Page 455 - TNFlipTest
P. 455
Toronto Notes 2019 Pancreas
■ distal pancreatectomy ± splenectomy, lymphadenectomy if carcinoma of midbody and tail of pancreas
■ adjuvant chemotherapy recommended (gemcitabine ± capecitabine, 5-FU/Leucovorin) • locallyadvanced,borderlineresectable
■ tumours that abut the SMA, SMV, portal vein, hepatic artery, or celiac artery • locallyadvanced,non-resectable(palliative→relievepain,obstruction)
■ encasement of major vascular structures including arteries
■ most body/tail tumours are not resectable (due to late presentation)
■ relieve biliary/duodenal obstruction with endoscopic stenting or double bypass procedure
(choledochoenterostomy + gastroenterostomy)
■ palliative chemotherapy (gemcitabine + nab-paclitaxel, FOLFIRNOX) ± radiotherapy
Prognosis
• mostimportantpoorprognosticindicatorsarelymphnodestatus,marginstatus,size>3cm,perineural invasion (invasion of tumour into microscopic nerves of pancreas)
• overall 5 yr survival for all patients with pancreas cancer is 1%; following surgical resection 5 yr survival is 20%
• mediansurvivalforunresectabledisease:3-6moifmetastatic,8-12moiflocallyadvancedat presentation
Table 20. TNM Classification System for Exocrine Tumours of the Pancreas (AJCC 8th edition)
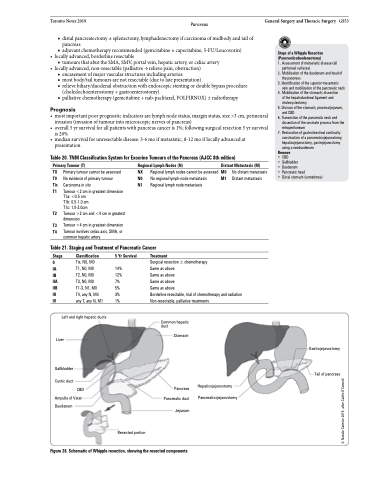
Steps of a Whipple Resection (Pancreaticoduodenectomy)
1. Assessment of metastatic disease (all
peritoneal surfaces)
2. Mobilization of the duodenum and head of
the pancreas
3. Identification of the superior mesenteric
vein and mobilization of the pancreatic neck 4. Mobilization of the stomach; dissection
of the hepatoduodenal ligament and
cholecystectomy
5. Division of the stomach, proximal jejunum,
and CBD
6. Transection of the pancreatic neck and
dissection of the uncinate process from the
retroperitoneum
7. Restoration of gastrointestinal continuity:
construction of a pancreaticojejunostomy, hepaticojejunostomy, gastrojejunostomy using a neoduodenum
Remove
• CBD
• Gallbladder
• Duodenum
• Pancreatic head
• Distal stomach (sometimes)
General Surgery and Thoracic Surgery GS53
Primary Tumour (T)
TX Primary tumour cannot be assessed T0 No evidence of primary tumour
Tis Carcinoma in situ
T1 Tumour <2 cm in greatest dimension
T1a: <0.5 cm T1b: 0.5-1.0 cm T1c: 1.0-2.0cm
T2 Tumour >2 cm and <4 cm in greatest dimension
T3 Tumour >4 cm in greatest dimension
T4 Tumour involves celiac axis, SMA, or
common hepatic artery
Regional Lymph Nodes (N) Distant Metastasis (M)
NX Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed M0 N0 No regional lymph node metastasis M1 N1 Regional lymph node metastasis
No distant metastasis Distant metastasis
Table 21. Staging and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer
Stage
0 IA IB IIA IIB III IV
Classification
Tis, N0, M0
T1, N0, M0
T2, N0, M0
T3, N0, M0 T1-3, N1, M0 T4, any N, M0 any T, any N, M1
Left and right hepatic ducts
5 Yr Survival
14% 12% 7% 5% 3% 1%
Treatment
Surgical resection ± chemotherapy Same as above
Same as above
Same as above
Same as above
Borderline resectable, trial of chemotherapy and radiation Non-resectable, palliative treatments
Liver
Gallbladder Cystic duct
CBD Ampulla of Vater
Duodenum
Common hepatic duct
Stomach
Pancreas Pancreatic duct
Jejunum
Gastrojejunostomy
Tail of pancreas
Resected portion
Hepaticojejunostomy Pancreaticojejunostomy
Figure 26. Schematic of Whipple resection, showing the resected components
© Natalie Cormier 2015, after Caitlin O’Connell