Page 548 - TNFlipTest
P. 548
H8 Hematology
Common Presenting Problems
Toronto Notes 2019
References
APS: see Hematology, H34
Aplastic Anemia: see Hematology, H17 B12/Folate Deficiency: see Hematology, H23 DIC: see Hematology, H32
HIT: see Hematology, H29
HIV: see Infectious Diseases, ID27
ITP: see Hematology, H27
Myelodysplasia: see Hematology, H39 Preeclampsia: see Obstetrics, OB24
SLE: see Rheumatology, RH11
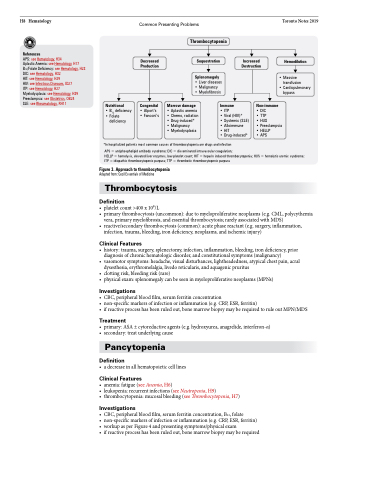
Decreased Production
Congenital
• Alport’s • Fanconi’s
Thrombocytopenia
Sequestration
Splenomegaly
• Liver diseases • Malignancy
• Myelofibrosis
Increased Destruction
Nutritional
• B12 deficiency • Folate
deficiency
Marrow damage
• Aplastic anemia • Chemo, radiation • Drug-induced*
• Malignancy
• Myelodysplasia
Immune
• ITP
• Viral (HIV)*
• Systemic (SLE) • Alloimmune
• HIT
• Drug-induced*
Hemodilution
• Massive transfusion
• Cardiopulmonary bypass
Non-immune
• DIC
• TTP
• HUS
• Preeclampsia • HELLP
• APS
*In hospitalized patients most common causes of thrombocytopenia are drugs and infection
APS = antiphospholipid antibody syndrome; DIC = disseminated intravascular coagulation;
HELLP = hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count; HIT = heparin induced thrombocytopenia; HUS = hemolytic uremic syndrome; ITP = idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura; TTP = thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Figure 3. Approach to thrombocytopenia
Adapted from: Cecil Essentials of Medicine
Thrombocytosis
Definition
• plateletcount>400x109/L
• primarythrombocytosis(uncommon):duetomyeloproliferativeneoplasms(e.g.CML,polycythemia
vera, primary myelofibrosis, and essential thrombocytosis; rarely associated with MDS)
• reactive/secondarythrombocytosis(common):acutephasereactant(e.g.surgery,inflammation,
infection, trauma, bleeding, iron deficiency, neoplasms, and ischemic injury)
Clinical Features
• history:trauma,surgery,splenectomy,infection,inflammation,bleeding,irondeficiency,prior diagnosis of chronic hematologic disorder, and constitutional symptoms (malignancy)
• vasomotorsymptoms:headache,visualdisturbances,lightheadedness,atypicalchestpain,acral dysesthesia, erythromelalgia, livedo reticularis, and aquagenic pruritus
• clottingrisk,bleedingrisk(rare)
• physicalexam:splenomegalycanbeseeninmyeloproliferativeneoplasms(MPNs)
Investigations
• CBC,peripheralbloodfilm,serumferritinconcentration
• non-specificmarkersofinfectionorinflammation(e.g.CRP,ESR,ferritin)
• ifreactiveprocesshasbeenruledout,bonemarrowbiopsymayberequiredtoruleoutMPN/MDS
Treatment
• primary:ASA±cytoreductiveagents(e.g.hydroxyurea,anagrelide,interferon-α) • secondary:treatunderlyingcause
Pancytopenia
Definition
• adecreaseinallhematopoieticcelllines
Clinical Features
• anemia:fatigue(seeAnemia,H6)
• leukopenia:recurrentinfections(seeNeutropenia,H9)
• thrombocytopenia:mucosalbleeding(seeThrombocytopenia,H7)
Investigations
• CBC,peripheralbloodfilm,serumferritinconcentration,B12,folate
• non-specificmarkersofinfectionorinflammation(e.g.CRP,ESR,ferritin) • workupasperFigure4andpresentingsymptoms/physicalexam
• ifreactiveprocesshasbeenruledout,bonemarrowbiopsymayberequired