Page 512 - TNFlipTest
P. 512
GY26 Gynecology
Gynecological Infections
Toronto Notes 2019
INFECTIOUS VULVOVAGINITIS
Table 15. Infectious Vulvovaginitis
Organisms
Pathophysiology or Transmission
Discharge
Other Signs/Symptoms
pH
Saline Wetmount
Treatment
Other
Candidasis
Candida albicans (90%) Candida glabrata (<5%) Candida tropicalis (<5%)
Predisposing factors include: Immunosuppressed host (DM, AIDS, etc.) Recent antibiotic use
Increased estrogen levels (e.g. pregnancy, OCP)
Whitish, “cottage cheese,” minimal 20% asymptomatic
Intense pruritus
Swollen, inflamed genitals
Vulvar burning, dysuria, dyspareunia
≤4.5
KOH wetmount reveals hyphae and spores
Clotrimazole, butoconazole, miconazole, terconazole suppositories, and/or creams for 1, 3, or 7 d treatments
Treatment in pregnancy is usually topical Fluconazole 150 mg PO in single dose (can be used in pregnancy)
Prophylaxis for recurrent infection includes boric acid, vaginal suppositories, luteal phase fluconazole
Routine treatment of partner(s) not recommended (not sexually transmitted)
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
Gardnerella vaginalis
Mycoplasma hominis
Anaerobes: Prevotella, Mobiluncus, Bacteroides
Replacement of vaginal Lactobacillus with organisms above
Grey, thin, diffuse
50-75% asymptomatic
Fishy odour, especially after coitus Absence of vulvar/vaginal irritation
≥4.5
>20% clue cells = squamous epithelial cells dotted
with coccobacilli (Gardnerella)
Paucity of WBC
Paucity of Lactobacilli
Positive whiff test: fishy odour with addition of KOH to slide (due to formation of amines)
No treatment if non-pregnant and asymptomatic, unless scheduled for pelvic surgery or procedure
Oral
Metronidazole 500 mg PO bid x 7 d
Topical
Metronidazole gel 0.75% x 5 d OD (may be used in pregnancy)
Clindamycin 2% 5 g intravaginally at bedtime for 7 d Probiotics (Lactobacillus sp.): oral or topical alone or as adjuvant
Associated with recurrent preterm labour, preterm birth, and postpartum endometritis
Need to warn patients on metronidazole not to consume alcohol (disulfiram-like action)
Routine treatment of partner(s) not recommended (not sexually transmitted)
Trichomoniasis
Trichomonas vaginalis (flagellated protozoan) Sexual transmission
Yellow-green, malodourous, diffuse, frothy 25% asymptomatic
Petechiae on vagina and cervix Occasionally irritated tender vulva Dysuria, frequency
≥4.5
Motile flagellated organisms
Many WBC
Inflammatory cells (PMNs) Can have positive whiff test
Treat even if asymptomatic
Metronidazole 2 g PO single dose or 500 mg bid x 7 d (alternative)
Symptomatic pregnant women should be treated with 2 g metronidazole once
Warnings accompanying metronidazole use Treat partner(s)
Sexually Transmitted Infections
CDC Notifiable Diseases
• Chancroid
• Chlamydia
• Gonorrhea
• Hepatitis A, B, C • HIV
• Syphilis
Risk Factors for STIs
• History of previous STI
• Contact with infected person
• Sexually active individual <25 yr
• Multiple partners
• New partner in last 3 mo
• Lack of barrier protection use
• Street involvement (homelessness, drug
use)
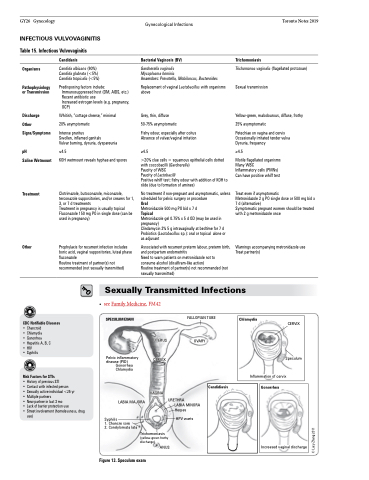
• seeFamilyMedicine,FM42 SPECULUM EXAM
UTERUS CERVIX
VAGINA
URETHRA
FALLOPIAN TUBE
OVARY
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Gonorrhea Chlamydia
Chlamydia
CERVIX
Speculum
Inflammation of cervix
Candidiasis
Gonorrhea
Increased vaginal discharge
LABIA MAJORA
Syphilis
1. Chancre sore
2. Condylomata lata
LABIA MINORA Herpes
HPV warts
Figure 13. Speculum exam
Trichomoniasis (yellow-green frothy discharge)
ANUS
© Lucy Zhang 2011