Page 1038 - TNFlipTest
P. 1038
P4 Pediatrics
Primary Care
Toronto Notes 2019
Canadian Immunization Guide
National Advisory Committee on Immunization. Canadian Immunization
Guide (CIG). Last Modified 2014. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2006. Available at: http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/publicat/cig-gci/
According to the CDC, the weight of currently available scientific evidence does not support the hypothesis that MMR vaccine causes either autism or IBD. The landmark paper linking autism to the MMR vaccine (Lancet 1998;351:637-641) was retracted due to false claims in the article (Lancet 2010;375:445)
Adverse Reactions Associaed With Any Vaccine
• Local: induration, tenderness, redness,
swelling
• Systemic: fever, rash, irritability
• Allergic: urticaria, rhinitis, anaphylaxis
• Contraindications
• Moderate/severe illness ± fever
• Allergy to vaccine component
• No need to delay vaccination for mild URTI
Vaccination in Cases of Asplenia or Hyposplenia (such as Sickle Cell Disease)
• Should receive all routine immunizations,
including the yearly influenza vaccine
• No vaccines are contraindicated
• Susceptible to infection by encapsulated
bacteria (“SHiNE KISS” –S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, N. meningitidis, E. coli, Klebsiella, Salmonella, Group B Strep), so must add:
• Quadrivalent conjugated Meningococcal C vaccine (Men-C-ACYW) and Meningococcal B vaccine (4CMenB) at timeofdiagnosisif ≥2mo(2-3doses given at least 8 wk apart) with booster at 12-23 mo, every 3-5 yr until 7 yr of age, and every 5 yr thereafter
• Can omit routine Meningococcal-C- Conjugate at 12 mo of age if received Men-C-ACYW and expected to receive a second dose within 8 wk
• Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (Pneu-P-23) at age ≥2 yr and single booster ≥5 yr after first dose
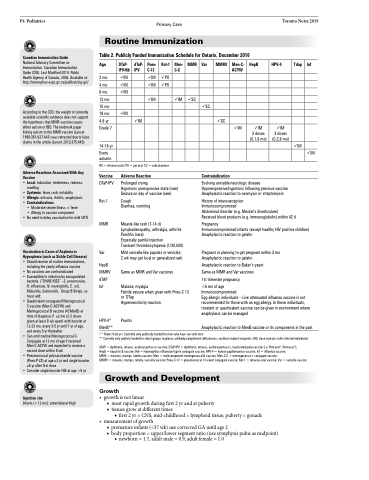
Routine Immunization
Table 2. Publicly Funded Immunization Schedule for Ontario, December 2016
DTaP- IPV-Hib
dTaP- IPV
Pneu- C-13
Rot-1
Men- C-C
MMR
Var
MMRV
Men-C- ACYW
HepB
HPV-4
Tdap
IM
IM
PO
IM
IM
PO
IM
IM
IM
SC
SC
IM
IM
SC
IM
IM
3 doses (0,1,6 mo)
IM
3 doses (0,2,6 mo)
IM
Age
2 mo
4 mo
6 mo 12 mo 15 mo 18 mo 4-6 yr Grade 7
14-16 yr
Every autumn
IM = intramuscular; PO = per oral; SC = subcutaneous
Vaccine Adverse Reaction
DTaP-IPV Prolonged crying
Hypotonic unresponsive state (rare)
Seizure on day of vaccine (rare)
Rot-1 Cough
Diarrhea, vomiting
MMR Measle-like rash (7-14 d) Lymphadenopathy, arthralgia, arthritis
Parotitis (rare)
Especially painful injection
Transient thrombocytopenia (1/30,000)
Var Mild varicella-like papules or vesicles; 2 wk may get local or generalized rash
HepB
MMRV Same as MMR and Var vaccines dTAP
Inf Malaise, myalgia
Febrile seizure when given with Pneu-C 13 or DTap
Hypersensitivity reaction
HPV-4* Pruritis MenB**
Inf
IM
Pregnancy
Immunocompromised infants (except healthy HIV positive children) Anaphylactic reaction to gelatin
Pregnant or planning to get pregnant within 3 mo Anaphylactic reaction to gelatin
Anaphylactic reaction to Baker’s yeast Same as MMR and Var vaccines
1st trimester pregnancy
<6 mo of age
Immunocompromised
Egg-allergic individuals – Live attenuated influenza vaccine is not recommended for those with an egg allergy. In these individuals, trivalent or quadrivalent vaccine can be given in environment where anaphylaxis can be managed
Anaphylactic reaction to MenB vaccine or its components in the past
Contraindication
Evolving unstable neurologic disease Hyporesponsive/hypotonic following previous vaccine Anaphylactic reaction to neomycin or streptomycin
History of intussusception
Immunocompromised
Abdominal disorder (e.g. Meckel’s diverticulum)
Received blood products (e.g. immunoglobulin) within 42 d
• Consider single booster HiB at age >5 yr
Injection site
Infants (<12 mo): anterolateral thigh
* * Males 9-26 yrs: Currently only publically funded for men who have sex with men
** Currently only publicly funded for select groups (asplenia, antibody/complement deficiencies, cochlear implant recipients, HIV, close contacts with infected individuals)
dTAP = diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis vaccine; DTaP-IPV = diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, inactivated polio vaccine (i.e. Pentacel®, Pentavax®);
HepB = hepatitis B vaccine; Hib = Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine; HPV-4 = human papillomavirus vaccine; Inf = influenza vaccine;
MMR = measles, mumps, rubella vaccine; Men = multicomponent meningococcal B vaccine; Men-C-C = meningococcal c conjugate vaccine;
MMRV = measles, mumps, rubella, varicella vaccine; Pneu-C-13 = pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate vaccine; Rot-1 = rotavirus oral vaccine; Var = varicella vaccine
Growth and Development
Growth
• growthisnotlinear
■ most rapid growth during first 2 yr and at puberty ■ tissues grow at different times
◆ first 2 yr = CNS; mid-childhood = lymphoid tissue; puberty = gonads • measurementofgrowth
■ premature infants (<37 wk) use corrected GA until age 2
■ body proportion = upper/lower segment ratio (use symphysis pubis as midpoint)
◆ newborn = 1.7, adult male = 0.9, adult female = 1.0