Page 442 - TNFlipTest
P. 442
GS40 General Surgery and Thoracic Surgery Anorectum Toronto Notes 2019 Anorectal Abscess
Definition
• infectiontypicallyoriginatingwithinanobstructedanalcryptwhichformsanabscess
• commonbacterial:E.coli,Proteus,Streptococci,Staphylococci,Bacteroides,andanaerobes
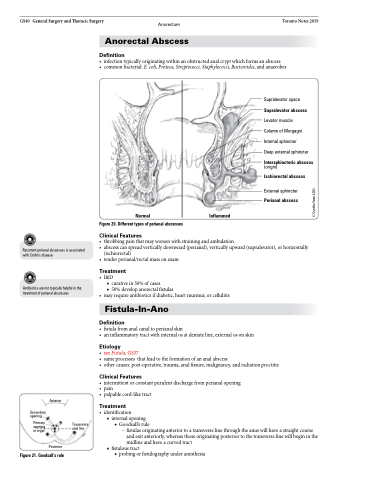
Supralevator space
Supralevator abscess
Levator muscle
Column of Morgagni
Internal sphincter
Deep external sphincter
Intersphincteric abscess
(origin)
Ischiorectal abscess
External sphincter
Perianal abscess
Normal
Figure 20. Different types of perianal abscesses
Clinical Features
Inflammed
Recurrent perianal abscesses is associated with Crohn’s disease
Antibiotics are not typically helpful in the treatment of perianal abscesses
• throbbingpainthatmayworsenwithstrainingandambulation
• abscesscanspreadverticallydownward(perianal),verticallyupward(supralevator),orhorizontally
(ischiorectal)
• tenderperianal/rectalmassonexam
Treatment
• I&D
■ curative in 50% of cases
■ 50% develop anorectal fistulas
• mayrequireantibioticsifdiabetic,heartmurmur,orcellulitis
Fistula-In-Ano
Definition
• fistulafromanalcanaltoperianalskin
• aninflammatorytractwithinternalosatdentateline,externalosonskin
Etiology
• seeFistula,GS37
• same processes that lead to the formation of an anal abscess
• othercauses:post-operative,trauma,analfissure,malignancy,andradiationproctitis
Clinical Features
• intermittentorconstantpurulentdischargefromperianalopening • pain
• palpablecord-liketract
Treatment
• identification
■ internal opening
◆ Goodsall’s rule
– fistulas originating anterior to a transverse line through the anus will have a straight course
and exit anteriorly, whereas those originating posterior to the transverse line will begin in the
midline and have a curved tract ■ fistulous tract
Secondary opening
Primary opening in crypt
Anterior
Posterior
Transverse anal line
Figure 21. Goodsall’s rule
◆ probing or fistulography under anesthesia
© Cynthia Yoon 2003