Page 494 - TNFlipTest
P. 494
GY8 Gynecology
Disorders of Menstruation
Toronto Notes 2019
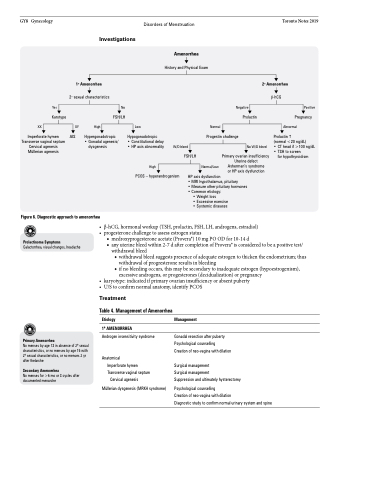
Figure 6. Diagnostic approach to amenorrhea
Investigations
Hypergonadotropic • Gonadal agenesis/
dysgenesis
W/D bleed FSH/LH
No W/D bleed
Primary ovarian insufficiency Uterine defect Asherman’s syndrome
or HP axis dysfunction
Amenorrhea
History and Physical Exam
1o Amenorrhea
2o sexual characteristics
2o Amenorrhea
β-hCG
Prolactin
(normal <20 ng/dL)
• CT head if >100 ng/dL • TSH to screen
for hypothyroidism
Yes
Karotype XX
Imperforate hymen Transverse vaginal septum Cervical agenesis Müllerian agenesis
No FSH/LH
Negative Prolactin
Positive Pregnancy
XY AIS
High
Low
Hypogonadotropic
• Constitutional delay • HP axis abnormality
Normal
Progestin challenge
Abnormal
High
PCOS – hyperandrogenism
Normal/Low
• β-hCG,hormonalworkup(TSH,prolactin,FSH,LH,androgens,estradiol) • progesteronechallengetoassessestrogenstatus
HP axis dysfunction
• MRI hypothalamus, pituitary
• Measure other pituitary hormones • Common etiology:
• Weight loss
• Excessive exercise • Systemic diseases
Prolactinoma Symptoms
Galactorrhea, visual changes, headache
■ medroxyprogesterone acetate (Provera®) 10 mg PO OD for 10-14 d
■ any uterine bleed within 2-7 d after completion of Provera® is considered to be a positive test/
withdrawal bleed
◆ withdrawal bleed suggests presence of adequate estrogen to thicken the endometrium; thus
withdrawal of progresterone results in bleeding
◆ if no bleeding occurs, this may be secondary to inadequate estrogen (hypoestrogenism),
excessive androgens, or progesterones (decidualization) or pregnancy • karyotype:indicatedifprimaryovarianinsufficiencyorabsentpuberty
• U/Stoconfirmnormalanatomy,identifyPCOS
Primary Amenorrhea
No menses by age 13 in absence of 2o sexual characteristics, or no menses by age 15 with 2o sexual characteristics, or no menses 2 yr after thelarche
Secondary Amenorrhea
No menses for >6 mo or 3 cycles after documented menarche
Treatment
Table 4. Management of Amenorrhea
Etiology
1o AMENORRHEA
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
Anatomical
Imperforate hymen Transverse vaginal septum
Cervical agenesis
Müllerian dysgenesis (MRKH syndrome)
Management
Gonadal resection after puberty Psychological counselling
Creation of neo-vagina with dilation
Surgical management
Surgical management
Suppression and ultimately hysterectomy
Psychological counselling
Creation of neo-vagina with dilation
Diagnostic study to confirm normal urinary system and spine