Page 732 - TNFlipTest
P. 732
NP32 Nephrology
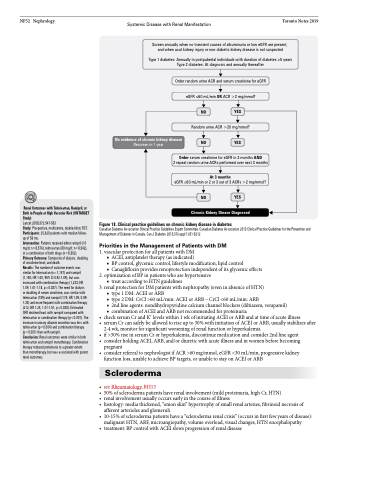
Systemic Disease with Renal Manifestation Toronto Notes 2019 Screen annually when no transient causes of albuminuria or low eGFR are present,
and when acut kidney injury or non-diabetic kidney disease is not suspected
Type 1 diabetes: Annually in postpubertal individuals with duration of diabetes ≥5 years Type 2 diabetes: At diagnosis and annually thereafter
Order random urine ACR and serum creatinine for eGFR
No evidence of chronic kidney disease
Rescreen in 1 year
eGFR ≤60 mL/min OR ACR >2 mg/mmol?
NO YES
Random urine ACR >20 mg/mmol?
NO YES
Renal Outcomes with Telmisartan, Ramipril, or Both in People at High Vascular Risk (ONTARGET Study)
Lancet 2008;372:547-553
Study: Prospective, multicentre, double-blind, RCT. Participants: 25,620 patients with median follow- upof56mo.
Intervention: Patients received either ramipril (10 mg/d; n=8,576), telmisartan (80 mg/d; n=8,542), or a combination of both drugs (n=8,502). Primary Outcome: Composite of dialysis, doubling of creatinine level, and death.
Results: The number of outcome events was similar for telmisartan (n=1,147) and ramipril (1,150; HR 1.00, 95% CI 0.92-1.09), but was increased with combination therapy (1,233; HR 1.09, 1.01-1.18, p=0.037). The need for dialysis
or doubling of serum creatinine, was similar with telmisartan (189) and ramipril (174; HR 1.09, 0.89- 1.34) and more frequent with combination therapy (212; HR 1.24, 1.01-1.51, p=0.038). Estimated GFR declined least with ramipril compared with telmisartan or combination therapy (p<0.001). The increase in urinary albumin excretion was less with telmisartan (p=0.004) and combination therapy (p=0.001) than with ramipril.
Conclusion: Renal outcomes were similar in both telmisartan and ramipril monotherapy. Combination therapy reduced proteinuria to a greater extent than monotherapy, but was associated with poorer renal outcomes.
Order serum creatinine for eGFR in 3 months AND
2 repeat random urine ACRs performed over next 3 months
At 3 months
eGFR ≤60 mL/min or 2 or 3 out of 3 ACRs >2 mg/mmol?
NO YES
Chronic Kidney Diease Diagnosed
Figure 18. Clinical practice guidelines on chronic kidney disease in diabetes
Canadian Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Canadian Diabetes Association 2013 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada. Can J Diabetes 2013;37(suppl 1):S1-S212
Priorities in the Management of Patients with DM
1. vascular protection for all patients with DM
■ ACEI, antiplatelet therapy (as indicated)
■ BP control, glycemic control, lifestyle modification, lipid control
■ Canagliflozin provides renoprotection independent of its glycemic effects
2. optimization of BP in patients who are hypertensive ■ treat according to HTN guidelines
3. renal protection for DM patients with nephropathy (even in absence of HTN)
■ type1DM:ACEIorARB
■ type 2 DM: CrCl >60 mL/min: ACEI or ARB – CrCl <60 mL/min: ARB
■ 2nd line agents: nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (diltiazem, verapamil) ■ combination of ACEI and ARB not recommended for proteinuria
• check serum Cr and K+ levels within 1 wk of initiating ACEI or ARB and at time of acute illness
• serumCrcansafelybeallowedtoriseupto30%withinitiationofACEIorARB,usuallystabilizesafter
2-4 wk, monitor for significant worsening of renal function or hyperkalemia
• if>30%riseinserumCrorhyperkalemia,discontinuemedicationandconsider2ndlineagent • considerholdingACEI,ARB,and/ordiureticwithacuteillnessandinwomenbeforebecoming
pregnant
• considerreferraltonephrologistifACR>60mg/mmol,eGFR<30mL/min,progressivekidney
function loss, unable to achieve BP targets, or unable to stay on ACEI or ARB
Scleroderma
• seeRheumatology,RH13
• 50%ofsclerodermapatientshaverenalinvolvement(mildproteinuria,highCr,HTN)
• renalinvolvementusuallyoccursearlyinthecourseofillness
• histology:mediathickened,“onionskin”hypertrophyofsmallrenalarteries,fibrinoidnecrosisof
afferent arterioles and glomeruli
• 10-15%ofsclerodermapatientshavea“sclerodermarenalcrisis”(occursinfirstfewyearsofdisease):
malignant HTN, ARF, microangiopathy, volume overload, visual changes, HTN encephalopathy • treatment:BPcontrolwithACEIslowsprogressionofrenaldisease