Page 490 - TNFlipTest
P. 490
GY4 Gynecology Menstruation Toronto Notes 2019 Menstruation
Menstrual Cycle
© Tess Peters 2009 and Sonya Amim 2003
E = estrogen; FSH = follicle-stimulating hormone; GnRH = gondatopin-releasing hormone; HPO = hypothalamic pituitary-ovarian; LH = luteinizing hormone; P = progesterone
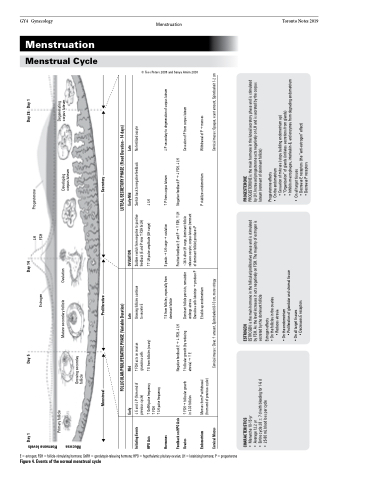
Figure 4. Events of the normal menstrual cycle
Mucosa Hormone levels
Day 1
Day 5
Day 14
Day 28 Day 1
Initiating Events HPO Axis
E andP (from end of previous cycle)
FSH acts on ovarian granulosa cells
Growing follicles continue to secrete E
Sudden switch from negative to positive feedback (E and P nowFSH & LH)
Switch back to negative feedback LH
No fertilized oocyte
Hormones
E from follicles, especially from dominant follicle
P from corpus luteum
Negative feedback PFSH,LH
P secondary to degeneration of corpus luteum
Feedback on HPO Axis Ovaries
FSHfollicular growth in 3-30 follicles
Negative feedback EFSH,LH follicular growth (by reducing
Dominant follicle persists, remainder undergo atresia
Granulosa cells luteinizeproduce P
Positive feedback: E and PFSH,LH ~36 h after LH surge, dominant follicle
Cessation of P from corpus luteum
Endometrium Cervical Mucus
Menses from P withdrawal (from end of previous cycle)
E builds up endometrium Cervical mucus: Clear, amount, Spinnbarkeit 8-10 cm, more stringy
P stabilizes endometrium
Withdrawal of Pmenses
Cervical mucus: Opaque, scant amount, Spinnbarkeit 1-2 cm
Primary follicle
Mature secondary follicle
Ovulation
Developing corpus luteum
Degenerating corpus luteum
CHARACTERISTICS
ESTROGEN
PROGESTERONE
Early
Mid
Late
OVULATION
Early-Mid
Late
• Menarche 10-15 yr
• Average 12.2 yr
• Entire cycle 28 ± 7 d with bleeding for 1-6 d • 25-80 mL blood loss per cycle
ESTROGEN is the main hormone in the follicular/proliferative phase and is stimulated by FSH. As the level increases it acts negatively on FSH. The majority of estrogen is secreted by the dominant follicle
PROGESTERONE is the main hormone in the luteal/secretory phase and is stimulated by LH. Increased progesterone acts negatively on LH and is secreted by the corpus luteum (remnant of dominant follicle)
Menstrual
Proliferative
Secretory
GnRH pulse frequency FSH
LH pulse frequency
E from follicles (ovary)
LH pulse amplitude (LH surge) E peaksLH surgeovulation
Growing seconday follicle
FOLLICULAR/PROLIFERATIVE PHASE (Variable Duration)
LUTEAL/SECRETORY PHASE (Fixed Duration - 14 days)
atresia)E
releases oocyte; corpus luteum (remnant of dominant follicle) produces P
Estrogen effects
• On the follicles in the ovaries
Progesterone effects
• On the endometrium
• Reduces atresia
• Cessation of mitoses (stops building endometrium up)
• “Organization” of glands (initiates secretions from glands)
• Inhibits macrophages, interleukin-8, and enzymes from degrading endometrium
Estrogen
• On the endometrium
• Proliferation of glandular and stromal tissue
• On all target tissues
• Decreases E receptors
• On all target tissues
• Decrease E receptors (the “anti-estrogen” effect) • Decrease P receptors
LH FSH
Progesterone