of an IA inflammatory process when infection has been ruled out
Used for mild-moderate OA of the knees, however little supporting evidence, and not considered to be effective Precaution with chicken/egg allergy
% wt/wt topical diclofenac (Pennsaid®) Voltaren Emulgel
May use for patients who fail acetaminophen treatment and who wish to avoid systemic therapy, better on small joints
Mild decrease in pain
Limited clinical studies. No regulation by Health Canada