Page 252 - TNFlipTest
P. 252
E10 Endocrinology
Disorders of Glucose Metabolism
Toronto Notes 2019
Effects of Combination Lipid Therapy in Type 2 DM: the ACCORD Trial
NEJM 2010;362:1563-1574
Study: RCT, double-blinded trial with 4.7 yr of mean follow-up.
Population: 5,518 patients with type 2 DM. Intervention: Statin with or without fibrate therapy. Primary Outcome: Major cardiovascular (CV) event (composite nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or CV-related death).
Results: No significant differences in primary outcome between the two arms. No difference in all MI, all stroke, or all-cause mortality between study arms. Conclusions: The addition of fibrate therapy to statin therapy in patients with type 2 DM does not reduce major CV event risk.
Effects of a Mediterranean Diet in Preventing Cardiovascular Events in Type 2 DM: The PREDIMED Trial
NEJM 2013;368:1279-1290
Study: RCT, with 4.8 yr of median follow-up. Population: 7,447 patients with type 2 DM or other high cardiovascular risk factors.
Intervention: Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil, Mediterranean diet supplemented with mixed nuts, or control diet with advice to reduce dietary fat.
Primary Outcome: Major cardiovascular (CV) event (MI, stroke, or death from CV causes).
Results: Both Mediterranean diets were associated with a reduced incidence of major CV events compared to the control diet.
Conclusions: A Mediterranean diet with extra-virgin olive oil or nuts reduces rates of MI, stroke, and CV death in those at high risk for CV disease.
Sick Day Management
If patient is ill and is unable to maintain adequate fluid intake, or has an acute decline in renal function, they should hold the following medications:
SAD MANS – Sulfonylureuas, ACEIs. Diuretics and direct renin inhibitors, Metformin, ARBs, NSAIDs, SGLT2i
Conversion Chart
for Percentage HbA1c
to Average Blood Sugar Control
Table 9. Available Insulin Formulations
Insulin Type (trade name)
PRANDIAL (BOLUS) INSULINS
Rapid-acting insulin analogues
Insulin aspart (NovoRapid®)
Insulin faster aspart (Fiasp)
Insulin lispro (Humalog®, Humalog 200 units/mL) Insulin glulisine (Apidra®)
Short-acting insulins Humulin R® Novolin Toronto®
BASAL INSULINS
Intermediate-acting Humulin N® Novolin NPH®
Long-acting basal insulin analogues
Insulin detemir (Levemir®)
Insulin glargine 100 units/mL (Lantus®/ Basaglar) Insulin glargine 300 units/mL (Toujeo)
Insulin glargine (BasaglarTM)
Insulin degludec (Tresiba®)
PRE-MIXED INSULINS
Premixed regular insulin – NPH Humulin 30/70®
Novolin 30/70®
Premixed insulin analogues
Biphasic insulin aspart (NovoMix 30®)
Insulin lispro/lispro protamine
(Humulin 30/70, Novolin 30/70, Novomix 30 and Humalog Mix 25)
Onset
10-15 min 4 min 10-15 min 10-15 min
30 min
1-3 h
90 min 90 min Up to 6 h 90 min 60 min
Peak Duration
1-1.5 h 3-5 h
1 h 3-4 h
1-2 h 3.5-4.75 h 1-1.5 h 3-5 h
2-3 h 6.5 h
5-8 h Up to 18 h
Not applicable
Up to 24 h (detemir 16-24 h) Up to 24 h (glargine 24 h) Up to 30 h
Up to 24 h (glargine 24 h) Ultralong acting (42 h)
A single vial or cartridge contains a fixed ratio of insulin
(% of rapid acting or short-acting insulin to % of intermediate-acting insulin)
Activity
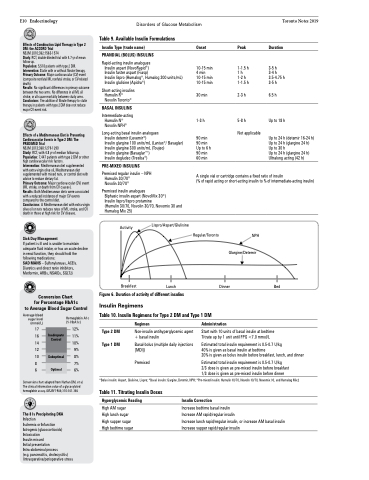
Breakfast
Lispro/Aspart/Glulisine
Lunch
Regular/Toronto
NPH Glargine/Detemir
Dinner Bed
Average blood sugar level (mmol/L)
Hemoglobin A1c (% HbA1c)
Table 10. Insulin Regimens for Type 2 DM and Type 1 DM
Figure 6. Duration of activity of different insulins
Insulin Regimens
17 12% 16 11% 14 10%
Type 2 DM Type 1 DM
Regimen
Non-insulin antihyperglycemic agent + basal insulin
Basal-bolus (multiple daily injections [MDI])
Premixed
Administration
Start with 10 units of basal insulin at bedtime Titrate up by 1 unit until FPG <7.0 mmol/L
Estimated total insulin requirement is 0.5-0.7 U/kg
40% is given as basal insulin at bedtime
20% is given as bolus insulin before breakfast, lunch, and dinner
Estimated total insulin requirement is 0.5-0.7 U/kg
2/3 dose is given as pre-mixed insulin before breakfast 1/3 dose is given as pre-mixed insulin before dinner
Inadequate Controll
Suboptimal
Optimal
12
10 8% 87% 6 6%
Conversion chart adapted from Nathan DM, et al. The clinical information value of a glycosylated hemoglobin assay. NEJM 1984;310:341-346
The 8 Is Precipitating DKA Infection
Ischemia or Infarction Iatrogenic (glucocorticoids) Intoxication
Insulin missed
Initial presentation Intra-abdominal process
(e.g. pancreatitis, cholecystitis)
9%
*Bolus insulin: Aspart, Glulisine, Lispro; *Basal insulin: Gargine, Detemir, NPH; *Pre-mixed insulin: Humulin 30/70, Novolin 30/70, Novomix 30, and Humalog Mix2
Table 11. Titrating Insulin Doses
Hyperglycemic Reading
High AM sugar High lunch sugar High supper sugar High bedtime sugar
Insulin Correction
Increase bedtime basal insulin
Increase AM rapid/regular insulin
Increase lunch rapid/regular insulin, or increase AM basal insulin Increase supper rapid/regular insulin
Intraoperative/perioperative stress