Page 41 - TNFlipTest
P. 41
Toronto Notes 2019 Airway Management
Routine Monitors for All Cases
• pulseoximeter,BPmonitor,electrocardiography,capnography(requiredforgeneralanesthesiaand deep procedural sedation, Ramsey Sedation Scale 4-6), and an agent-specific anesthetic gas monitor when inhalational anesthetic agents are used
• thefollowingmustalsobeavailable:temperatureprobe,peripheralnervestimulator,stethoscope, appropriate lighting, spirometry, manometer to measure endotracheal tube cuff pressure
Elements to Monitor
• anestheticdepth
■ end-tidal inhaled anesthetic monitoring and EEG monitoring, such as a Bispectral Index monitor,
can be used as assessments of anesthetic depth
■ inadequate: blink reflex present when eyelashes lightly touched, HTN, tachycardia, tearing or
sweating. However, these findings are non-specific ■ excessive: hypotension, bradycardia
• oxygenation:pulseoximetry,FiO2
• ventilation: verify correct position of ETT, chest excursions, breath sounds, ETCO2 analysis, end tidal
inhaled anesthesia analysis
• circulation:heartrate,rhythm,BP,telemetry,oximetry,pulmonarycapillarywedgepressure
• temperature
• hourlyurineoutput
Anesthesia A7
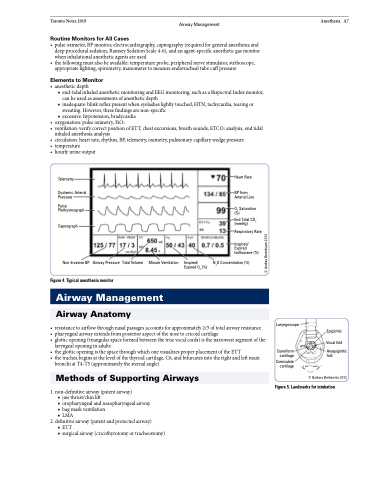
Telemetry
Systemic Arterial Pressure
Pulse Plethysmograph
Capnograph
Non-Invasive BP
Heart Rate
BP from Arterial Line
O Saturation 2
End Tidal CO2 (mmHg)
Respiratory Rate
Inspired/ Expired Isofluorane (%)
N2O Concentration (%)
(%)
Figure 4. Typical anesthesia monitor
Airway Pressure
Tidal Volume
Minute Ventilation
Inspired/ Expired O2 (%)
Airway Management
Airway Anatomy
• resistancetoairflowthroughnasalpassagesaccountsforapproximately2/3oftotalairwayresistance
• pharyngealairwayextendsfromposterioraspectofthenosetocricoidcartilage
• glotticopening(triangularspaceformedbetweenthetruevocalcords)isthenarrowestsegmentofthe
laryngeal opening in adults
• theglotticopeningisthespacethroughwhichonevisualizesproperplacementoftheETT
• thetracheabeginsatthelevelofthethyroidcartilage,C6,andbifurcatesintotherightandleftmain
bronchi at T4-T5 (approximately the sternal angle)
Methods of Supporting Airways
1. non-definitive airway (patent airway)
■ jawthrust/chinlift
■ oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal airway ■ bag mask ventilation
■ LMA
2. definitive airway (patent and protected airway) ■ ETT
■ surgical airway (cricothyrotomy or tracheostomy)
Laryngoscope
Cuneiform cartilage
Corniculate cartilage
Epiglottis
Vocal fold
Aryepiglottic fold
© Barbara Brehovsky 2012
Figure 5. Landmarks for intubation
© Andrea Berenbaum 2014