Page 530 - TNFlipTest
P. 530
GY44 Gynecology
Gynecological Oncology
Toronto Notes 2019
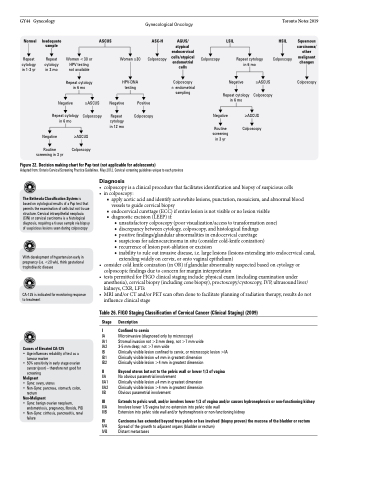
Normal
Repeat cytology in 1-3 yr
Inadequate sample
Repeat cytology in 3 mo
ASCUS
Women <30 or Women ≥30 HPV testing
not available
Repeat cytology HPV-DNA
ASC-H
Colposcopy
AGUS/ atypical endocervical cells/atypical endometrial cells
Colposcopy ± endometrial sampling
LSIL
HSIL
Colposcopy
Squamous carcinoma/ other malignant changes
Colposcopy
Colposcopy
Repeat cytology in 6 mo
in 6 mo
≥ASCUS Negative
testing
Negative
Repeat cytology in 6 mo
≥ASCUS Colposcopy
Negative
Repeat cytology in 6 mo
Colposcopy Repeat cytology in 12 mo
Positive Colposcopy
Negative
Routine screening in 3 yr
≥ASCUS Colposcopy
Negative
≥ASCUS Colposcopy
Routine screening in 3 yr
Figure 22. Decision making chart for Pap test (not applicable for adolescents)
Adapted from: Ontario Cervical Screening Practice Guidelines. May 2012. Cervical screening guidelines unique to each province
Diagnosis
The Bethesda Classification System is based on cytological results of a Pap test that permits the examination of cells but not tissue structure. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or cervical carcinoma is a histological diagnosis, requiring a tissue sample via biopsy of suspicious lesions seen during colposcopy
With development of hypertension early in pregnancy (i.e. <20 wk), think gestational trophoblastic disease
CA-125 is indicated for monitoring response to treatment
Causes of Elevated CA-125
• Age influences reliability of test as a tumour marker
• 50% sensitivity in early stage ovarian cancer (poor) – therefore not good for screening
Malignant
• Gyne: ovary, uterus
• Non-Gyne: pancreas, stomach, colon,
rectum
Non-Malignant
• Gyne: benign ovarian neoplasm, endometriosis, pregnancy, fibroids, PID
• Non-Gyne: cirrhosis, pancreatitis, renal
failure
■ apply acetic acid and identify acetowhite lesions, punctation, mosaicism, and abnormal blood vessels to guide cervical biopsy
■ endocervical curettage (ECC) if entire lesion is not visible or no lesion visible ■ diagnostic excision (LEEP) if:
◆ unsatisfactory colposcopy (poor visualization/access to transformation zone) ◆ discrepancy between cytology, colposcopy, and histological findings
◆ positive findings/glandular abnormalities in endocervical curettage
◆ suspicious for adenocarcinoma in situ (consider cold-knife conization)
◆ recurrence of lesion post-ablation or excision
◆ inability to rule out invasive disease, i.e. large lesions (lesions extending into endocervical canal,
extending widely on cervix, or onto vaginal epithelium)
• considercoldknifeconization(inOR)ifglandularabnormalitysuspectedbasedoncytologyor
colposcopic findings due to concern for margin interpretation
• testspermittedforFIGOclinicalstaginginclude:physicalexam(includingexaminationunder
anesthesia), cervical biopsy (including cone biopsy), proctoscopy/cystoscopy, IVP, ultrasound liver/
kidneys, CXR, LFTs
• MRI and/or CT and/or PET scan often done to facilitate planning of radiation therapy, results do not
influence clinical stage
Table 26. FIGO Staging Classification of Cervical Cancer (Clinical Staging) (2009)
Stage Description
I Confined to cervix
IA Microinvasive (diagnosed only by microscopy)
IA1 Stromal invasion not >3 mm deep, not >7 mm wide
IA2 3-5 mm deep; not >7 mm wide
IB Clinically visible lesion confined to cervix, or microscopic lesion >IA IB1 Clinically visible lesion ≤4 mm in greatest dimension
IB2 Clinically visible lesion >4 mm in greatest dimension
II Beyond uterus but not to the pelvic wall or lower 1/3 of vagina
IIA No obvious parametrial involvement
IIA1 Clinically visible lesion ≤4 mm in greatest dimension IIA2 Clinically visible lesion >4 mm in greatest dimension IIB Obvious parametrial involvement
III Extends to pelvic wall, and/or involves lower 1/3 of vagina and/or causes hydronephrosis or non-functioning kidney
IIIA Involves lower 1/3 vagina but no extension into pelvic side wall
IIIB Extension into pelvic side wall and/or hydronephrosis or non-functioning kidney
IV Carcinoma has extended beyond true pelvis or has involved (biopsy proven) the mucosa of the bladder or rectum
IVA Spread of the growth to adjacent organs (bladder or rectum) IVB Distant metastases
• colposcopyisaclinicalprocedurethatfacilitatesidentificationandbiopsyofsuspiciouscells • incolposcopy: