Page 549 - TNFlipTest
P. 549
Toronto Notes 2019
Common Presenting Problems
Hematology H9
Pancytopenia
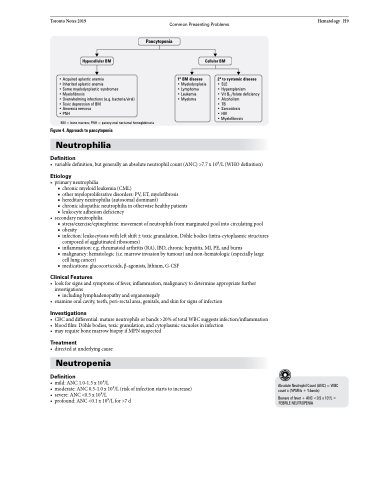
Hypocellular BM
• Acquired aplastic anemia
• Inherited aplastic anemia
• Some myelodysplastic syndromes
• Myelofibrosis
• Overwhelming infections (e.g. bacteria/viral) • Toxic depression of BM
• Anorexia nervosa
• PNH
Cellular BM
BM = bone marrow; PNH = paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Figure 4. Approach to pancytopenia
Neutrophilia
Definition
1o BM disease
• Myelodysplasia • Lymphoma
• Leukemia
• Myeloma
2o to systemic disease
• SLE
• Hypersplenism
• Vit B12/folate deficiency • Alcoholism
• TB
• Sarcoidosis
• HIV
• Myelofibrosis
• variabledefinition,butgenerallyanabsoluteneutrophilcount(ANC)>7.7x109/L(WHOdefinition)
Etiology
• primaryneutrophilia
■ chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
■ other myeloproliferative disorders: PV, ET, myelofibrosis
■ hereditary neutrophilia (autosomal dominant)
■ chronic idiopathic neutrophilia in otherwise healthy patients ■ leukocyte adhesion deficiency
• secondaryneutrophilia
■ stress/exercise/epinephrine: movement of neutrophils from marginated pool into circulating pool
■ obesity
■ infection: leukocytosis with left shift ± toxic granulation, Döhle bodies (intra-cytoplasmic structures
composed of agglutinated ribosomes)
■ inflammation: e.g. rheumatoid arthritis (RA), IBD, chronic hepatitis, MI, PE, and burns
■ malignancy: hematologic (i.e. marrow invasion by tumour) and non-hematologic (especially large
cell lung cancer)
■ medications: glucocorticoids, β-agonists, lithium, G-CSF
Clinical Features
• lookforsignsandsymptomsoffever,inflammation,malignancytodetermineappropriatefurther investigations
■ including lymphadenopathy and organomegaly
• examineoralcavity,teeth,peri-rectalarea,genitals,andskinforsignsofinfection
Investigations
• CBCanddifferential:matureneutrophilsorbands>20%oftotalWBCsuggestsinfection/inflammation • bloodfilm:Döhlebodies,toxicgranulation,andcytoplasmicvacuolesininfection
• mayrequirebonemarrowbiopsyifMPNsuspected
Treatment
• directedatunderlyingcause
Neutropenia
Definition
• mild:ANC1.0-1.5x109/L
• moderate:ANC0.5-1.0x109/L(riskofinfectionstartstoincrease) • severe:ANC<0.5x109/L
• profound:ANC<0.1x109/Lfor>7d
Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) = WBC count x (%PMNs + %bands)
Beware of fever + ANC <0.5 x 109/L = FEBRILE NEUTROPENIA