Page 921 - TNFlipTest
P. 921
Toronto Notes 2019 Malignancies Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect
Ophthalmology OP31
Direct response
Constriction of stimulated eye
Pretectal nucleus
Edinger-Westphal nucleus (III)
Oculomotor nerves (III)
Optic nerve (II)
Cilliary ganglion
Constrictor muscles of pupil
Consensual response
Constriction of unstimulated eye
Normal Pupillary Response
1. Swinging Light Test
Normal eye Pathological eye Constriction of both pupils normal
2. Swinging Light Test
Normal eye Pathological eye Constriction of both pupils normal
Aqueduct
Optic chiasm
3. Swinging Light Test
Normal eye Pathological eye Pupils appear to dilate – positive RAPD
Rapidly swing light to pathological eye
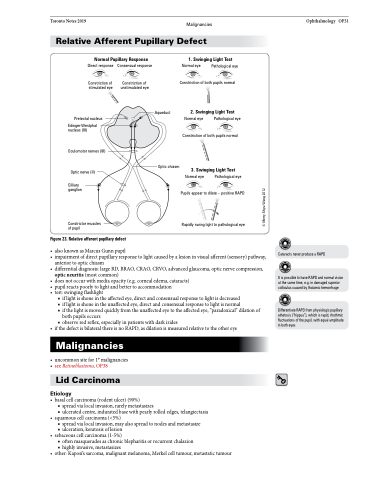
Figure 23. Relative afferent pupillary defect
• alsoknownasMarcusGunnpupil
• impairmentofdirectpupillaryresponsetolightcausedbyalesioninvisualafferent(sensory)pathway,
anterior to optic chiasm
• differentialdiagnosis:largeRD,BRAO,CRAO,CRVO,advancedglaucoma,opticnervecompression,
optic neuritis (most common)
• doesnotoccurwithmediaopacity(e.g.cornealedema,cataracts)
• pupil reacts poorly to light and better to accommodation
• test:swingingflashlight
■ if light is shone in the affected eye, direct and consensual response to light is decreased
■ if light is shone in the unaffected eye, direct and consensual response to light is normal
■ if the light is moved quickly from the unaffected eye to the affected eye, “paradoxical” dilation of
both pupils occurs
■ observe red reflex, especially in patients with dark irides
• ifthedefectisbilateralthereisnoRAPD,asdilationismeasuredrelativetotheothereye
Malignancies
• uncommonsitefor1°malignancies
• seeRetinoblastoma,OP38
Lid Carcinoma
Etiology
• basalcellcarcinoma(rodentulcer)(90%)
■ spread via local invasion, rarely metastasizes
■ ulcerated centre, indurated base with pearly rolled edges, telangiectasia
• squamouscellcarcinoma(<5%)
■ spread via local invasion, may also spread to nodes and metastasize ■ ulceration, keratosis of lesion
• sebaceouscellcarcinoma(1-5%)
■ often masquerades as chronic blepharitis or recurrent chalazion ■ highly invasive, metastasizes
• other:Kaposi’ssarcoma,malignantmelanoma,Merkelcelltumour,metastatictumour
Cataracts never produce a RAPD
It is possible to have RAPD and normal vision at the same time, e.g. in damaged superior colliculus caused by thalamic hemorrhage
Differentiate RAPD from physiologic pupillary athetosis (“hippus”), which is rapid, rhythmic fluctuations of the pupil, with equal amplitude in both eyes
© Merry Shiyu Wang 2012