Page 519 - TNFlipTest
P. 519
Toronto Notes 2019 Menopause
• dyspareunia(3-6%):painfulintercourse,superficialordeep ■ vaginismus (15%)
■ vulvodynia
■ vaginal atrophy
■ vulvar vestibulitis: associated with history of frequent yeast infections ■ PID
Gynecology GY33
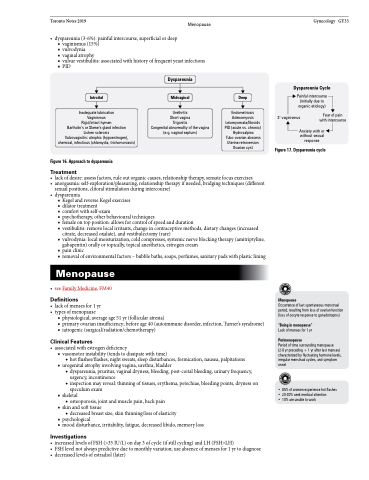
Introital
Inadequate lubrication
Vaginismus
Rigid/intact hymen
Bartholin’s or Skene’s gland infection Lichen sclerosis
Vulvovaginitis: atrophic (hypoestrogen), chemical, infectious (chlamydia, trichomoniasis)
Figure 16. Approach to dyspareunia
Treatment
Dyspareunia
Midvaginal
Urethritis
Short vagina
Trigonitis
Congenital abnormality of the vagina (e.g. vaginal septum)
Deep
Endometriosis
Adenomyosis Leiomyomata/fibroids PID (acute vs. chronic) Hydrosalpinx Tubo-ovarian abscess Uterine retroversion Ovarian cyst
Dyspareunia Cycle
Painful intercourse (initially due to organic etiology)
2o vaginismus
Fear of pain with intercourse
Anxiety with or without sexual response
Figure 17. Dyspareunia cycle
• lackofdesire:assessfactors,ruleoutorganiccauses,relationshiptherapy,sensatefocusexercises
• anorgasmia:self-exploration/pleasuring,relationshiptherapyifneeded,bridgingtechniques(different
sexual positions, clitoral stimulation during intercourse)
• dyspareunia
■ Kegel and reverse Kegel exercises
■ dilator treatment
■ comfort with self-exam
■ psychotherapy, other behavioural techniques
■ female on top position: allows for control of speed and duration
■ vestibulitis: remove local irritants, change in contraceptive methods, dietary changes (increased
citrate, decreased oxalate), and vestibulectomy (rare)
■ vulvodynia: local moisturization, cold compresses, systemic nerve blocking therapy (amitriptyline,
gabapentin) orally or topically, topical anesthetics, estrogen cream
■ painclinic
■ removal of environmental factors – bubble baths, soaps, perfumes, sanitary pads with plastic lining
Menopause
• seeFamilyMedicine,FM40 Definitions
• lackofmensesfor1yr • typesofmenopause
■ physiological; average age 51 yr (follicular atresia)
■ primary ovarian insufficiency; before age 40 (autoimmune disorder, infection, Turner’s syndrome) ■ iatrogenic (surgical/radiation/chemotherapy)
Clinical Features
• associatedwithestrogendeficiency
■ vasomotor instability (tends to dissipate with time)
◆ hot flushes/flashes, night sweats, sleep disturbances, formication, nausea, palpitations ■ urogenital atrophy involving vagina, urethra, bladder
◆ dyspareunia, pruritus, vaginal dryness, bleeding, post-coital bleeding, urinary frequency, urgency, incontinence
◆ inspection may reveal: thinning of tissues, erythema, petechiae, bleeding points, dryness on speculum exam
■ skeletal
◆ osteoporosis, joint and muscle pain, back pain
■ skinandsofttissue
◆ decreased breast size, skin thinning/loss of elasticity
■ psychological
■ mood disturbance, irritability, fatigue, decreased libido, memory loss
Investigations
• increasedlevelsofFSH(>35IU/L)onday3ofcycle(ifstillcycling)andLH(FSH>LH)
• FSHlevelnotalwayspredictiveduetomonthlyvariation;useabsenceofmensesfor1yrtodiagnose • decreasedlevelsofestradiol(later)
Menopause
Occurrence of last spontaneous menstrual period, resulting from loss of ovarian function (loss of oocyte response to gonadotropins)
“Being in menopause”
Lack of menses for 1 yr
Perimenopause
Period of time surrounding menopause
(2-8 yr preceding + 1 yr after last menses) characterized by fluctuating hormone levels, irregular menstrual cycles, and symptom onset
• 85% of women experience hot flashes • 20-30% seek medical attention
• 10% are unable to work