Page 1085 - TNFlipTest
P. 1085
Toronto Notes 2019 Infectious Diseases Pediatrics P51 Infectious Pediatric Exanthems
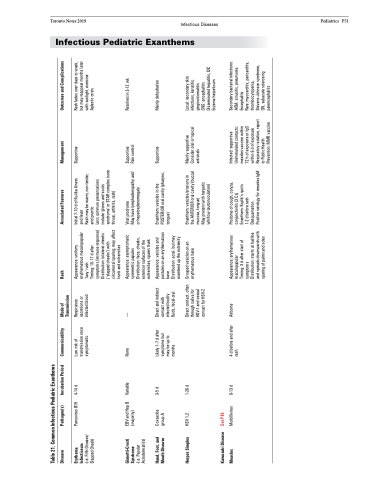
Table 21. Common Infectious Pediatric Exanthems
Disease
Pathogen(s)
Incubation Period
Communicability
Mode of Transmission
Rash
Associated Features
Management
Outcomes and Complications
Erythema Infectiosum
(i.e. Fifth Disease/ Slapped Cheek)
Parvovirus B19
4-14 d
Low risk of transmission once symptomatic
Respiratory secretions or infected blood
Appearance: uniform, erythematous maculopapular ‘lacy’ rash
Timing: 10-17 d after symptoms (immune response) Distribution: bilateral cheeks (‘slapped cheeks’) with circumoral sparing; may affect trunk and extremities
Initial 7-10 d of flu-like illness and fever
Rash may be warm, non-tender, and pruritic
Supportive
Rash fades over days to week, but may reappear months later with sunlight, exercise Aplastic crisis
Gianotti-Crosti Syndrome
(i.e. Papular Acrodermatitis)
EBV and Hep B (majority)
Variable
None
—
Appearance: asymptomatic symmetric papules Distribution: face, cheeks, extensor surfaces of the extremities, spares trunk
Viral prodrome
May have lymphadenopathy and/ or hepatosplenomegaly
Supportive Pain control
Resolves in 3-12 wk
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Coxsackie group A
3-5 d
Likely 1-7 d after symptoms but may be up to months
Direct and indirect contact with infected bodily fluids, fecal-oral
Appearance: vesicles and pustules on an erythematous base
Distribution: acral. but may exentend up the extremity
Enanthem: vesicles in the POSTERIOR oral cavity (pharynx, tongue)
Supportive
Mainly dehydration
Herpes Simplex
HSV 1,2
1-26 d
Direct contact, often through saliva for HSV-1 and sexual contact for HSV-2
Grouped vesicles on an erythematous base
Enanthem: vesicles/erosions in the ANTERIOR oral cavity (buccal mucosa, tongue)
May present with herpetic whitlow (autoinoculation)
Mainly supportive Consider oral or topical antivirals
Local: secondary skin infections, keratitis, gingivostomatitis
CNS: encephalitis Disseminated hepatitis, DIC Eczema herpeticum
Kawasaki Disease Measles
See P86
Morbillivirus
8-13 d
4 d before and after rash
Airborne
Appearance: erythematous maculopapular
Timing: 3 d after start of symptoms
Prodome of cough, coryza, conjunctivitis (3 Cs) Enanthem: Koplik’s spots 1-2 d before rash Desquamation
Infected: supportive Unimmunized contacts: measles vaccine within
72 h of exposure or IgG within 6 d of exposure Respiratory isolation, report to Public Health Prevention: MMR vaccine
Secondary bacterial infections: AOM, sinusitis, pneumonia Encephalitis
Rare: myocarditis, pericarditis, thrombocytopenia, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, GN, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
Distribution: starts at hairline and spreads downwards with sparing of palms and soles
Positive serology for measles IgM
Less common presentations include ‘gloves and socks syndrome’ or STAR complex (sore throat, arthritis, rash)