Page 1223 - TNFlipTest
P. 1223
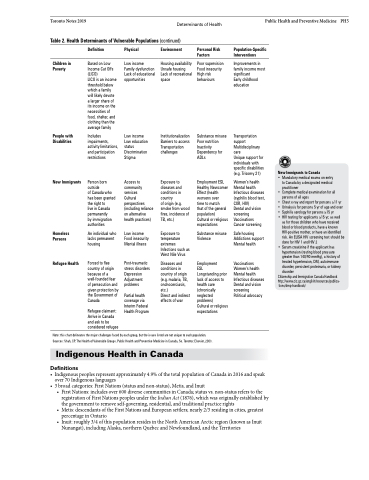
Toronto Notes 2019 Determinants of Health Table 2. Health Determinants of Vulnerable Populations (continued)
Public Health and Preventive Medicine PH5
Children in Poverty
People with Disabilities
New Immigrants
Homeless Persons
Refugee Health
Definition
Based on Low Income Cut Offs (LICO)
LICO is an income threshold below which a family will likely devote a larger share of its income on the necessities of food, shelter, and clothing than the average family
Includes impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions
Person born outside
of Canada who has been granted the right to
live in Canada permanently
by immigration authorities
An individual who lacks permanent housing
Forced to flee country of origin because of a well-founded fear of persecution and given protection by the Government of Canada
Refugee claimant: Arrive in Canada and ask to be considered refugee
Physical
Low income Family dysfunction Lack of educational opportunities
Low income Low education status Discrimination Stigma
Access to community services
Cultural perspectives (including reliance on alternative health practices)
Low income Food insecurity Mental illness
Post-traumatic stress disorders Depression Adjustment problems
Partial health coverage via Interim Federal Health Program
Environment
Housing availability Unsafe housing Lack of recreational space
Institutionalization Barriers to access Transportation challenges
Exposure to diseases and conditions in country
of origin (e.g. smoke from wood fires, incidence of TB, etc.)
Exposure to temperature extremes Infections such as West Nile Virus
Diseases and conditions in country of origin (e.g. malaria, TB, onchocerciasis, etc.)
Direct and indirect effects of war
Personal Risk Factors
Poor supervision Food insecurity High risk behaviours
Substance misuse Poor nutrition Inactivity Dependency for ADLs
Employment ESL Healthy Newcomer Effect (health worsens over
time to match
that of the general population) Cultural or religious expectations
Substance misuse Violence
Employment
ESL
Longstanding prior lack of access to health care (chronically neglected problems)
Cultural or religious expectations
Population-Specific Interventions
Improvements in family income most significant
Early childhood education
Transportation support Multidisciplinary care
Unique support for individuals with specific disabilities (e.g. Trisomy 21)
Women’s health Mental health Infectious diseases (syphilis blood test, CXR, HIV)
Dental and vision screening Vaccinations Cancer screening
Safe housing Addictions support Mental health
Vaccinations Women’s health Mental health Infectious diseases Dental and vision screening
Political advocacy
New Immigrants to Canada
• Mandatory medical exams on entry to Canada by a designated medical practitioner
• Complete medical examination for all persons of all ages
• Chest x-ray and report for persons ≥11 yr • Urinalysis for persons 5 yr of age and over • Syphilis serology for persons ≥15 yr
• HIV testing for applicants ≥15 yr, as well
as for those children who have received blood or blood products, have a known HIV-positive mother, or have an identified risk. An ELISA HIV screening test should be doneforHIV1andHIV2
• Serum creatinine if the applicant has hypertension (resting blood pressure greater than 140/90 mmHg), a history of treated hypertension, DM, autoimmune disorder, persistent proteinuria, or kidney disorder
Citizenship and Immigration Canada Handbook http://www.cic.gc.ca/english/resources/publica-
tions/dmp-handbook/
Note: this chart delineates the major challenges faced by each group, but the issues listed are not unique to each population. Sources: Shah, CP. The Health of Vulnerable Groups. Public Health and Preventive Medicine in Canada, 5e. Toronto: Elsevier, 2003.
Indigenous Health in Canada
Definitions
• Indigenouspeoplesrepresentapproximately4.9%ofthetotalpopulationofCanadain2016andspeak over 70 Indigenous languages
• 3broadcategories:FirstNations(statusandnon-status),Metis,andInuit
• FirstNations:includesover600diversecommunitiesinCanada;statusvs.non-statusreferstothe
registration of First Nations peoples under the Indian Act (1876), which was originally established by
the government to remove self-governing, residential, and traditional practice rights
• Metis:descendantsoftheFirstNationsandEuropeansettlers;nearly2/3residingincities,greatest
percentage in Ontario
• Inuit:roughly3/4ofthispopulationresidesintheNorthAmericanArcticregion(knownasInuit
Nunangat), including Alaska, northern Quebec and Newfoundland, and the Territories