Page 1210 - TNFlipTest
P. 1210
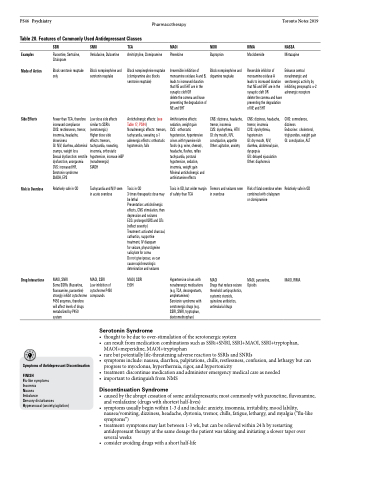
PS46 Psychiatry Pharmacotherapy Table 20. Features of Commonly Used Antidepressant Classes
Toronto Notes 2019
NASSA
Mirtazapine
Enhance central noradrenergic and serotonergic activity by inhibiting presynaptic α-2 adrenergic receptors
CNS: somnolence, dizziness
Endocrine: cholesterol, triglycerides. weight gain GI: constipation, ALT
Relatively safe in OD
Examples Mode of Action
Side Effects
Risk in Overdose
SSRI
Fluoxetine, Sertraline, Citalopram
Block serotonin reuptake only
Fewer than TCA, therefore increased compliance CNS: restlessness, tremor, insomnia, headache, drowsiness
GI: N/V, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, weight loss Sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction, anorgasmia CVS: increased HR, Serotonin syndrome SIADH, EPS
Relatively safe in OD
SNRI
Venlafaxine, Duloxetine
Block norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake
Low dose side effects similar to SSRIs (serotonergic)
Higher dose side
effects: tremors, tachycardia, sweating, insomnia, orthostatic hypotension, increase inBP (noradrenergic)
SIADH
Tachycardia and N/V seen in acute overdose
TCA
Amitriptyline, Clomipramine
Block norepinephrine reuptake (clomipramine also blocks serotonin reuptake)
Anticholinergic effects: (see Table 17, PS44)
Noradrenergic effects: tremors, tachycardia, sweating α-1 adrenergic effects: orthostatic hypotension, falls
Toxic in OD
3 times therapeutic dose may be lethal
Presentation: anticholinergic effects, CNS stimulation, then depression and seizures
ECG: prolonged QRS and QTc (reflect severity)
Treatment: activated charcoal, cathartics, supportive treatment, IV diazepam
for seizure, physostigmine salicylate for coma
Do not give ipecac, as can cause rapid neurologic deterioration and seizures
MAOI, SSRI EtOH
MAOI
Phenelzine
Irreversible inhibition of monoamine oxidase A and B, leads to increased duration that NE and 5HT are in the synaptic cleft OR
delete the comma and have preventing the degradation of NE and 5HT
Antihistamine effects: sedation, weight gain
CVS: orthostatic hypotension, hypertensive crises with tyramine rich foods (e.g. wine, cheese):, headache, flushes, reflex tachycardia, postural hypotension, sedation, insomnia, weight gain Minimal anticholinergic and antihistamine effects
Toxic in OD, but wider margin of safety than TCA
NDRI
Buproprion
Block norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake
CNS: dizziness, headache, tremor, insomnia
CVS: dysrhythmia, HTN GI: dry mouth, N/V, constipation, appetite Other: agitation, anxiety
Tremors and seizures seen in overdose
RIMA
Moclobemide
Reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A leads to increased duration that NE and 5HT are in the synaptic cleft OR
delete the comma and have preventing the degradation of NE and 5HT
CNS: dizziness, headache, tremor, insomnia
CVS: dysrhythmia, hypotension
GI: dry mouth, N/V, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia
GU: delayed ejaculation Other: diaphoresis
Risk of fatal overdose when combined with citalopram or clomipramine
Drug Interactions
MAOI, SNRI
Some SSRIs (fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine) strongly inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes, therefore will affect levels of drugs metabolized by P450 system
MAOI, SSRI
Low inhibition of cytochrome P450 compounds
Hypertensive crises with noradrenergic medications (e.g. TCA, decongestants, amphetamines)
Serotonin syndrome with serotonergic drugs (e.g. SSRI, SNRI, tryptophan, dextromethorphan)
MAOI
Drugs that reduce seizure threshold: antipsychotics, systemic steroids, quinolone antibiotics, antimalarial drugs
MAOI, paroxetine, Opioids
MAOI, RIMA
Symptoms of Antidepressant Discontinuation
FINISH
Flu-like symptoms
Insomnia
Nausea
Imbalance
Sensory disturbances Hyperarousal (anxiety/agitation)
• thoughttobeduetoover-stimulationoftheserotonergicsystem
• canresultfrommedicationcombinationssuchasSSRi+SNRI,SSRI+MAOI,SSRI+tryptophan,
MAOI+meperidine, MAOI+tryptophan
• rarebutpotentiallylife-threateningadversereactiontoSSRIsandSNRIs
• symptomsinclude:nausea,diarrhea,palpitations,chills,restlessness,confusion,andlethargybutcan
progress to myoclonus, hyperthermia, rigor, and hypertonicity
• treatment:discontinuemedicationandadministeremergencymedicalcareasneeded
• importanttodistinguishfromNMS
Discontinuation Syndrome
• causedbytheabruptcessationofsomeantidepressants;mostcommonlywithparoxetine,fluvoxamine, and venlafaxine (drugs with shortest half-lives)
• symptomsusuallybeginwithin1-3dandinclude:anxiety,insomnia,irritability,moodlability, nausea/vomiting, dizziness, headache, dystonia, tremor, chills, fatigue, lethargy, and myalgia (“flu-like symptoms”)
• treatment:symptomsmaylastbetween1-3wk,butcanberelievedwithin24hbyrestarting antidepressant therapy at the same dosage the patient was taking and initiating a slower taper over several weeks
• consideravoidingdrugswithashorthalf-life
Serotonin Syndrome