Page 1366 - TNFlipTest
P. 1366
VS2 Vascular Surgery Acronyms
AAA abdominal aortic aneurysm
ABI ankle-brachial index
ACEI angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor
AFib atrial fibrillation
AKA above-knee amputation
AKI acute kidney injury
aPTT activated partial thromboplastin time (i.e. PTT) ASA acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin®)
AT anterior tibial artery
BKA below-knee amputation
BP blood pressure
CABG coronary artery bypass graft
CAD coronary artery disease
CAS carotid artery angioplasty + stenting
CBC complete blood count
CCB calcium channel blocker
CLI critical limb ischemia
Acronyms
Toronto Notes 2019
CTA computed tomography angiography CVA cerebrovascular accident
CVD cerebrovascular disease
CVI chronic venous insufficiency
CXR chest x-ray
DIC disseminated intravascular
coagulation
DM diabetes mellitus
DVT deep vein thrombosis ECASA enteric coated ASA ECG electrocardiogram Echo echocardiogram
ET essential thrombocythemia
EVAR endovascular aortic aneurysm repair
EVLT endovenous laser therapy GSV greater saphenous vein
HITS heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
syndrome
HITT heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
with thrombosis
HTN hypertension
IBD inflammatory bowel disease INR international normalized ratio LMWH low molecular weight heparin LSV lesser saphenous vein
MCA middle cerebral artery
MRA magnetic resonance angiography MSK musculoskeletal
OCP oral contraceptive pill
PE pulmonary embolism
PT prothrombin time
PTT partial thromboplastin time (i.e. aPTT) PVD peripheral vascular disease
RIND reversible ischemic neurologic deficit SFA superficial femoral artery
SVT superficial venous thrombosis
TAA thoracic aortic aneurysm
TEE transesophageal echocardiography TEVAR thoracic endovascular aortic
aneurysm repair
TIA transient ischemic attack
TTE transthoracic echocardiogram
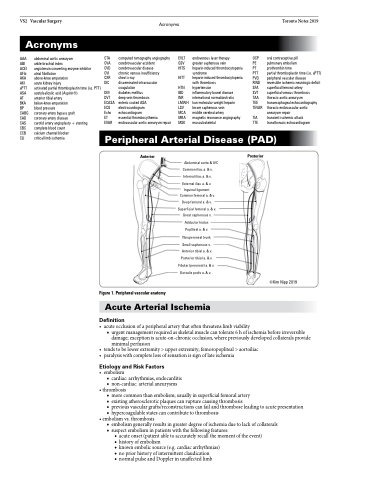
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Anterior
Posterior
Abdominal aorta & IVC Common iliac a. & v. Internal iliac a. & v. External iliac a. & v.
Inguinal ligament Common femoral a. & v. Deep femoral a. & v. Superficial femoral a. & v. Great saphenous v.
Adductor hiatus Popliteal a. & v. Tibioperoneal trunk
Small saphenous v.
Anterior tibial a. & v. Posterior tibial a. & v. Fibular (peroneal) a. & v.
Dorsalis pedis a. & v.
©Kim Nipp 2019
Figure 1. Peripheral vascular anatomy
Acute Arterial Ischemia
Definition
• acuteocclusionofaperipheralarterythatoftenthreatenslimbviability
■ urgent management required as skeletal muscle can tolerate 6 h of ischemia before irreversible
damage; exception is acute-on-chronic occlusion, where previously developed collaterals provide
minimal perfusion
• tendstobelowerextremity>upperextremity;femoropopliteal>aortoiliac • paralysiswithcompletelossofsensationissignoflateischemia
Etiology and Risk Factors
• embolism
■ cardiac: arrhythmias, endocarditis ■ non-cardiac: arterial aneurysms
• thrombosis
■ more common than embolism; usually in superficial femoral artery
■ existing atherosclerotic plaques can rupture causing thrombosis
■ previous vascular grafts/reconstructions can fail and thrombose leading to acute presentation ■ hypercoagulable states can contribute to thrombosis
• embolism vs. thrombosis
■ embolism generally results in greater degree of ischemia due to lack of collaterals ■ suspect embolism in patients with the following features:
◆ acute onset (patient able to accurately recall the moment of the event) ◆ history of embolism
◆ known embolic source (e.g. cardiac arrhythmias)
◆ no prior history of intermittent claudication
◆ normal pulse and Doppler in unaffected limb