Page 272 - TNFlipTest
P. 272
E30 Endocrinology
Ôblood glucose, trauma, infection, emotion, circadian rhythm
Adrenal Cortex Toronto Notes 2019 Adrenal Cortex
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
• apolypeptide(cleavedfromprohormonePOMC),secretedinapulsatilefashionfromtheanterior pituitary with diurnal variability (peak: 0200-0400 h; trough: 1800-2400 h)
• secretionregulatedbycorticotropin-releasinghormone(CRH)andargininevasopressin(AVP)
• stimulatesgrowthofadrenalcortexandreleaseofglucocorticoids,androgensand,toaverylimited
extent, mineralocorticoids
• somemelanocytestimulatingactivity
Adrenocortical Hormones
Aldosterone + –
• a mineralocorticoid which regulates extracellular fluid (ECF) volume through Na (and Cl ) retention
and K+ (and H+) excretion (stimulates distal tubule Na+/K+ ATPase)
• regulatedbytherenin-angiotensin-aldosteronesystemandbyhyperkalemia
• negative feedback to juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) by long loop (aldosterone ↑ volume expansion)
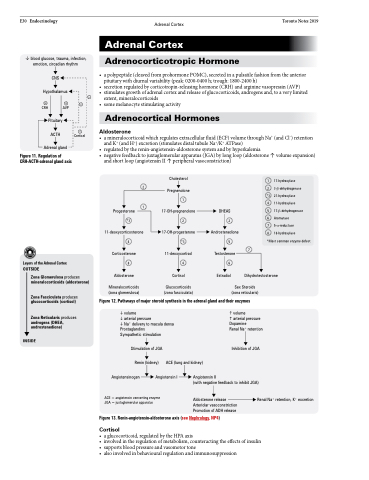
CNS Hypothalamus
CRH
ACTH Adrenal gland
Figure 11. Regulation of CRH-ACTH-adrenal gland axis
Pituitary
AVP
Cortisol
and short loop (angiotensin II ↑ peripheral vasoconstriction) Cholesterol
1 17-hydroxylase
2 3-β-dehydrogenase
*3 21-hydroxylase
4 11-hydroxylase
5 17-β-dehydrogenase
6 Aromatase
7 5-α-reductase
8 18-hydroxylase
*Most common enzyme defect
2
1
Pregnenolone
1
Progesterone 17-OH-pregnenolone DHEAS
*3 2 2
11-deoxycorticosterone
4
Corticosterone
17-OH-progesterone
*3
11-deoxycortisol
Androstenedione
5
Testosterone
7
Layers of the Adrenal Cortex OUTSIDE
846
Zona Glomerulosa produces mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
Aldosterone
Mineralocorticoids (zona glomerulosa)
Cortisol
Glucocorticoids (zona fasciculata)
Estradiol
Dihydrotestosterone
Sex Steroids (zona reticularis)
Zona Fasciculata produces glucocorticoids (cortisol)
Zona Reticularis produces androgens (DHEA, androstenedione)
INSIDE
Figure 12. Pathways of major steroid synthesis in the adrenal gland and their enzymes
volume
arterial pressure
Na+ delivery to macula densa Prostaglandins
Sympathetic stimulation
Stimulation of JGA
Renin (kidney) Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I
ACE = angiotensin converting enzyme JGA = juxtaglomerular apparatus
volume
arterial pressure Dopamine
Renal Na+ retention
Inhibition of JGA
Angiotensin II
(with negative feedback to inhibit JGA)
ACE (lung and kidney)
Figure 13. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis (see Nephrology, NP4)
Cortisol
Aldosterone release Arteriolar vasoconstriction Promotion of ADH release
Renal Na+ retention, K+ excretion
• aglucocorticoid,regulatedbytheHPAaxis
• involvedintheregulationofmetabolism,counteractingtheeffectsofinsulin • supportsbloodpressureandvasomotortone
• alsoinvolvedinbehaviouralregulationandimmunosuppression