Page 1368 - TNFlipTest
P. 1368
VS4 Vascular Surgery
Critical limb ischemia
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Toronto Notes 2019
• heart:riskofarrhythmia,MI,cardiacarrestanddeathwithreperfusioninjury
• kidneys/otherorgans:renalfailureandmulti-organfailureduetotoxicmetabolitesfromischemic
muscle
Prognosis
• 12-15%mortalityrate
• 5-40%morbidityrate(amputation)
Chronic Limb Ischemia
Definition
• chronicischemiaduetoinadequatearterialsupplytomeetcellularmetabolicdemandsduringwalking (claudication) or at rest (critical limb ischemia)
Etiology and Risk Factors
• predominantlyduetoatherosclerosis(forpathogenesis,seeCardiologyandCardiacSurgery,C25); primarily occurs in the lower extremities
• major risk factors: smoking, DM, older age
• minorriskfactors:HTN,hyperlipidemia,obesity,sedentarylifestyle,PMHxorFMHxPAD/CAD/CVD
Clinical Features
• claudication:mustdifferentiatevascularfromneurogenicclaudicationorMSKpain
1. pain with exertion: usually in calves or any exercising muscle group
2. relieved by short rest: 2-5 min and no postural changes necessary
3. reproducible: same distance or time to elicit pain, same location of pain, same amount of rest to
relieve pain
• criticallimbischemia(CLI)
1. includes rest pain, night pain, tissue loss (ulceration or gangrene)
2. pain most commonly over the forefoot/toes, waking person from sleep, and often relieved by
hanging foot off bed
3. ankle pressure <40 mmHg, toe pressure <30 mmHg, ABI <0.40
◆ pulses may be absent at some locations, bruits may be present
◆ signs of poor perfusion: hair loss, hypertrophic nails, atrophic muscle, ulcerations and infections,
slow capillary refill, prolonged pallor with elevation and rubor on dependency, venous troughing
(collapse of superficial veins of foot)
4. high risk of 1 year limb amputation and mortality
Investigations
• routinebloodwork,fastingmetabolicprofile
• ABI:highestanklepressure(dorsalispedisorposteriortibial)foreachsidedividedbyhighestbrachial
pressure (see Table 2 for cut-offs)
• arterialduplexultrasound:combinestraditionalandDopplerultrasoundtovisualizebloodvesselsand
characterize flow
• CTAandMRA
■ excellent for large arteries (aorta, iliac, femoral, popliteal) but may have difficulty with tibial arteries (especially in the presence of disease)
■ require IV injection of nephrotoxic contrast (iodinated contrast for CT, gadolinium for MR)
■ used primarily for planning interventions
• invasive
■ arteriography: superior resolution to CTA/MRA, better for tibial arteries, can be done intraoperatively as part of intervention
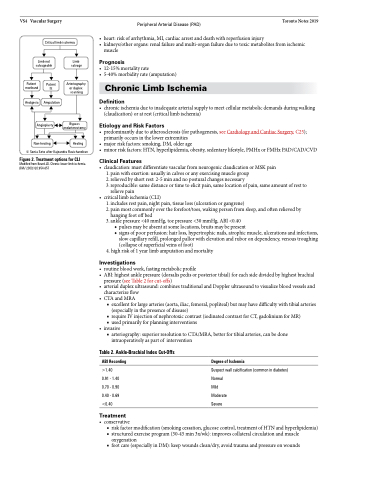
Limb not salvageable
Limb salvage
Arteriography or duplex scanning
Bypass endarterectomy
Non-healing
© Sonia Seto after Kajeandra Ravichandiran
Figure 2. Treatment options for CLI
Modified from Beard JD. Chronic lower limb ischemia. BMJ 2000;320:854-857
Patient moribund
Patient fit
Analgesia Amputation
Angioplasty
Healing
Table 2. Ankle-Brachial Index Cut-Offs
ABI Recording
>1.40 0.91 - 1.40 0.70 - 0.90 0.40 - 0.69 <0.40
Treatment
Degree of Ischemia
Suspect wall calcification (common in diabetes) Normal
Mild
Moderate
Severe
• conservative
■ risk factor modification (smoking cessation, glucose control, treatment of HTN and hyperlipidemia)
■ structured exercise program (30-45 min 3x/wk): improves collateral circulation and muscle
oxygenation
■ foot care (especially in DM): keep wounds clean/dry, avoid trauma and pressure on wounds