Page 1280 - TNFlipTest
P. 1280
R34 Respirology
Introduction to Intensive Care Toronto Notes 2019
Causes of SHOCK
Spinal (neurogenic), Septic Hemorrhagic
Obstructive (e.g. tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, PE)
Cardiogenic (e.g. arrhythmia, MI) AnaphylaKtic
Shock
• seeEmergencyMedicine,ER3
• inadequatetissueperfusionpotentiallyresultinginendorganinjury
■ categories of shock
◆ hypovolemic: hemorrhage, dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea, interstitial fluid redistribution ◆ cardiogenic: myopathic (myocardial ischemia ± infarction), mechanical, arrhythmic,
pharmacologic
◆ obstructive: massive PE (saddle embolus), pericardial tamponade, constrictive pericarditis,
Shock: Clinical Correlation
Hypovolemic: patients have cool extremities due to peripheral vasoconstriction Cardiogenic: patients usually have signs of left-sided heart failure
Obstructive: varied presentation Distributive: patients have warm extremities due to peripheral vasodilation
increased intrathoracic pressure (e.g. tension pneumothorax) ◆ distributive: sepsis, anaphylaxis, neurogenic, endocrine, toxins
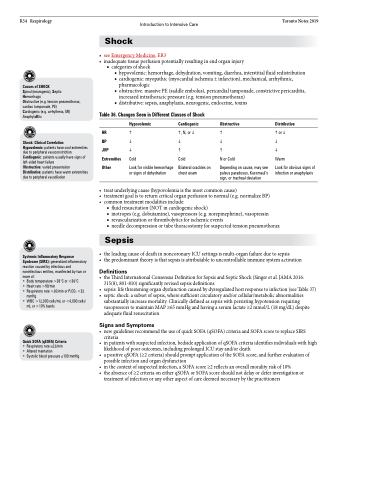
Table 36. Changes Seen in Different Classes of Shock
Hypovolemic Cardiogenic Obstructive
HR , N, or BP JVP
Distributive
or
Warm
Look for obvious signs of infection or anaphylaxis
Extremities Other
Cold
Look for visible hemorrhage or signs of dehydration
Cold
Bilateral crackles on chest exam
N or Cold
Depending on cause, may see pulsus paradoxus, Kussmaul’s sign, or tracheal deviation
• treatunderlyingcause(hypovolemiaisthemostcommoncause)
• treatmentgoalistoreturncriticalorganperfusiontonormal(e.g.normalizeBP) • commontreatmentmodalitiesinclude:
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS): generalized inflammatory reaction caused by infectious and noninfectious entities, manifested by two or more of:
• Body temperature >38°C or <36°C
• Heart rate >90/min
• Respiratory rate >20/min or PaCO2 <32
mmHg
• WBC >12,000 cells/mL or <4,000 cells/
mL or >10% bands
Quick SOFA (qSOFA) Criteria
• Respiratory rate ≥22/min
• Altered mentation
• Systolic blood pressure ≤100 mmHg
■ fluid resuscitation (NOT in cardiogenic shock)
■ inotropes (e.g. dobutamine), vasopressors (e.g. norepinephrine), vasopressin
■ revascularization or thrombolytics for ischemic events
■ needle decompression or tube thoracostomy for suspected tension pneumothorax
Sepsis
• theleadingcauseofdeathinnoncoronaryICUsettingsismulti-organfailureduetosepsis
• thepredominanttheoryisthatsepsisisattributabletouncontrollableimmunesystemactivation
Definitions
• theThirdInternationalConsensusDefinitionforSepsisandSepticShock(Singeretal.JAMA2016: 315(8), 801-810) significantly revised sepsis definitions
• sepsis:lifethreateningorgandysfunctioncausedbydysregulatedhostresponsetoinfection(seeTable37) • septic shock: a subset of sepsis, where sufficient circulatory and/or cellular/metabolic abnormalities
substantially increase mortality. Clinically defined as sepsis with persisting hypotension requiring vasopressors to maintain MAP ≥65 mmHg and having a serum lactate ≥2 mmol/L (18 mg/dL) despite adequate fluid resuscitation
Signs and Symptoms
• newguidelinesrecommendtheuseofquickSOFA(qSOFA)criteriaandSOFAscoretoreplaceSIRS criteria
• inpatientswithsuspectedinfection,bedsideapplicationofqSOFAcriteriaidentifiesindividualswithhigh likelihood of poor outcomes, including prolonged ICU stay and/or death
• apositiveqSOFA(≥2criteria)shouldpromptapplicationoftheSOFAscore,andfurtherevaluationof possible infection and organ dysfunction
• inthecontextofsuspectedinfection,aSOFAscore≥2reflectsanoverallmoralityriskof10%
• theabsenceof≥2criteriaoneitherqSOFAorSOFAscoreshouldnotdelayordeferinvestigationor
treatment of infection or any other aspect of care deemed necessary by the practitioners