Page 258 - TNFlipTest
P. 258
E16 Endocrinology
Pituitary Gland
Toronto Notes 2019
Features of Metabolic Syndrome (≥ 3 measures to make a Dx)
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Hormones
Measure Men
Women
≥88 cm (35 inches)
≥80 cm (31.5 inches)
≥80 cm (31.5 inches)
Abdominal Obesity (Elevated Waist Circumference
Canada, USA
Europid, Middle Eastern, Sub- Saharan Africa, Mediterranean
Asian, Japanese, South & Central America
Triglyceride Level
HDL-C Level
Blood Pressure
Fasting Glucose Level
Dopamine
Prolactin
Breast
TRH
TSH
Thyroid gland
T3, T4
Somatostatin
ACTH
Adrenal cortex
Cortisol
Multiple target organs
≥102 cm (40 inches)
≥94 cm (37 inches)
≥90 cm (35 inches)
CRH
GHRH
GH FSH
GnRH
LH
≥1.7 mmol/L (150 mg/dL)
<1.0 mmol/L <1.3 mmol/L (<40 mg/dL) (<50 mg/dL)
≥130/85 mmHg
≥5.6 mmol/L (>100 mg/dL)
Liver
Somatomedins (IGF-1)
Endocrine cells of gonads
Male Androgens
Female
Estrogens, progesterone
Drug treatment for any elevated marker is an alternate indicator
Gonadal germ cells, Multiple target organs
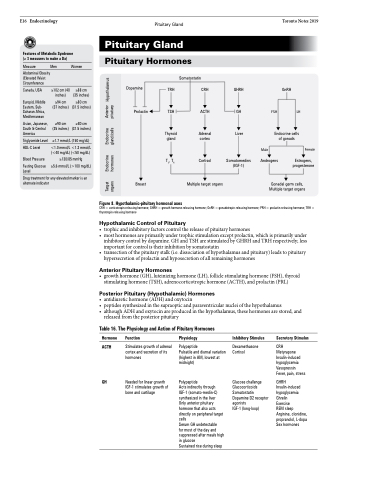
Figure 8. Hypothalamic-pituitary hormonal axes
CRH = corticotropin-releasing hormone; GHRH = growth hormone-releasing hormone; GnRH = gonadotropin-releasing hormone; PRH = prolactin-releasing hormone; TRH = thyrotropin-releasing hormone
Hypothalamic Control of Pituitary
• trophicandinhibitoryfactorscontrolthereleaseofpituitaryhormones
• mosthormonesareprimarilyundertrophicstimulationexceptprolactin,whichisprimarilyunder
inhibitory control by dopamine. GH and TSH are stimulated by GHRH and TRH respectively; less
important for control is their inhibition by somatostatin
• transectionofthepituitarystalk(i.e.dissociationofhypothalamusandpituitary)leadstopituitary
hypersecretion of prolactin and hyposecretion of all remaining hormones
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
• growthhormone(GH),luteinizinghormone(LH),folliclestimulatinghormone(FSH),thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), and prolactin (PRL)
Posterior Pituitary (Hypothalamic) Hormones
• antidiuretichormone(ADH)andoxytocin
• peptidessynthesizedinthesupraopticandparaventricularnucleiofthehypothalamus
• althoughADHandoxytocinareproducedinthehypothalamus,thesehormonesarestored,and
released from the posterior pituitary
Table 16. The Physiology and Action of Pituitary Hormones
Hormone Function
ACTH Stimulates growth of adrenal cortex and secretion of its
hormones
GH Needed for linear growth IGF-1 stimulates growth of
bone and cartilage
Physiology
Polypeptide
Pulsatile and diurnal variation (highest in AM, lowest at midnight)
Polypeptide
Acts indirectly through IGF-1 (somato-medin-C) synthesized in the liver
Only anterior pituitary hormone that also acts directly on peripheral target cells
Serum GH undetectable
for most of the day and suppressed after meals high in glucose
Sustained rise during sleep
Inhibitory Stimulus
Dexamethasone Cortisol
Glucose challenge Glucocorticoids Somatostatin Dopamine D2 receptor agonists
IGF-1 (long-loop)
Secretory Stimulus
CRH
Metyrapone Insulin-induced hypoglycemia Vasopressin Fever, pain, stress
GHRH Insulin-induced hypoglycemia Ghrelin
Exercise
REM sleep Arginine, clonidine, propranolol, L-dopa Sex hormones
Target Endocrine Endocrine Anterior Hypothalamus organs hormones gland/cells pituitary