Page 740 - TNFlipTest
P. 740
NP40 Nephrology
Landmark Nephrology Trials
Toronto Notes 2019
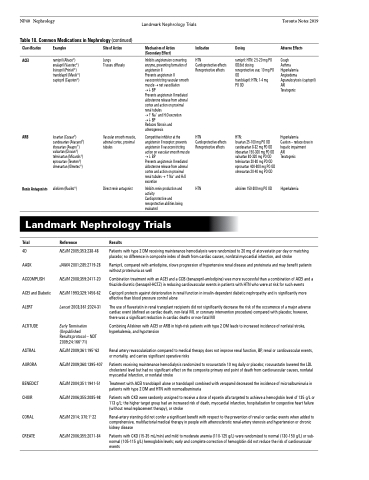
Table 18. Common Medications in Nephrology (continued)
Classification
ACEI
Examples
ramipril (Altace®) enalapril (Vasotec®) lisinopril (Prinivil®) trandolapril (Mavik®) captopril (Capoten®)
losartan (Cozaar®) candesartan (Atacand®) irbesartan (Avapro®) valsartan (Diovan®) telmisartan (Micardis®) eprosartan (Teveten®) olmesartan (Olmetec®)
aliskiren (Rasilez®)
Site of Action
Lungs
Tissues diffusely
Vascular smooth muscle, adrenal cortex, proximal tubules
Direct renin antagonist
Mechanism of Action (Secondary Effect)
Inhibits angiotension converting enzyme, preventing formation of angiotensin II
Prevents angiotensin II vasoconstricting vascular smooth muscle → net vasodilation →BP
Prevents angiotensin II mediated aldosterone release from adrenal cortex and action on proximal renal tubules
→Na+ and H2O excretion →BP
Reduces fibrosis and atherogenesis
Competitive inhibitor at the angiotensin II receptor: prevents angiotensin II vasoconstricting action on vascular smooth muscle →BP
Prevents angiotensin II mediated aldosterone release from adrenal cortex and action on proximal renal tubules →Na+ and H2O excretion
Inhibits renin production and activity
Cardioprotective and renoprotective abilities being evaluated
Indication
HTN
Cardioprotective effects Renoprotective effects
HTN
Cardioprotective effects Renoprotective effects
HTN
Dosing
ramipril: HTN: 2.5-20 mg PO OD/bid dosing
renoprotective use; 10 mg PO OD
trandolapril: HTN; 1-4 mg PO OD
HTN:
losartan 25-100 mg PO OD candesartan 8-32 mg PO OD irbesartan 150-300 mg PO OD valsartan 80-320 mg PO OD telmisartan 20-80 mg PO OD eprosartan 400-800 mg PO OD olmesartan 20-40 mg PO OD
aliskiren 150-300 mg PO OD
Adverse Effects
Cough
Asthma
Hyperkalemia Angioedema Agranulocytosis (captopril) AKI
Teratogenic
Hyperkalemia
Caution – reduce dose in hepatic impairment
AKI
Teratogenic
Hyperkalemia
ARB
Renin Antagonists
Landmark Nephrology Trials
Trial
4D
AASK ACCOMPLISH ACEI and Diabetic ALERT
ALTITUDE
ASTRAL AURORA
BENEDICT CHOIR
CORAL CREATE
Reference
NEJM 2005;353:238-48 JAMA 2001;285:2719-28 NEJM 2008;359:2417-20 NEJM 1993;329:1456-62 Lancet 2003;361:2024-31
Early Termination
(Unpublished Results;protocol – NDT 2009;24:1663-71)
NEJM 2009;361:1953-62 NEJM 2009;360:1395-407
NEJM 2004;351:1941-51 NEJM 2006;355:2085-98
NEJM 2014; 370:13-22 NEJM 2006;355:2071-84
Results
Patients with type 2 DM receiving maintenance hemodialysis were randomized to 20 mg of atorvastatin per day or matching placebo; no difference in composite index of death from cardiac causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and stroke
Ramipril, compared with amlodipine, slows progression of hypertensive renal disease and proteinuria and may benefit patients without proteinuria as well
Combination treatment with an ACEI and a CCB (benazepril-amlodipine) was more successful than a combination of ACEI and a thiazide diuretic (benzapril-HCTZ) in reducing cardiovascular events in patients with HTN who were at risk for such events
Captopril protects against deterioration in renal function in insulin-dependent diabetic nephropathy and is significantly more effective than blood pressure control alone
The use of fluvastatin in renal transplant recipients did not significantly decrease the risk of the occurrence of a major adverse cardiac event (defined as cardiac death, non-fatal MI, or coronary intervention procedure) compared with placebo; however, there was a significant reduction in cardiac deaths or non-fatal MI
Combining Aliskiren with ACEI or ARB in high-risk patients with type 2 DM leads to increased incidence of nonfatal stroke, hyperkalemia, and hypotension
Renal artery revascularization compared to medical therapy does not improve renal function, BP, renal or cardiovascular events, or mortality, and carries significant operative risks
Patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis randomized to rosuvastatin 10 mg daily or placebo; rosuvastatin lowered the LDL cholesterol level but had no significant effect on the composite primary end point of death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke
Treatment with ACEI trandolapril alone or trandolapril combined with verapamil decreased the incidence of microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 DM and HTN with normoalbuminuria
Patients with CKD were randomly assigned to receive a dose of epoetin alfa targeted to achieve a hemoglobin level of 135 g/L or 113 g/L; the higher target group had an increased risk of death, myocardial infarction, hospitalization for congestive heart failure (without renal replacement therapy), or stroke
Renal-artery stenting did not confer a significant benefit with respect to the prevention of renal or cardiac events when added to comprehensive, multifactorial medical therapy in people with atherosclerotic renal-artery stenosis and hypertension or chronic kidney disease
Patients with CKD (15-35 mL/min) and mild to moderate anemia (110-125 g/L) were randomized to normal (130-150 g/L) or sub- normal (105-115 g/L) hemoglobin levels; early and complete correction of hemoglobin did not reduce the risk of cardiovascular events