Page 173 - TNFlipTest
P. 173
Toronto Notes 2019 Nails and Disorders of the Nail Apparatus Dermatology D39
■ central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA): seen in up to 40% of black women, starting at central scalp; one of most commonly diagnosed scarring alopecias, may be associated with hair care practices in this population
Investigations
• biopsyfromactiveborder
Management
• infections:treatunderlyinginfection
• inflammatory:topical/intralesionalsteroids,anti-inflammatoryantibiotics,antimalarials
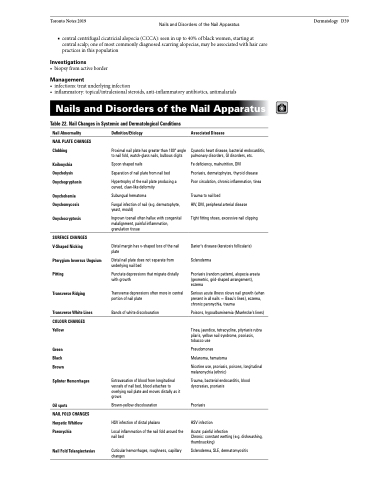
Nails and Disorders of the Nail Apparatus
Table 22. Nail Changes in Systemic and Dermatological Conditions
Nail Abnormality
NAIL PLATE CHANGES Clubbing
Koilonychia Onycholysis Onychogryphosis
Onychohemia Onychomycosis
Onychocryptosis
SURFACE CHANGES V-Shaped Nicking
Pterygium Inversus Unguium Pitting
Transverse Ridging
Transverse White Lines
COLOUR CHANGES Yellow
Green Black Brown
Splinter Hemorrhages
Oil spots
NAIL FOLD CHANGES Herpetic Whitlow Paronychia
Nail Fold Telangiectasias
Definition/Etiology
Proximal nail plate has greater than 180° angle to nail fold, watch-glass nails, bulbous digits
Spoon shaped nails
Separation of nail plate from nail bed
Hypertrophy of the nail plate producing a curved, claw-like deformity
Subungual hematoma
Fungal infection of nail (e.g. dermatophyte, yeast, mould)
Ingrown toenail often hallux with congenital malalignment, painful inflammation, granulation tissue
Distal margin has v-shaped loss of the nail plate
Distal nail plate does not separate from underlying nail bed
Punctate depressions that migrate distally with growth
Transverse depressions often more in central portion of nail plate
Bands of white discolouration
Extravasation of blood from longitudinal vessels of nail bed, blood attaches to overlying nail plate and moves distally as it grows
Brown-yellow discolouration
HSV infection of distal phalanx
Local inflammation of the nail fold around the nail bed
Cuticular hemorrhages, roughness, capillary changes
Associated Disease
Cyanotic heart disease, bacterial endocarditis, pulmonary disorders, GI disorders, etc.
Fe deficiency, malnutrition, DM
Psoriasis, dermatophytes, thyroid disease Poor circulation, chronic inflammation, tinea
Trauma to nail bed
HIV, DM, peripheral arterial disease
Tight fitting shoes, excessive nail clipping
Darier’s disease (keratosis follicularis) Scleroderma
Psoriasis (random pattern), alopecia areata (geometric, grid-shaped arrangement), eczema
Serious acute illness slows nail growth (when present in all nails = Beau’s lines), eczema, chronic paronychia, trauma
Poisons, hypoalbuminemia (Muehrcke’s lines)
Tinea, jaundice, tetracycline, pityriasis rubra pilaris, yellow nail syndrome, psoriasis, tobacco use
Pseudomonas Melanoma, hematoma
Nicotine use, psoriasis, poisons, longitudinal melanonychia (ethnic)
Trauma, bacterial endocarditis, blood dyscrasias, psoriasis
Psoriasis
HSV infection
Acute: painful infection
Chronic: constant wetting (e.g. dishwashing, thumbsucking)
Scleroderma, SLE, dermatomyositis