Page 376 - TNFlipTest
P. 376
G26 Gastroenterology
Small and Large Bowel
Toronto Notes 2019
Yes
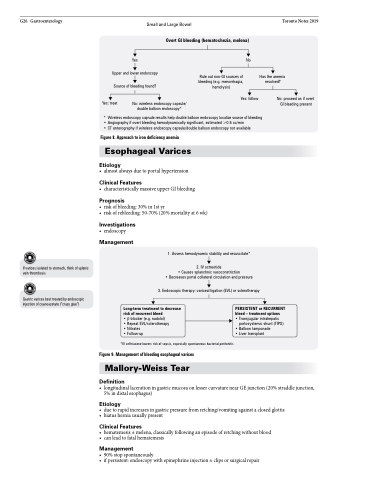
Upper and lower endoscopy Source of bleeding found?
Yes: treat No: wireless endoscopy capsule/ double balloon endoscopy*
No
Overt GI bleeding (hematochezia, melena)
Rule out non-GI sources of bleeding (e.g. menorrhagia, hemolysis)
Has the anemia resolved?
No: proceed as if overt GI bleeding present
* Wireless endoscopy capsule results help double balloon endoscopy localize source of bleeding • Angiography if overt bleeding hemodynamically significant, estimated >0.5 cc/min
• CT enterography if wireless endoscopy capsule/double balloon endoscopy not available
Figure 8. Approach to iron deficiency anemia
Esophageal Varices
Etiology
• almostalwaysduetoportalhypertension
Clinical Features
• characteristicallymassiveupperGIbleeding
Prognosis
• riskofbleeding:30%in1styr
• riskofrebleeding:50-70%(20%mortalityat6wk)
Yes: follow
Investigations
• endoscopy
Management
If varices isolated to stomach, think of splenic vein thrombosis
Gastric varices best treated by endoscopic injection of cyanoacetate (“crazy glue”)
1. Assess hemodynamic stability and resuscitate*
2. IV octreotide
• Causes splanchnic vasoconstriction
• Decreases portal collateral circulation and pressure
3. Endoscopic therapy: variceal ligation (EVL) or sclerotherapy
Long-term treatment to decrease risk of recurrent bleed
• β-blocker (e.g. nadolol)
• Repeat EVL/sclerotherapy
• Nitrates • Follow-up
*IV ceftriaxone lowers risk of sepsis, especially spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Figure 9. Management of bleeding esophageal varices
Mallory-Weiss Tear
Definition
PERSISTENT or RECURRENT bleed – treatment options
• Transjugular intrahepatic
portosystemic shunt (TIPS) • Balloon tamponade
• Liver transplant
• longitudinallacerationingastricmucosaonlessercurvaturenearGEjunction(20%straddlejunction, 5% in distal esophagus)
Etiology
• duetorapidincreasesingastricpressurefromretching/vomitingagainstaclosedglottis • hiatusherniausuallypresent
Clinical Features
• hematemesis±melena,classicallyfollowinganepisodeofretchingwithoutblood • canleadtofatalhematemesis
Management
• 90%stopspontaneously
• ifpersistent:endoscopywithepinephrineinjection±clipsorsurgicalrepair