Page 285 - TNFlipTest
P. 285
Toronto Notes 2019
Metabolic Bone Disease
Endocrinology E43
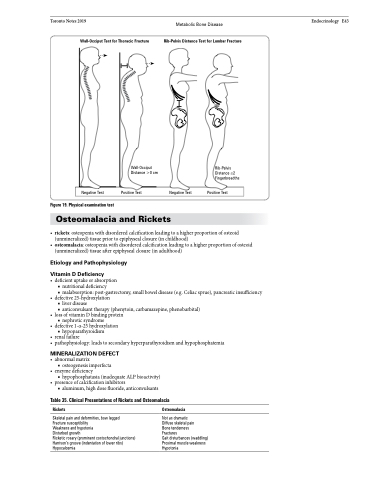
Wall-Occiput Test for Thoracic Fracture
Rib-Pelvis Distance Test for Lumbar Fracture
Wall-Occiput Distance >0 cm
Negative Test Positive Test
Figure 19. Physical examination test
Negative Test
Rib-Pelvis Distance ≤2 Fingerbreadths
Positive Test
Osteomalacia and Rickets
• rickets:osteopeniawithdisorderedcalcificationleadingtoahigherproportionofosteoid (unmineralized) tissue prior to epiphyseal closure (in childhood)
• osteomalacia:osteopeniawithdisorderedcalcificationleadingtoahigherproportionofosteoid (unmineralized) tissue after epiphyseal closure (in adulthood)
Etiology and Pathophysiology
Vitamin D Deficiency
• deficientuptakeorabsorption
■ nutritional deficiency
■ malabsorption: post-gastrectomy, small bowel disease (e.g. Celiac sprue), pancreatic insufficiency
• defective25-hydroxylation ■ liver disease
■ anticonvulsant therapy (phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital) • lossofvitaminDbindingprotein
■ nephrotic syndrome
• defective1-α-25hydroxylation
■ hypoparathyroidism • renalfailure
• pathophysiology:leadstosecondaryhyperparathyroidismandhypophosphatemia
MINERALIZATION DEFECT
• abnormalmatrix
■ osteogenesis imperfecta
• enzymedeficiency
■ hypophosphatasia (inadequate ALP bioactivity)
• presenceofcalcificationinhibitors
■ aluminum, high dose fluoride, anticonvulsants
Table 35. Clinical Presentations of Rickets and Osteomalacia
Rickets
Skeletal pain and deformities, bow legged Fracture susceptibility
Weakness and hypotonia
Disturbed growth
Ricketic rosary (prominent costochondral junctions) Harrison’s groove (indentation of lower ribs) Hypocalcemia
Osteomalacia
Not as dramatic
Diffuse skeletal pain
Bone tenderness
Fractures
Gait disturbances (waddling) Proximal muscle weakness Hypotonia