Page 1350 - TNFlipTest
P. 1350
U32 Urology Penile Complaints
Toronto Notes 2019
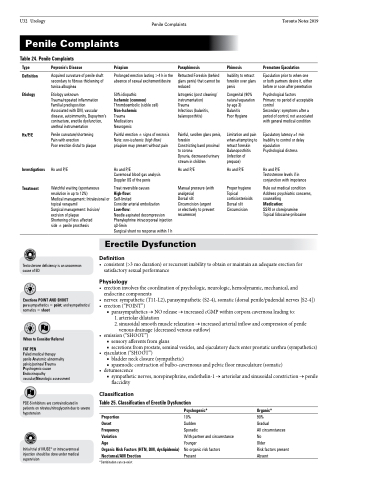
Penile Complaints
Table 24. Penile Complaints
Type
Definition Etiology
Hx/P/E
Investigations Treatment
Peyronie’s Disease
Acquired curvature of penile shaft secondary to fibrous thickening of tunica albuginea
Etiology unknown
Trauma/repeated inflammation Familial predisposition
Associated with DM, vascular disease, autoimmunity, Dupuytren’s contracture, erectile dysfunction, urethral instrumentation
Penile curvature/shortening Pain with erection
Poor erection distal to plaque
Hx and P/E
Watchful waiting (spontaneous resolution in up to 12%)
Medical management: Intralesional or topical verapamil
Surgical management: Incision/ excision of plaque
Shortening of less affected side ± penile prosthesis
Priapism
Prolonged erection lasting >4 h in the absence of sexual excitement/desire
50% idiopathic
Ischemic (common)
Thromboembolic (sickle cell)
Non-Ischemic
Trauma Medications Neurogenic
Painful erection ± signs of necrosis Note: non-ischemic (high flow) priapism may present without pain
Hx and P/E
Cavernosal blood gas analysis Doppler US of the penis
Treat reversible causes
High-flow:
Self-limited
Consider arterial embolization Low-flow:
Needle aspirated decompression Phenylephrine intracorporeal injection q3-5min
Surgical shunt no response within 1 h
Paraphimosis
Retracted Foreskin (behind glans penis) that cannot be reduced
Iatrogenic (post cleaning/ instrumentation)
Trauma
Infectious (balanitis, balanoposthitis)
Painful, swollen glans penis, foreskin
Constricting band proximal to corona
Dysuria, decreased urinary stream in children
Hx and P/E
Manual pressure (with analgesia)
Dorsal slit Circumcision (urgent or electively to prevent recurrence)
Phimosis
Inability to retract foreskin over glans penis
Congenital (90% natural separation by age 3) Balanitis
Poor Hygiene
Limitation and pain when attempting to retract foreskin Balanoposthitis (infection of prepuce)
Hx and P/E
Proper hygiene Topical corticiosterioids Dorsal slit Circumcision
Premature Ejaculation
Ejaculation prior to when one or both partners desire it, either before or soon after penetration
Psychological factors
Primary: no period of acceptable control
Secondary: symptoms after a period of control, not associated with general medical condition
Ejaculatory latency ≥1 min Inability to control or delay ejaculation
Psychological distress
Hx and P/E
Testosterone levels if in conjunction with impotence
Rule out medical condition Address psychiatric concerns, counselling
Medication:
SSRI or clomipramine Topical lidocaine-prilocaine
Erectile Dysfunction
Definition
Testosterone deficiency is an uncommon cause of ED
Erections POINT AND SHOOT parasympathetics = point; and sympathetics/ somatics = shoot
When to Consider Referral
FAT PEN
Failed medical therapy
penile Anatomic abnormality pelvic/perineal Trauma Psychogenic cause Endocrinopathy vascular/Neurologic assessment
PDE-5 inhibitors are contraindicated in patients on nitrates/nitroglycerin due to severe hypotension
Initial trial of MUSE® or intracavernosal injection should be done under medical supervision
• consistent(>3moduration)orrecurrentinabilitytoobtainormaintainanadequateerectionfor satisfactory sexual performance
Physiology
• erectioninvolvesthecoordinationofpsychologic,neurologic,hemodynamic,mechanical,and endocrine components
• nerves: sympathetic (T11-L2), parasympathetic (S2-4), somatic (dorsal penile/pudendal nerves [S2-4]) • erection(“POINT”)
■ parasympathetics→NOrelease→increasedcGMPwithincorporacavernosaleadingto:
1. arteriolar dilatation
2. sinusoidal smooth muscle relaxation → increased arterial inflow and compression of penile
venous drainage (decreased venous outflow) • emission(“SHOOT”)
■ sensoryafferentsfromglans
■ secretionsfromprostate,seminalvesicles,andejaculatoryductsenterprostaticurethra(sympathetics) • ejaculation (“SHOOT”)
■ bladder neck closure (sympathetic)
■ spasmodic contraction of bulbo-cavernosus and pelvic floor musculature (somatic) • detumescence
■ sympathetic nerves, norepinephrine, endothelin-1 → arteriolar and sinusoidal constriction → penile flaccidity
Classification
Table 25. Classification of Erectile Dysfunction
Proportion
Onset
Frequency
Variation
Age
Organic Risk Factors (HTN, DM, dyslipidemia) Nocturnal/AM Erection
*Combination can co-exist
Psychogenic*
10%
Sudden
Sporadic
With partner and circumstance Younger
No organic risk factors Present
Organic*
90%
Gradual
All circumstances No
Older
Risk factors present Absent