Page 1099 - TNFlipTest
P. 1099
Toronto Notes 2019 Neonatology Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia
Definition
• total serum bilirubin >95th percentile (high risk zone) on Bhutani nomogram in infants >35 wk GA
Clinical Presentation
• jaundicetypicallyvisibleatserumbilirubinlevelsof85-120μmol/L
• visualassessmentisoftenmisleading,howeverexaminationofconjunctivaortipofnoseinnatural
Pediatrics P65
Jaundice is very common – 60% of term newborns develop visible jaundice
Jaundice in the first 24 h of life and conjugated hyperbilirubinemia are always pathological
Jaundice must be investigated if:
• It occurs within 24 h of birth
• Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia is present • Unconjugated bilirubin rises rapidly or is
excessive for patient’s age and weight
• Persistent jaundice lasts beyond 1-2 wk of
age
lighting may prove helpful
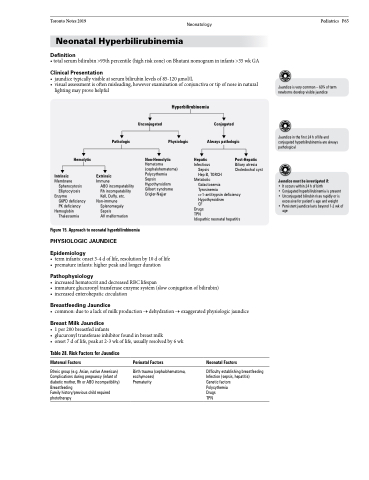
Hyperbilirubinemia
Unconjugated
Conjugated Always pathologic
Hemolytic
Intrinsic
Membrane Spherocytosis Elliptocytosis
Enzyme
G6PD deficiency PK deficiency
Hemoglobin Thalassemia
Pathologic
Immune
ABO incompatability Rh incompatability Kell, Duffy, etc.
Non-immune Splenomegaly Sepsis
AV malformation
Physiologic
Non-Hemolytic
Hematoma (cephalohematoma) Polycythemia Sepsis Hypothyroidism Gilbert syndrome Crigler-Najjar
Hepatic
Infectious Sepsis
Hep B, TORCH Metabolic
Post-Hepatic
Biliary atresia Choledochal cyst
Figure 15. Approach to neonatal hyperbilirubinemia
PHYSIOLOGIC JAUNDICE
Epidemiology
Extrinsic
• terminfants:onset3-4doflife,resolutionby10doflife • prematureinfants:higherpeakandlongerduration
Pathophysiology
• increasedhematocritanddecreasedRBClifespan
• immatureglucuronyltransferaseenzymesystem(slowconjugationofbilirubin) • increasedenterohepaticcirculation
Breastfeeding Jaundice
• common:duetoalackofmilkproduction→dehydration→exaggeratedphysiologicjaundice
Breast Milk Jaundice
• 1per200breastfedinfants
• glucuronyltransferaseinhibitorfoundinbreastmilk
• onset7doflife,peakat2-3wkoflife,usuallyresolvedby6wk
Table 28. Risk Factors for Jaundice
Maternal Factors
Ethnic group (e.g. Asian, native American) Complications during pregnancy (infant of diabetic mother, Rh or ABO incompatibility) Breastfeeding
Family history/previous child required phototherapy
Perinatal Factors
Birth trauma (cephalohematoma, ecchymoses)
Prematurity
Neonatal Factors
Difficulty establishing breastfeeding Infection (sepsis, hepatitis)
Genetic factors
Polycythemia
Drugs TPN
Galactosemia Tyrosinemia α-1-antitrypsin deficiency Hypothyroidism
CF Drugs
TPN
Idiopathic neonatal hepatitis