Page 482 - TNFlipTest
P. 482
GM14 Geriatric Medicine
Common Medications Toronto Notes 2019
Preventing Polypharmacy
• consider drug: safer side effect profiles, convenient dosing schedules, convenient route, efficacy
• consider patient: other medications, clinical indications, medical comorbidities
• consider patient-drug interaction risk factors for ADRs
• review drug list regularly to eliminate medications with no clinical indication or with evidence of
toxicity
• avoid treating an ADR with another medication
Inappropriate Prescribing in the Elderly
Epidemiology
• the estimated prevalence of potentially inappropriate prescribing ranges from 12-40%
Beers Criteria
• a list of medications to avoid in adults ≥65 yr due to safety concerns
• 2015 update lists drugs that should be avoided or have their dose adjusted based on the individual’s
kidney function, as well as select drug-drug interactions associated with harms in older adults • examples include long-acting benzodiazepines, strong anticholinergics, high-dose sedatives
• the elderly are also often under-treated (ACEI, ASA, β-blockers, thrombolytics, warfarin)
Principles for Prescribing in the Elderly
CARED
Caution/Compliance
Age (adjust dosage for age)
Review regimen regularly
Educate
Discontinue unnecessary medications Geriatric Pearls. Philadelphia: FA Davis Company, 1999
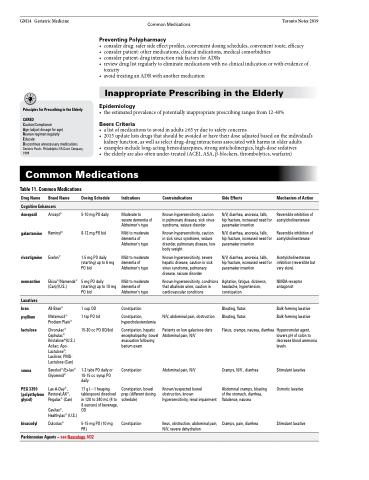
Common Medications
Table 11. Common Medications
Drug Name Brand Name
Cognitive Enhancers
Dosing Schedule
5-10 mg PO daily 8-12 mg PO bid
1.5 mg PO daily (starting) up to 6 mg PO bid
5 mg PO daily (starting) up to 10 mg PO bid
1 cup OD
1 tsp PO tid
15-30 cc PO OD/bid
1-2 tabs PO daily or 10-15 cc syrup PO daily
17 g (~1 heaping tablespoon) dissolved in 120 to 240 mL (4 to 8 ounces) of beverage, OD
5-15 mg PO (10 mg PR)
Indications
Moderate to severe dementia of Alzheimer’s type
Mild to moderate dementia of Alzheimer’s type
Mild to moderate dementia of Alzheimer’s type
Mild to moderate dementia of Alzheimer’s type
Constipation
Constipation, hypercholesterolemia
Constipation, hepatic encephalopathy, bowel evacuation following barium exam
Constipation
Constipation, bowel prep (different dosing schedule)
Constipation
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity, caution in pulmonary disease, sick sinus syndrome, seizure disorder
Known hypersensitivity, caution in sick sinus syndrome, seizure disorder, pulmonary disease, low body weight
Known hypersensitivity, severe hepatic disease, caution in sick sinus syndrome, pulmonary disease, seizure disorder
Known hypersensitivity, conditions that alkalinize urine, caution in cardiovascular conditions
N/V, abdominal pain, obstruction
Patients on low galactose diets Abdominal pain, N/V
Abdominal pain, N/V
Known/suspected bowel obstruction, known hypersensitivity, renal impairment
Ileus, obstruction, abdominal pain, N/V, severe dehydration
Side Effects
N/V, diarrhea, anorexia, falls, hip fracture, increased need for pacemaker insertion
N/V, diarrhea, anorexia, falls, hip fracture, increased need for pacemaker insertion
N/V, diarrhea, anorexia, falls, hip fracture, increased need for pacemaker insertion
Agitation, fatigue, dizziness, headache, hypertension, constipation
Bloating, flatus Bloating, flatus
Flatus, cramps, nausea, diarrhea
Cramps, N/V , diarrhea
Abdominal cramps, bloating of the stomach, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea
Cramps, pain, diarrhea
Mechanism of Action
Reversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase
Reversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase inhibition (reversible but very slow)
NMDA-receptor antagonist
Bulk-forming laxative Bulk-forming laxative
Hyperosmolar agent, lowers pH of colon to decrease blood ammonia levels
Stimulant laxative Osmotic laxative
Stimulant laxative
donepezil galantamine
rivastigmine
memantine
Laxatives
bran psyllium
lactulose
senna
PEG 3350 (polyethylene glycol)
bisacodyl
Aricept® Reminyl®
Exelon®
Ebixa®/Namenda® (Can)/(U.S.)
All-Bran®
Metamucil® Prodiem Plain®
Chronulac® Cephulac® Kristalose®(U.S.) Acilac; Apo- Lactulose®; Laxilose; PMS- Lactulose (Can)
Senokot®/Ex-lax® Glysennid®
Lax-A-Day®, RestoraLAX®, Pegalax® (Can)
Gavilax®, Healthylax® (U.S.)
Dulcolax®
Parkinsonian Agents – see Neurology, N32