Page 646 - TNFlipTest
P. 646
ID46 Infectious Diseases
Infections in the Immunocompromised Host
Toronto Notes 2019
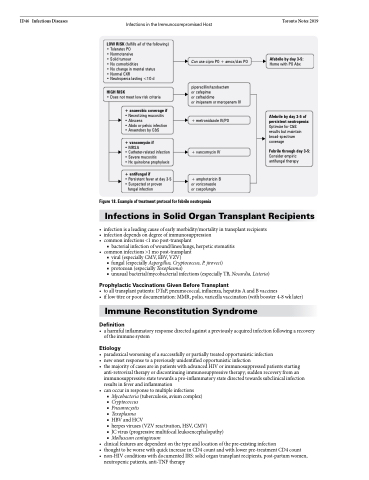
LOW RISK (fulfills all of the following) • Tolerates PO
• Normotensive
• Solid tumour
• No comorbidities
• No change in mental status • Normal CXR
• Neutropenia lasting <1O d
HIGH RISK
• Does not meet low risk criteria
+ anaerobic coverage if
• Necrotizing mucositis • Abscess
• Abdo or pelvic infection • Anaerobes by C&S
+ vancomycin if
• MRSA
• Catheter-related infection • Severe mucositis
• Hx quinolone prophylaxis
+ antifungal if
• Persistent fever at day 3-5 • Suspected or proven
fungal infection
Can use cipro PO + amox/clav PO
piperacillin/tazobactam
or cefepime
or ceftazidime
or imipenem or meropenem IV
+ metronidazole IV/PO
+ vancomycin IV
+ amphotericin B or voriconazole
or caspofungin
Afebrile by day 3-5:
Home with PO Abx
Afebrile by day 3-5 of persistent neutropenia: Optimize for C&S
results but maintain broad-spectrum coverage
Febrile through day 3-5:
Consider empiric antifungal therapy
Figure 18. Example of treatment protocol for febrile neutropenia
Infections in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
• infectionisaleadingcauseofearlymorbidity/mortalityintransplantrecipients • infectiondependsondegreeofimmunosuppression
• commoninfections<1mopost-transplant
■ bacterial infection of wound/lines/lungs, herpetic stomatitis • commoninfections>1mopost-transplant
■ viral (especially CMV, EBV, VZV)
■ fungal (especially Aspergillus, Cryptococcus, P. jiroveci)
■ protozoan (especially Toxoplasma)
■ unusual bacterial/mycobacterial infections (especially TB, Nocardia, Listeria)
Prophylactic Vaccinations Given Before Transplant
• toalltransplantpatients:DTaP,pneumococcal,influenza,hepatitisAandBvaccines
• iflowtitreorpoordocumentation:MMR,polio,varicellavaccination(withbooster4-8wklater)
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Definition
• aharmfulinflammatoryresponsedirectedagainstapreviouslyacquiredinfectionfollowingarecovery of the immune system
Etiology
• paradoxicalworseningofasuccessfullyorpartiallytreatedopportunisticinfection
• newonsetresponsetoapreviouslyunidentifiedopportunisticinfection
• themajorityofcasesareinpatientswithadvancedHIVorimmunosuppressedpatientsstarting
anti-retroviral therapy or discontinuing immunosuppressive therapy; sudden recovery from an immunosuppressive state towards a pro-inflammatory state directed towards subclinical infection results in fever and inflammation
• canoccurinresponsetomultipleinfections
■ Mycobacteria (tuberculosis, avium complex)
■ Cryptococcus
■ Pneumocystis
■ Toxoplasma
■ HBVandHCV
■ herpes viruses (VZV reactivation, HSV, CMV)
■ JC virus (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy) ■ Molluscumcontagiosum
• clinicalfeaturesaredependentonthetypeandlocationofthepre-existinginfection
• thoughttobeworsewithquickincreaseinCD4countandwithlowerpre-treatmentCD4count
• non-HIVconditionswithdocumentedIRS:solidorgantransplantrecipients,post-partumwomen,
neutropenic patients, anti-TNF therapy