Page 185 - TNFlipTest
P. 185
Toronto Notes 2019 Patient Assessment/Management Table 4. 2010 AHA CPR Guidelines
Emergency Medicine ER5
Step/Action
Airway Breaths
Foreign-Body Airway Obstruction Compressions
Compression landmarks
Compression method: push hard and fast, and allow for complete recoil
Compression depth Compression rate Compression-ventilation ratio
Compression-only CPR
Defibrillation
Adult: >8 yr Child: 1-8 yr
Head tilt-chin lift
2 breaths at 1 s/breath – stop once see chest rise
Abdominal thrust
In the centre of the chest, between nipples
Infant: <1 yr
Back slaps and chest thrusts
Just below nipple line 2 fingers, or thumbs
2 hands: heel of 1 hand with second hand on top
2-2.4 inches
See Anesthesia and Perioperative Medicine, A30
for ACLS Guidelines
2 hands: heel of 1 hand with second on top, or
1 hand: heel of 1 hand only
About 1/3 to 1/2 the depth of the chest
100-120/min with complete chest wall recoil between compressions
30 compressions to 2 ventilations
Hands-only CPR is preferred if the bystander is not trained or does not feel confident in their ability to provide conventional CPR or if the bystander is trained but chooses to use compressions only
Immediate defibrillation for all rescuers responding to a sudden witnessed collapse Compressions (5 cycles/2 min) before AED is considered if unwitnessed arrest Manual defibrillators are preferred for children and infants but can use adult dose AED if a manual defibrillator is not available
3. Secondary Survey
• doneafterprimarysurveyoncepatientishemodynamicallyandneurologicallystabilized
• identifiesmajorinjuriesorareasofconcern
• fullphysicalexamandx-rays(C-spine,chest,andpelvis–requiredinblunttrauma,considerT-spine
and L-spine if indicated)
HISTORY
• “SAMPLE”: Signs and symptoms, Allergies, Medications, Past medical history, Last meal, Events related to injury
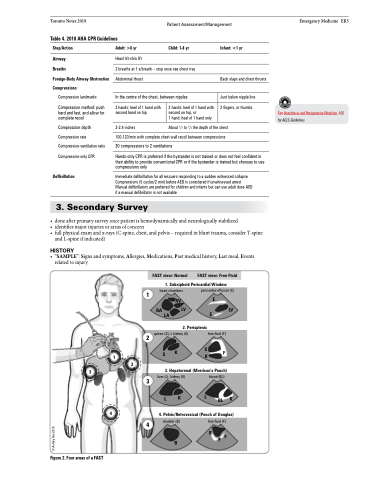
FAST view: Normal FAST view: Free Fluid
1. Subxiphoid Pericardial Window
heart chambers pericardial effusion (E)
1
RA
RV E
LV E LV LA
2. Perisplenic
spleen (S), L kidney (K) free fluid (F)
K SK F 3. Hepatorenal (Morrison’s Pouch)
3
LK LBLK
4. Pelvic/Retrovesical (Pouch of Douglas)
free fluid (F)
B
2
1
2
S
3
liver (L), kidney (K) blood (BL)
4
bladder (B)
4
B
FF
Figure 2. Four areas of a FAST
© Ashley Hui 2015