Page 1162 - TNFlipTest
P. 1162
PL40 Plastic Surgery
Pediatric Plastic Surgery Toronto Notes 2019
Congenital Hand Anomalies
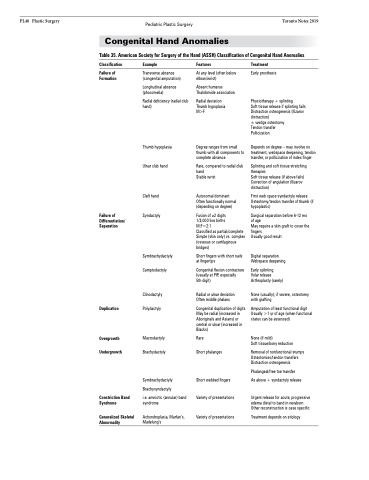
Table 35. American Society for Surgery of the Hand (ASSH) Classification of Congenital Hand Anomalies
Classification
Failure of Formation
Example
Transverse absence (congenital amputation)
Longitudinal absence (phocomelia)
Radial deficiency (radial club hand)
Thumb hypoplasia Ulnar club hand
Cleft hand Syndactyly
Symbrachydactyly Camptodactyly
Clinodactyly Polydactyly
Macrodactyly Brachydactyly
Symbrachydactyly Brachysyndactyly
i.e. amniotic (annular) band syndrome
Achondroplasia, Marfan’s, Madelung’s
Features
At any level (often below elbow/wrist)
Absent humerus Thalidomide association
Radial deviation Thumb hypoplasia M>F
Degree ranges from small thumb with all components to complete absence
Rare, compared to radial club hand
Stable wrist
Autosomal dominant Often functionally normal (depending on degree)
Fusion of ≥2 digits
1/3,000 live births
M:F=2:1
Classified as partial/complete Simple (skin only) vs. complex (osseous or cartilaginous bridges)
Short fingers with short nails at fingertips
Congenital flexion contracture (usually at PIP, especially
5th digit)
Radial or ulnar deviation Often middle phalanx
Congenital duplication of digits May be radial (increased in Aboriginals and Asians) or central or ulnar (increased in Blacks)
Rare
Short phalanges
Short webbed fingers Variety of presentations
Variety of presentations
Treatment
Early prosthesis
Physiotherapy + splinting
Soft tissue release if splinting fails Distraction osteogenesis (Ilizarov distraction)
± wedge osteotomy
Tendon transfer
Pollicization
Depends on degree – may involve no treatment, webspace deepening, tendon transfer, or pollicization of index finger
Splinting and soft tissue stretching therapies
Soft tissue release (if above fails) Correction of angulation (Ilizarov distraction)
First web space syndactyly release Osteotomy/tendon transfer of thumb (if hypoplastic)
Surgical separation before 6-12 mo of age
May require a skin graft to cover the fingers
Usually good result
Digital separation Webspace deepening
Early splinting
Volar release Arthroplasty (rarely)
None (usually); if severe, osteotomy with grafting
Amputation of least functional digit Usually >1 yr of age (when functional status can be assessed)
None (if mild)
Soft tissue/bony reduction
Removal of nonfunctional stumps Osteotomies/tendon transfers Distraction osteogenesis
Phalangeal/free toe transfer
As above + syndactyly release
Urgent release for acute, progressive edema distal to band in newborn Other reconstruction is case specific
Treatment depends on etiology
Failure of Differentiation/ Separation
Duplication
Overgrowth Undergrowth
Constriction Band Syndrome
Generalized Skeletal Abnormality