Page 381 - TNFlipTest
P. 381
Toronto Notes 2019
Liver
Gastroenterology G31
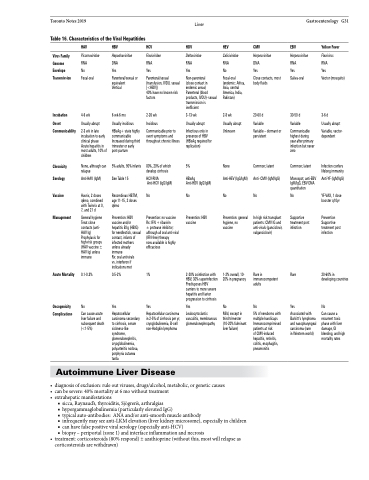
Table 16. Characteristics of the Viral Hepatitides
Virus Family Genome Envelope Transmission
Incubation
Onset Communicability
Chronicity Serology
Vaccine
Management
Acute Mortality
Oncogenicity Complications
HAV
Picornaviridae
RNA
No Fecal-oral
4-6 wk
Usually abrupt
2-3 wk in late incubation to early clinical phase Acute hepatitis in most adults, 10% of children
None, although can relapse
Anti-HAV (IgM)
Havrix, 2 doses q6mo, combined with Twinrix at 0, 7,and21d
General hygiene Treat close contacts (anti- HAV Ig) Prophylaxis for high-risk groups (HAV vaccine ± HAV Ig) unless immune
0.1-0.3%
No
Can cause acute liver failure and subsequent death (<1-5%)
HBV
Hepadnaviridae
DNA Yes
Parenteral/sexual or equivalent
Vertical
6 wk-6 mo
Usually insidious
HBsAg+ state highly communicable Increased during third trimester or early post-partum
5% adults, 90% infants See Table 15
Recombivax HBTM, age 11-15, 2 doses q6mo
Prevention: HBV vaccine and/or hepatitis B Ig (HBIG) for needlestick, sexual contact, infants of infected mothers unless already immune
Rx: oral antivirals vs. interferon if indications met
0.5-2%
Yes
Hepatocellular carcinoma secondary to cirrhosis, serum sickness-like syndrome, glomerulonephritis, cryoglobulinemia, polyarteritis nodosa, porphyria cutanea tarda
HCV
Flaviviridae
RNA Yes
Parenteral/sexual (transfusion, IVDU, sexual [<HBV])
40% have no known risk factors
2-26 wk
Insidious
Communicable prior to overt symptoms and throughout chronic illness
80%, 20% of which develop cirrhosis
HCV-RNA Anti-HCV (IgG/IgM)
No
Prevention: no vaccine Rx: IFN + ribavirin
± protease inhibitor; although all oral anti-viral (IFN-free) therapy
now available is highly efficacious
1%
Yes
Hepatocellular carcinoma in 2-5% of cirrhosis per yr, cryoglobulinemia, B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
HDV
Deltaviridae
RNA
Yes
Non-parenteral
(close contact in endemic areas) Parenteral (blood products, IVDU)- sexual transmission is inefficient
3-13 wk
Usually abrupt
Infectious only in presence of HBV (HBsAg required for replication)
5%
HBsAg
Anti-HDV (IgG/IgM)
No
Prevention: HBV vaccine
2-20% coinfection with HBV, 30% superinfection Predisposes HBV carriers to more severe hepatitis and faster progression to cirrhosis
Yes
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis, membranous glomerulonephropathy
HEV
Caliciviridae
RNA No
Fecal-oral (endemic: Africa, Asia, central America, India, Pakistan)
2-8 wk
Usually abrupt Unknown
None
Anti-HEV (IgG/IgM)
No
Prevention: general hygiene, no vaccine
1-2% overall, 10- 20% in pregnancy
No
Mild, except in third trimester (10-20% fulminant liver failure)
CMV
Herpesviridae
DNA Yes
Close contacts, most body fluids
20-60 d
Variable
Variable – dormant or persistent
Common; latent Anti- CMV (IgM/IgG)
No
In high risk transplant patients: CMV IG and anti-virals (ganciclovir, valganciclovir)
Rare in immunocompetent adults
No
5% of newborns with multiple handicaps Immunocomprimised patients at risk
of CMV-induced hepatitis, retinitis, colitis, esophagitis, pneumonitis
EBV
Herpesviridae
RNA
Yes Saliva-oral
30-50 d
Variable
Communicable highest during year after primary infection but never zero
Common; latent
Monospot; anti-EBV IgM/IgG, EBV DNA quantitation
No
Supportive treatment post infection
Rare
Yes
Associated with Burkitt’s lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (rare
in Western world)
Yellow Fever
Flavivirus
RNA
Yes
Vector (mosquito)
3-6d
Usually abrupt
Variable, vector- dependent
Infection confers lifelong immunity
Anti-YF (IgM/IgG)
YF-VAX, 1 dose booster q10yr
Prevention Supportive treatment post infection
20-60% in developing countries
No
Can cause a recurrent toxic phase with liver damage, GI bleeding, and high mortality rates
Autoimmune Liver Disease
• diagnosisofexclusion:ruleoutviruses,drugs/alcohol,metabolic,orgeneticcauses
• canbesevere:40%mortalityat6mowithouttreatment
• extrahepaticmanifestations
■ sicca, Raynaud’s, thyroiditis, Sjögren’s, arthralgias
■ hypergammaglobulinemia (particularly elevated IgG)
■ typical auto-antibodies: ANA and/or anti-smooth muscle antibody
■ infrequently may see anti-LKM elevation (liver kidney microsome), especially in children ■ can have false positive viral serology (especially anti-HCV)
■ biopsy – periportal (zone 1) and interface inflammation and necrosis
• treatment:corticosteroids(80%respond)±azathioprine(withoutthis,mostwillrelapseas corticosteroids are withdrawn)