Page 1248 - TNFlipTest
P. 1248
R2 Respirology
Acronyms
Toronto Notes 2019
Acronyms
A-a
A-aDO2 alveolar-arterial oxygen diffusion gradient ABG arterial blood gas
ACEI angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor ACV assist-control ventilation
AECOPD acute exacerbation of COPD
AFB acid-fast bacillus
AFP alpha-fetoprotein
AFOP acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia AHI apnea hypopnea index
AIP acute interstitial pneumonia
ALI acute lung injury
ALS amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
ANA antinuclear antibody
ANCA anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody APTT activated partial thromboplastin time ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome ASA acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin®)
ASD atrial septal defect
AV arteriovenous
AVM arteriovenous malformation
AVN avascular necrosis
BG blood glucose
BiPAP bilevel positive airway pressure
BOOP bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing
pneumonia
BSA body surface area
CA cancer
CCB calcium channel blocker CD Crohn’s disease
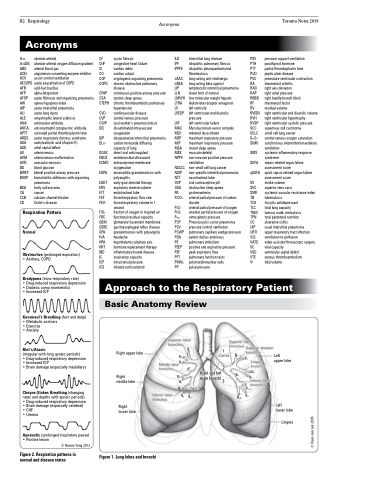
Respiration Pattern Normal
Obstructive (prolonged expiration) • Asthma, COPD
Bradypnea (slow respiratory rate)
• Drug-induced respiratory depression • Diabetic coma (nonketotic)
• Increased ICP
Kussmaul’s Breathing (fast and deep) • Metabolic acidosis
• Exercise
• Anxiety
Biot’s/Ataxic
(irregular with long apneic periods)
• Drug-induced respiratory depression • Increased ICP
• Brain damage (especially medullary)
Cheyne-Stokes Breathing (changing rates and depths with apneic periods) • Drug-induced respiratory depression • Brain damage (especially cerebral) • CHF
• Uremia
Apneustic (prolonged inspiratory pause) • Pontine lesion
© Bonnie Tang 2012
Figure 2. Respiration patterns in normal and disease states
alveolar-arterial
CF cystic fibrosis
CHF congestive heart failure
CI cardiac index
CO cardiac output
COP cryptogenic organizing pneumonia COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease
CPAP continuous positive airway pressure CSA central sleep apnea
CTEPH chronic thromboembolic pulmonary
hypertension
CVD cardiovascular disease CVP central venous pressure
CWP coal worker’s pneumoconiosis DIC disseminated intravascular
coagulation
DIP desquamative interstitial pneumonia DLCO carbon monoxide diffusing
capacity of lung
DOAC direct oral anticoagulant EBUS endobronchial ultrasound
ECMO extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
EGPA eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
EGDT early goal-directed therapy ERV expiratory reserve volume ETT endotracheal tube
FEF forced expiratory flow rate FEV1 forced expiratory volume in 1
second
FiO2 fraction of oxygen in inspired air FRC functional residual capacity GBM glomerular basement membrane GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease GPA granulomatosis with polyangiitis H/A headache
HPA hypothalamic-pituitary axis
HRT hormone replacement therapy
ILD interstitial lung disease
IPF idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis IPPFE idiopathic pleuroparenchymal
fibroelastosis
LAAC long-acting anti-cholinergic
LABA long-acting beta-agonist
LIP lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia LLN lower limit of normal
LMWH low molecular weight heparin LTRA leukotriene receptor antagonist
LV left ventricle
LVEDP left ventricular end diastolic
pressure
LVF left ventricular failure
MAC Mycobacterium avium complex MDI metered dose inhaler
MEP maximum expiratory pressure MIP maximum inspiratory pressure MSA mixed sleep apnea
MSK musculoskeletal
NPPV non-invasive positive pressure
ventilation
NSCLC non-small cell lung cancer
NSIP non-specific interstitial pneumonia NTT nasotracheal tube
OCP oral contraceptive pill
OSA obstructive sleep apnea
PA posteroanterior
PaCO2 arterial partial pressure of carbon
dioxide
PaO2 arterial partial pressure of oxygen PAO2 alveolar partial pressure of oxygen Patm atmospheric pressure
PCP Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia PCV pressure control ventilation
PCWP pulmonary capillary wedge pressure PDA patent ductus arteriosus
PE pulmonary embolism
PEEP positive end expiratory pressure PEF peak expiratory flow
PFT pulmonary function tests
PMNs polymorphonuclear cells
PP pulse pressure
PSV pressure support ventilation PTH parathyroid hormone
PTT partial thromboplastin time PUD peptic ulcer disease
PVC premature ventricular contraction RA rheumatoid arthritis
RAD right axis deviation
RAP right atrial pressure
RBBB right bundle branch block
RF rheumatoid factor
RV residual volume
RVEDV right ventricular end diastolic volume RVH right ventricular hypertrophy
RVSP right ventricular systolic pressure SCC squamous cell carcinoma
SCLC small cell lung cancer
ScvO2 central venous oxygen saturation SIMV synchronous intermittent mandatory
ventilation
SIRS systemic inflammatory response
syndrome
SOFA sepsis-related organ failure
assessment score
qSOFA quick sepsis-related organ failure
assessment score SV stroke volume
SVC superior vena cava
SVRI systemic vascular resistance index TB tuberculosis
TCA tricyclic antidepressant
TLC total lung capacity
TNM tumour, node, metastasis
TPN total parenteral nutrition
UC ulcerative colitis
UIP usual interstitial pneumonia
URTI upper respiratory tract infection V/Q ventilation-to-perfusion
VATS video-assisted thorascopic surgery VC vital capacity
VSD ventricular septal defect
VTE venous thromboembolism
VT tidal volume
IBD IC ICP ICS
inflammatory bowel disease inspiratory capacity intracranial pressure inhaled corticosteroid
Approach to the Respiratory Patient
Basic Anatomy Review
Right upper lobe
Right lower lobe
B1
1
B2 B3
B4 middle lobe B5
B1+2
B3
Left
upper lobe
Left
lower lobe
Lingula
B6 2B4
Right
Right and left main bronchi
3
B6
B10
B5
B7+8 B9
B7
B8 B9
Figure 1. Lung lobes and bronchi
© Hyun Joo Lee 2005