Page 280 - TNFlipTest
P. 280
E38 Endocrinology
Calcium Homeostasis Toronto Notes 2019
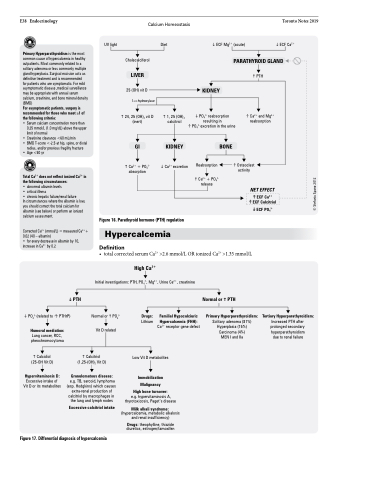
UV light
Diet
h 1, 25 (OH) calcitriol 2
KIDNEY
iCa2+ excretion
iECF Mg2+ (acute) iECF Ca2+ PARATHYROID GLAND
Primary Hyperparathyroidism is the most common cause of hypercalcemia in healthy outpatients. Most commonly related to a solitary adenoma or less commonly multiple gland hyperplasia. Surgical excision acts as definitive treatment and is recommended
for patients who are symptomatic. For mild asymptomatic disease ,medical surveillance may be appropriate with annual serum calcium, creatinine, and bone mineral density (BMD)
For asymptomatic patients, surgery is recommended for those who meet ≥1 of the following criteria:
• Serum calcium concentration more than
0.25 mmol/L (1.0 mg/dL) above the upper
limit of normal
• Creatinine clearance <60 mL/min
• BMD T-score <-2.5 at hip, spine, or distal
radius, and/or previous fragility fracture
• Age <50 yr
Total Ca2+ does not reflect ionized Ca2+ in the following circumstances:
• abnormal albumin levels
• critical illness
• chronic hepatic failure/renal failure
In circumstances where the albumin is low, you should correct the total calcium for albumin (see below) or perform an ionized calcium assessment.
Corrected Ca2+ (mmol/L) = measured Ca2++ 0.02 (40 – albumin)
• for every decrease in albumin by 10, increase in Ca2+ by 0.2
i PTH iPO43- (related toÓPTHrP)
Humoral mediation:
Lung cancer, RCC, pheochromocytoma
h Calcidiol (25-OH Vit D)
Hypervitaminosis D:
Excessive intake of Vit D or its metabolites
Cholecalciferol
LIVER
25 (OH) vit D
1-α-hydroxylase h 24, 25 (OH) vit D
KIDNEY
i PO43- reabsorption
resulting in
h PO 3- excretion in the urine 4
h PTH
h Ca2+ and Mg2+ reabsorption
(inert) 2
GI
hCa2+ + PO43- absorption
BONE
Reabsorption
hCa2+ + PO43- release
hOsteoclast activity
NET EFFECT
iECF PO43-
hECF Ca2+ hECF Calcitriol
Figure 16. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulation
Hypercalcemia
Definition
• total corrected serum Ca2+ >2.6 mmol/L OR ionized Ca2+ >1.35 mmol/L
High Ca2+
Initial investigations: PTH, PO43-, Mg2+, Urine Ca2+, creatinine
Normal orhPO43- Vit D related
Drugs:
Lithium
Familial Hypocalciuric
Hypercalcemia (FHH):
Ca2+ receptor gene defect
Normal or h PTH
Primary Hyperparathyroidism:
Solitary adenoma (81%) Hyperplasia (15%) Carcinoma (4%) MEN I and IIa
Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism:
Increased PTH after prolonged secondary hyperparathyroidism due to renal failure
h Calcitriol (1,25-(OH)2 Vit D)
Granulomatous disease:
e.g. TB, sarcoid, lymphoma (esp. Hodgkins) which causes extra-renal production of calcitriol by macrophages in the lung and lymph nodes
Excessive calcitriol intake
Low Vit D metabolites
Immobilization
Malignancy
High bone turnover:
e.g. hypervitaminosis A, thyrotoxicosis, Paget’s disease
Milk alkali syndrome:
(hypercalcemia, metabolic alkalosis and renal insufficiency)
Drugs: theophylline, thiazide diuretics, estrogen/tamoxifen
Figure 17. Differential diagnosis of hypercalcemia
© Stefania Spano 2012