Page 1357 - TNFlipTest
P. 1357
Toronto Notes 2019 Pediatric Urology
Treatment
• spontaneousresolutionin60%ofprimaryreflux
■ in lower grades (I-III), goal is to prevent infection or renal damage via medical treatment
• medicaltreatment:dailyABxprophylaxisathalfthetreatmentdoseforacuteinfection(seeTable8- TMP/SMX, trimethoprim, amoxicillin, or nitrofurantoin)
• surgicaltreatment:ureteralreimplantation±ureteroplasty,orsubureteralinjectionwithbulkingagents (Deflux® or Macroplastique®)
■ indications include failure of medical management, renal scarring (e.g. renal insufficiency, HTN), breakthrough UTIs, persistent high grade (IV or V) reflux
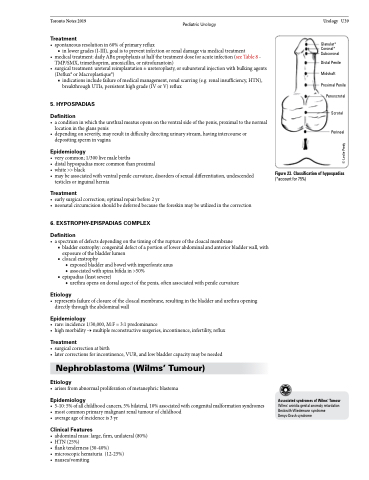
5 . HYPOSPADIAS
Definition
• aconditioninwhichtheurethralmeatusopensontheventralsideofthepenis,proximaltothenormal location in the glans penis
• dependingonseverity,mayresultindifficultydirectingurinarystream,havingintercourseor depositing sperm in vagina
Epidemiology
• verycommon;1/300livemalebirths
• distalhypospadiasmorecommonthanproximal
• white>>black
• maybeassociatedwithventralpenilecurvature,disordersofsexualdifferentiation,undescended
testicles or inguinal hernia
Treatment
• earlysurgicalcorrection;optimalrepairbefore2yr
• neonatalcircumcisionshouldbedeferredbecausetheforeskinmaybeutilizedinthecorrection
6 . EXSTROPHY-EPISPADIAS COMPLEX
Definition
• aspectrumofdefectsdependingonthetimingoftheruptureofthecloacalmembrane
■ bladder exstrophy: congenital defect of a portion of lower abdominal and anterior bladder wall, with
exposure of the bladder lumen
■ cloacal exstrophy
◆ exposed bladder and bowel with imperforate anus
◆ associated with spina bifida in >50%
■ epispadias (least severe)
◆ urethra opens on dorsal aspect of the penis, often associated with penile curvature
Etiology
• representsfailureofclosureofthecloacalmembrane,resultinginthebladderandurethraopening directly through the abdominal wall
Epidemiology
• rare:incidence1/30,000,M:F=3:1predominance
• highmorbidity→multiplereconstructivesurgeries,incontinence,infertility,reflux
Treatment
• surgicalcorrectionatbirth
• latercorrectionsforincontinence,VUR,andlowbladdercapacitymaybeneeded
Nephroblastoma (Wilms’ Tumour)
Etiology
• arisesfromabnormalproliferationofmetanephricblastema
Epidemiology
• 5-10:5%ofallchildhoodcancers,5%bilateral,10%associatedwithcongenitalmalformationsyndromes • mostcommonprimarymalignantrenaltumourofchildhood
• averageageofincidenceis3yr
Clinical Features
• abdominalmass:large,firm,unilateral(80%) • HTN(25%)
• flanktenderness(30-40%)
• microscopic hematuria (12-25%)
• nausea/vomiting
Urology U39
Glanular* Coronal* Subcoronal
Distal Penile Midshaft Proximal Penile
Penoscrotal Scrotal
Perineal
Figure 23. Classification of hypospadias
(*account for 75%)
Associated syndromes of Wilms' Tumour
Wilms' aniridia genital anomaly retardation Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome Denys-Drash syndrome
© Leslie Predy