Page 139 - TNFlipTest
P. 139
Toronto Notes 2019 Differential Diagnoses of Common Presentations Dermatology D5
Differential Diagnoses of Common Presentations
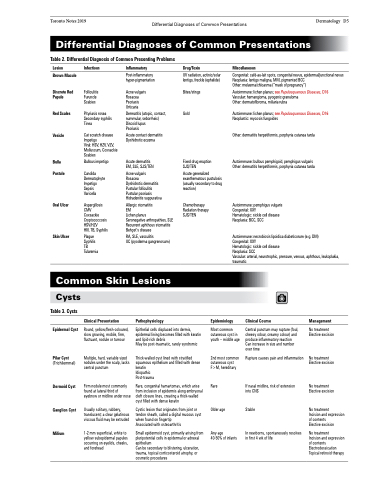
Table 2. Differential Diagnosis of Common Presenting Problems
Lesion
Brown Macule
Discrete Red Papule
Red Scales
Vesicle
Bulla Pustule
Oral Ulcer
Skin Ulcer
Infectious
Folliculitis Furuncle Scabies
Pityriasis rosea Secondary syphilis Tinea
Cat scratch disease Impetigo
Viral: HSV, HZV, VZV, Molluscum, Coxsackie Scabies
Bullous impetigo
Candida Dermatophyte Impetigo Sepsis Varicella
Aspergillosis CMV Coxsackie Cryptococcosis HSV/HZV
HIV, TB, Syphilis
Plague Syphilis TB Tularemia
Inflammatory
Post-inflammatory hyper-pigmentation
Acne vulgaris Rosacea Psoriasis Urticaria
Dermatitis (atopic, contact, nummular, seborrheic) Discoid lupus
Psoriasis
Acute contact dermatitis Dyshidrotic eczema
Acute dermatitis EM, SLE, SJS/TEN
Acne vulgaris
Rosacea
Dyshidrotic dermatitis Pustular folliculitis Pustular psoriasis Hidradenitis suppurativa
Allergic stomatitis
EM
Lichen planus
Seronegative arthropathies, SLE Recurrent aphthous stomatitis Behçet’s disease
RA, SLE, vasculitis
UC (pyoderma gangrenosum)
Drug/Toxin
UV radiation, actinic/solar lentigo, freckle (ephelide)
Bites/stings
Gold
Fixed drug eruption SJS/TEN
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (usually secondary to drug reaction)
Miscellaneous
Congenital: café-au-lait spots, congenital nevus, epidermal/junctional nevus Neoplasia: lentigo maligna, MM, pigmented BCC
Other: melasma/chloasma (“mask of pregnancy”)
Autoimmune: lichen planus; see Papulosquamous Diseases, D16 Vascular: hemangioma, pyogenic granuloma
Other: dermatofibroma, miliaria rubra
Autoimmune: lichen planus; see Papulosquamous Diseases, D16 Neoplastic: mycosis fungoides
Other: dermatitis herpetiformis, porphyria cutanea tarda
Autoimmune: bullous pemphigoid, pemphigus vulgaris Other: dermatitis herpetiformis, porphyria cutanea tarda
Autoimmune: pemphigus vulgaris Congenital: XXY
Hematologic: sickle cell disease Neoplasia: BCC, SCC
Autoimmune: necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum (e.g. DM) Congenital: XXY
Hematologic: sickle cell disease
Neoplasia: SCC
Vascular: arterial, neurotrophic, pressure, venous, aphthous, leukoplakia, traumatic
Chemotherapy Radiation therapy SJS/TEN
Common Skin Lesions
Cysts
Table 3. Cysts
Epidermal Cyst
Pilar Cyst
(Trichilemmal)
Dermoid Cyst
Ganglion Cyst
Milium
Clinical Presentation
Round, yellow/flesh-coloured, slow growing, mobile, firm, fluctuant, nodule or tumour
Multiple, hard, variable sized nodules under the scalp, lacks central punctum
Firm nodule most commonly found at lateral third of eyebrow or midline under nose
Usually solitary, rubbery, translucent; a clear gelatinous viscous fluid may be extruded
1-2 mm superficial, white to yellow subepidermal papules occurring on eyelids, cheeks, and forehead
Pathophysiology
Epidemiology
Most common cutaneous cyst in youth – middle age
2nd most common cutaneous cyst F>M, hereditary
Rare
Older age
Any age
40-50% of infants
Clinical Course
Central punctum may rupture (foul, cheesy odour, creamy colour) and produce inflammatory reaction Can increase in size and number over time
Rupture causes pain and inflammation
If nasal midline, risk of extension into CNS
Stable
In newborns, spontaneously resolves in first 4 wk of life
Management
No treatment Elective excision
No treatment Elective excision
No treatment Elective excision
No treatment
Incision and expression of contents
Elective excision
No treatment
Incision and expression of contents Electrodessication Topical retinoid therapy
Epithelial cells displaced into dermis, epidermal lining becomes filled with keratin and lipid-rich debris
May be post-traumatic, rarely syndromic
Thick-walled cyst lined with stratified squamous epithelium and filled with dense keratin
Idiopathic
Post-trauma
Rare, congenital hamartomas, which arise from inclusion of epidermis along embryonal cleft closure lines, creating a thick-walled cyst filled with dense keratin
Cystic lesion that originates from joint or tendon sheath, called a digital mucous cyst when found on fingertip
Associated with osteoarthritis
Small epidermoid cyst, primarily arising from pluripotential cells in epidermal or adnexal epithelium
Can be secondary to blistering, ulceration, trauma, topical corticosteroid atrophy, or cosmetic procedures