Page 1209 - TNFlipTest
P. 1209
Toronto Notes 2019 Pharmacotherapy Psychiatry PS45
• mustbevigilantoverthefirst2wkoftherapy;neurovegetativesymptomsmaystarttoresolvewhile emotional and cognitive symptoms may not (patients may be particularly at risk for suicidal behaviour during this time in particular children/adolescents)
• treatmentofbipolardepression
■ patients with bipolar disorder should only be treated with an antidepressant if combined with
a mood stabilizer or antipsychotic; monotherapy with antidepressants is not advisable as the depression can switch to mania
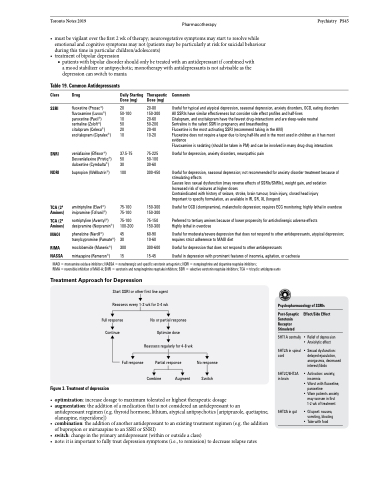
Table 19. Common Antidepressants
Class
SSRI
SNRI NDRI
TCA (3o Amines)
TCA (2o Amines)
MAOI
RIMA NASSA
Drug
fluoxetine (Prozac®) fluvoxamine (Luvox®) paroxetine (Paxil®) sertraline (Zoloft®) citalopram (Celexa®) escitalopram (Cipralex®)
venlafaxine (Effexor®) Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq®) duloxetine (Cymbalta®)
bupropion (Wellbutrin®)
amitriptyline (Elavil®) imipramine (Tofranil®)
nortriptyline (Aventyl®) desipramine (Norpramin®)
phenelzine (Nardil®) tranylcypromine (Parnate®)
moclobemide (Manerix®) mirtazapine (Remeron®)
Daily Starting Therapeutic Dose (mg) Dose (mg)
20 20-80 50-100 150-300 10 20-60 50 50-200 20 20-40 10 10-20
37.5-75 75-225 50 50-100 30 30-60
100 300-450
75-100 150-300 75-100 150-300
75-100 75-150 100-200 150-300
45 60-90 30 10-60
300 300-600 15 15-45
Comments
Useful for typical and atypical depression, seasonal depression, anxiety disorders, OCD, eating disorders All SSRIs have similar effectiveness but consider side effect profiles and half-lives
Citalopram, and escitalopram have the fewest drug-interactions and are sleep-wake neutral
Sertraline is the safest SSRI in pregnancy and breastfeeding
Fluoxetine is the most activating SSRI (recommend taking in the AM)
Fluoxetine does not require a taper due to long half-life and is the most used in children as it has most evidence
Fluvoxamine is sedating (should be taken in PM) and can be involved in many drug-drug interactions
Useful for depression, anxiety disorders, neuropathic pain
Useful for depression, seasonal depression; not recommended for anxiety disorder treatment because of stimulating effects
Causes less sexual dysfunction (may reverse effects of SSRIs/SNRIs), weight gain, and sedation Increased risk of seizures at higher doses
Contraindicated with history of seizure, stroke, brain tumour, brain injury, closed head injury Important to specify formulation, as available in IR, SR, XL (longest)
Useful for OCD (clomipramine), melancholic depression; requires ECG monitoring; highly lethal in overdose
Preferred to tertiary amines because of lower propensity for anticholinergic adverse effects Highly lethal in overdose
Useful for moderate/severe depression that does not respond to other antidepressants, atypical depression; requires strict adherence to MAOI diet
Useful for depression that does not respond to other antidepressants
Useful in depression with prominent features of insomnia, agitation, or cachexia
MAOI = monoamine oxidase inhibitors; NASSA = noradrenergic and specific serotonin antagonists; NDRI = norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitors;
RIMA = reversible inhibition of MAO-A; SNRI = serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors; SSRI = selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; TCA = tricyclic antidepressants
Treatment Approach for Depression
Start SSRI or other first line agent
Reassess every 1-2 wk for 3-4 wk
Psychopharmacology of SSRIs
Full response Continue
Full response
Figure 3. Treatment of depression
• optimization:increasedosagetomaximumtoleratedorhighesttherapeuticdosage
• augmentation:theadditionofamedicationthatisnotconsideredanantidepressanttoan
antidepressant regimen (e.g. thyroid hormone, lithium, atypical antipsychotics [aripiprazole, quetiapine,
olanzapine, risperidone])
• combination:theadditionofanotherantidepressanttoanexistingtreatmentregimen(e.g.theaddition
of bupropion or mirtazapine to an SSRI or SNRI)
• switch:changeintheprimaryantidepressant(withinoroutsideaclass)
• note:itisimportanttofullytreatdepressionsymptoms(i.e.,toremission)todecreaserelapserates
Post-Synaptic Serotonin Receptor Stimulated
5HT1A centrally
5HT2Ainspinal cord
5HT2C/5HT2A in brain
5HT3A in gut
Effect/Side Effect
• Relief of depression • Anxiolytic effect
•Sexualdysfunction: delayed ejaculation, anorgasmia, decreased interest/libido
• Activation: anxiety, insomnia
• Worst with fluoxetine, paroxetine
• Warn patients anxiety may worsen in first 1-2 wk of treatment
• GI upset: nausea, vomiting, bloating
• Take with food
No or partial response Optimize dose
Reassess regularly for 4-8 wk
Partial response
No response Switch
Combine
Augment