Page 399 - TNFlipTest
P. 399
Toronto Notes 2019
Common Medications
Gastroenterology G49
Common Medications
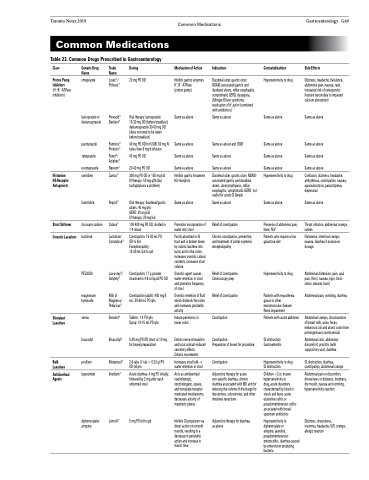
Table 23. Common Drugs Prescribed in Gastroenterology
Class
Proton Pump Inhibitors (H+/K+-ATPase inhibitors)
Generic Drug Name
omeprazole
lansoprazole or dexlansoprazole
pantoprazole rabeprazole esomeprazole
ranitidine
famotidine
docusate sodium
lactulose
PEG3350
magnesium hydroxide
senna
bisacodyl
psyllium
loperamide
diphenoxylate/ atropine
Trade Name
Losec®/ Prilosec®
Prevacid® Dexilant®
Pantoloc® Protonix®
Pariet®/ Aciphex®
Nexium®
Zantac®
Pepcid®
Colace®
Lactulose/ Constulose®
Lax-a-day®/ Golytely®
Milk of Magnesia/ Pedia-Lax®
Senokot®
Bisacodyl®
Metamucil®
Imodium®
Lomotil®
Dosing
20 mg PO OD
Oral therapy: lansoprazole 15-30 mg OD (before breakfast), dexlansoprazole 30-60 mg OD (does not need to be taken before breakfast)
40 mg PO OD for UGIB: 80 mg IV bolus then 8 mg/h infusion
40 mg PO OD 20-40 mg PO OD
300 mg PO OD or 150 mg bid IV therapy: 50 mg q8h (but tachyphylaxis a problem)
Oral therapy: duodenal/gastric ulcers: 40 mg qhs
GERD: 20 mg bid
IV therapy: 20 mg bid
100-400 mg PO OD, divided in 1-4 doses
Constipation: 15-30 mL PO OD to bid Encephalopathy:
15-30 mL bid to qid
Constipation: 17 g powder dissolved in 4-8 oz liquid PO OD
Constipation (adult): 400 mg/5 mL: 30-60 mL PO qhs
Tablets: 1-4 PO qhs Syrup: 10-15 mL PO qhs
5-30 mg PO OD (start at 10 mg for bowel preparation)
2-6 tabs (1 tab =0.52 g) PO OD-tid prn
Acute diarrhea: 4 mg PO initially, followed by 2 mg after each unformed stool
5mgPOtidtoqid
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits gastric enzymes H+/K+-ATPase
(proton pump)
Same as above
Same as above Same as above Same as above
Inhibits gastric histamine H2-receptors
Same as above
Promotes incorporation of water into stool
Poorly absorbed in GI tract and is broken down by colonic bacteria into lactic acid in the colon, increases osmotic colonic contents, increases stool volume
Osmotic agent causes water retention in stool and promotes frequency of stool
Osmotic retention of fluid which distends the colon and increases peristaltic activity
Induce peristalsis in lower colon
Enteric nerve stimulation and local contact-induced secretory effects
Colonic movements
Increases stool bulk → water retention in stool
Acts as antidiarrheal viacholinergic, noncholingeric, opiate, and nonopiate receptor- medicated mechanisms; decreases activity of myenteric plexus
Inhibits GI propulsion via direct action on smooth muscle, resulting in a decrease in peristaltic action and increase in transit time
Indications
Duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, NSAID-associated gastric and duodenal ulcers, reflux esophagitis, symptomatic GERD, dyspepsia, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, eradication of H. pylori (combined with antibiotics)
Same as above
Same as above and UGIB Same as above
Same as above
Duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, NSAID- associated gastric and duodenal ulcers, ulcer prophylaxis, reflux esophagitis, symptomatic GERD; not useful for acute GI bleeds
Same as above
Relief of constipation
Chronic constipation, prevention, and treatment of portal-systemic encephalopathy
Relief of constipation Colonoscopy prep
Relief of constipation
Constipation
Constipation
Preparation of bowel for procedure
Constipation
Adjunctive therapy for acute non-specific diarrhea, chronic diarrhea associated with IBD and for reducing the volume of discharge for ileostomies, colostomies, and other intestinal resections
Adjunctive therapy for diarrhea, as above
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to drug
Same as above
Same as above Same as above Same as above
Hypersensitivity to drug
Same as above
Presence of abdominal pain, fever, N/V
Patients who require a low galactose diet
Hypersensitivity to drug
Patients with myasthenia gravis or other neuromuscular disease Renal impairment
Patients with acute abdomen
GI obstruction Gastroenteritis
Hypersensitivity to drug GI obstruction
Children <2 yr, known hypersensitivity to
drug, acute dysentery characterized by blood in stools and fever, acute ulcerative colitis or pseudomembranous colitis associated with broad- spectrum antibiotics
Hypersensitivity to diphenoxylate or
atropine, jaundice, pseudomembranous enterocolitis, diarrhea caused by enterotoxin producing bacteria
Side Effects
Dizziness, headache, flatulence, abdominal pain, nausea, rash, increased risk of osteoporotic fracture (secondary to impaired calcium absorption)
Same as above
Same as above Same as above Same as above
Confusion, dizziness, headache, arrhythmias, constipation, nausea, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, depression
Same as above
Throat irritation, abdominal cramps, rashes
Flatulence, intestinal cramps, nausea, diarrhea if excessive dosage
Abdominal distension, pain, anal pain, thirst, nausea, rigor, tonic- clonic seizures (rare)
Abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea
Abdominal cramps, discolouration of breast milk, urine, feces, melanosis coli and atonic colon from prolonged use (controversial)
Abdominal colic, abdominal discomfort, proctitis (with suppository use), diarrhea
GI obstruction, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal cramps
Abdominal pain or discomfort, drowsiness or dizziness, tiredness, dry mouth, nausea and vomiting, hypersensitivity reaction
Dizziness, drowsiness,
insomnia, headache, N/V, cramps, allergic reaction
Histamine H2-Receptor Antagonists
Stool Softener
Osmotic Laxatives
Stimulant Laxatives
Bulk Laxatives
Antidiarrheal Agents