Page 400 - TNFlipTest
P. 400
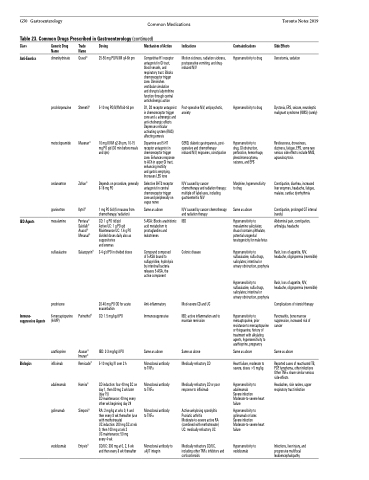
G50 Gastroenterology Common Medications Table 23. Common Drugs Prescribed in Gastroenterology (continued)
Toronto Notes 2019
Side Effects
Xerostomia, sedation
Dystonia, EPS, seizure, neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) (rarely)
Restlessness, drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue, EPS, some rare serious side effects include NMS, agranulocytosis
Constipation, diarrhea, increased liver enzymes, headache, fatigue, malaise, cardiac dysrhythmia
Constipation, prolonged QT interval (rarely)
Abdominal pain, constipation, arthralgia, headache
Rash, loss of appetite, N/V, headache, oligospermia (reversible)
Rash, loss of appetite, N/V, headache, oligospermia (reversible)
Complications of steroid therapy
Pancreatitis, bone marrow suppression, increased risk of cancer
Same as above
Reported cases of reactivated TB, PCP, lymphoma, other infections Other TNFα share similar serious side-effects
Headaches, skin rashes, upper respiratory tract infection
Infections, liver injury, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
Class
Anti-Emetics
Generic Drug Name
dimenhydrinate
prochlorperazine
metoclopramide
ondansetron
granisetron
mesalamine
sulfasalazine
prednisone
6-mercaptopurine (6-MP)
azathioprine
infliximab
adalimumab
golimumab
vedolizumab
Trade Name
Gravol®
Stemetil®
Maxeran®
Zofran®
Kytril®
Pentasa® Salofalk® Asacol® Mesasal®
Salazopyrin®
Purinethol®
Azasan® Imuran®
Remicade®
Humira®
Simponi®
Entyvio®
Dosing
25-50 mg PO/IV/IM q4-6h prn
5-10 mg PO/IV/IM bid-tid prn
10 mg IV/IM q2-3h pm, 10-15 mg PO qid (30 min before meals and qhs)
Depends on procedure, generally 8-16 mg PO
1 mg PO bid (for nausea from chemotherapy/ radiation)
CD: 1 g PO tid/qid
Active UC: 1 g PO qid Maintenance UC: 1.6 g PO divided doses daily also as suppositories
and enemas
3-4 g/d PO in divided doses
20-40 mg PO OD for acute exacerbation
CD: 1.5 mg/kg/d PO
IBD: 2-3 mg/kg/d PO
5-10 mg/kg IV over 2 h
CD induction: four 40 mg SC on day 1, then 80 mg 2 wk later (day 15)
CD maintenance: 40 mg every other wk beginning day 29
RA: 2 mg/kg at wks 0, 4 and then every 8 wk thereafter (use with methotrexate)
UC induction: 200 mg SC at wk 0, then 100 mg at wk 2
UC maintenance: 50 mg every 4 wk
CD/UC: 300 mg at 0, 2, 6 wk and then every 8 wk thereafter
Mechanism of Action
Competitive H1 receptor antagonist in GI tract, blood vessels, and respiratory tract. Blocks chemoreceptor trigger zone. Diminishes vestibular simulation and disrupts labyrinthine function through central anticholinergic action
D1, D2 receptor antagonist in chemoreceptor trigger zone and α adrenergic and anti-cholinergic effects Depresses reticular activating system (RAS) affecting emesis
Dopamine and 5-HT receptor antagonist in chemoreceptor trigger zone. Enhances response to ACh in upper GI tract, enhancing motility
and gastric emptying. Increases LES tone
Selective 5HT3 receptor antagonist in central chemoreceptor trigger zone and peripherally on vagus nerve
Same as above
5-ASA: Blocks arachidonic acid metabolism to prostaglandins and leukotrienes
Compound composed of 5-ASA bound to sulfapyridine, hydrolysis by intestinal bacteria releases 5-ASA, the active component
Anti-inflammatory Immunosuppressive
Same as above
Monoclonal antibody to TNFα
Monoclonal antibody to TNFα
Monoclonal antibody to TNFα
Monoclonal antibody to α4β7 integrin
Indications
Motion sickness, radiation sickness, postoperative vomiting, and drug- induced N/V
Post-operative N/V, antipsychotic, anxiety
GERD, diabetic gastroparesis, post- operative and chemotherapy induced N/V, migraines, constipation
N/V caused by cancer chemotherapy and radiation therapy; multiple off label uses, including gastroenteritis N/V
N/V caused by cancer chemotherapy and radiation therapy
IBD
Colonic disease
Mod-severe CD and UC
IBD: active inflammation and to maintain remission
Same as above
Medically refractory CD
Medically refractory CD or poor response to infliximab
Active ankylosing spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Moderate-to-severe active RA (combined with methotrexate) UC: medically refractory UC
Medically refractory CD/UC, including other TNFα inhibitors and corticosteroids
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to drug
Hypersensitivity to drug
Hypersensitivity to drug, GI obstruction, perforation, hemorrhage, pheochromocytoma, seizures, and EPS
Morphine, hypersensitivity to drug
Same as above
Hypersensitivity to mesalamine salicylates; Asacol contains phthalate, potential urogenital teratogenicity for male fetus
Hypersensitivity to sulfasalazine, sulfa drugs, salicylates; intestinal or urinary obstruction, porphyria
Hypersensitivity to sulfasalazine, sulfa drugs, salicylates; intestinal or urinary obstruction, porphyria
Hypersensitivity to mercaptopurine, prior resistance to mercaptopurine or thioguanine, history of treatment with alkylating agents, hypersensitivity to azathioprine, pregnancy
Same as above
Heart failure, moderate to severe, doses >5 mg/kg
Hypersensitivity to adalimumab
Severe infection Moderate-to-severe heart failure
Hypersensitivity to golimumab or latex Severe infection Moderate-to-severe heart failure
Hypersensitivity to vedolizumab
IBD Agents
Immuno- suppressive Agents
Biologics