Page 147 - TNFlipTest
P. 147
Toronto Notes 2019
Dermatitis (Eczema)
Dermatology D13
Dermatitis (Eczema)
Definition
• inflammationoftheskin
Clinical Presentation
• poorlydemarcatederythematouspatchesorplaques • symptomsincludepruritusandpain
• acutedermatitis:papules,vesicles
• subacutedermatitis:scaling,crusting,excoriations
• chronicdermatitis:lichenification,xerosis,fissuring
Asteatotic Dermatitis
Clinical Presentation
• diffuse,mildpruriticdermatitissecondarytodryskin
• verycommoninelderly,especiallyinthewinter(i.e.“winteritch”)butstartsinthefall • shinspredominate,lookslikea“driedriverbed”
Management
• skinrehydrationwithmoisturizingroutine±corticosteroidcreams
Atopic Dermatitis
Clinical Presentation
• subacuteandchroniceczematousreactionassociatedwithprolongedseverepruritus • distributiondependsonage
• inflammation,lichenification,excoriationsaresecondarytorelentlessscratching
• atopicpalms:hyperlinearityofthepalms(associatedwithichthyosisvulgaris)
• associatedwith:keratosispilaris(hyperkeratosisofhairfollicles,“chickenskin”),xerosis,occupational hand dryness
Epidemiology
• frequentlyaffectsinfants,children,andyoungadults
• 10-20%ofchildrenindevelopedcountriesundertheageof5areaffected
• associatedwithpersonalorfamilyhistoryofatopy(asthma,hayfever),anaphylaxis,eosinophilia • polygenicinheritance:oneparent>60%chanceforchild;twoparents>80%chanceforchild
• long-termconditionwith1/3ofpatientscontinuingtoshowsignsofADintoadulthood
Pathophysiology
• aT-celldriveninflammatoryprocesswithepidermalbarrierdysfunction
Investigations
• clinicaldiagnosis
• consider:skinbiopsy,patchtestingifallergiccontactdermatitisissuspected
Management
• goal:reducesignsandsymptoms,preventorreducerecurrences/flares
• betteroutcome(e.g.lessflare-ups,modifiedcourseofdisease)ifdiagnosismadeearly • avoidtriggersofAD
• non-pharmacologictherapy
■ moisturizers
■ apply liberally and reapply at least twice a day with goal of minimizing xerosis
■ include in treatment of mild to severe disease as well as in maintenance therapy
■ bathing practices
■ bathe in plain warm water for a short period of time once daily followed by lightly but not
completely drying the skin with a towel; immediately apply topical agents or moisturizers after this ■ use fragrance-free hypoallergenic non-soap cleansers
• pharmacologictherapy
■ topical corticosteroids
◆ effective in reducing acute and chronic symptoms as well as prevention of flares
◆ choice of steroid potency depends on age, body site, short vs. long-term use
◆ apply 1 adult fingertip unit (0.5 g) to an area the size of 2 adult palms bid for acute flares
◆ local side effects: skin atrophy, purpura, telangiectasia, striae, hypertrichosis, and acneiform
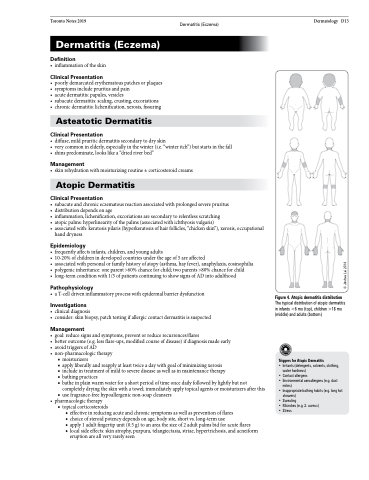
Figure 4. Atopic dermatitis distribution
The typical distribution of atopic dermatitis in infants <6 mo (top), children >18 mo (middle) and adults (bottom)
Triggers for Atopic Dermatitis
• Irritants (detergents, solvents, clothing, water hardness)
• Contact allergens
• Environmental aeroallergens (e.g. dust
mites)
• Inappropriate bathing habits (e.g. long hot
showers)
• Sweating
• Microbes (e.g. S. aureus) • Stress
eruption are all very rarely seen
© Joshua Lai 2014