Page 554 - TNFlipTest
P. 554
H14 Hematology
Microcytic Anemia Toronto Notes 2019
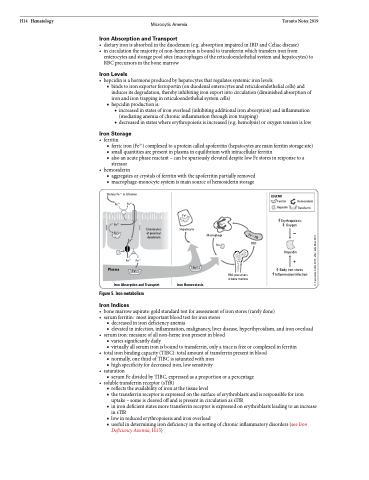
Iron Absorption and Transport
• dietaryironisabsorbedintheduodenum(e.g.absorptionimpairedinIBDandCeliacdisease) • incirculationthemajorityofnon-hemeironisboundtotransferrinwhichtransfersironfrom
enterocytes and storage pool sites (macrophages of the reticuloendothelial system and hepatocytes) to RBC precursors in the bone marrow
Iron Levels
• hepcidinisahormoneproducedbyhepatocytesthatregulatessystemicironlevels
■ binds to iron exporter ferroportin (on duodenal enterocytes and reticuloendothelial cells) and
induces its degradation, thereby inhibiting iron export into circulation (diminished absorption of
iron and iron trapping in reticuloendothelial system cells) ■ hepcidinproductionis:
◆ increased in states of iron overload (inhibiting additional iron absorption) and inflammation (mediating anemia of chronic inflammation through iron trapping)
◆ decreased in states where erythropoiesis is increased (e.g. hemolysis) or oxygen tension is low
Iron Storage
• ferritin
■ ferriciron(Fe3+)complexedtoaproteincalledapoferritin(hepatocytesaremainferritinstoragesite) ■ small quantities are present in plasma in equilibrium with intracellular ferritin
■ also an acute phase reactant – can be spuriously elevated despite low Fe stores in response to a
stressor • hemosiderin
■ aggregates or crystals of ferritin with the apoferritin partially removed ■ macrophage-monocyte system is main source of hemosiderin storage
Dietary Fe3+ in GI lumen Fe3+ Fe2+
Fe2+ Fe3+
Plasma
Enterocytes of proximal duodenum
Fe3+ Hepatocyte
Fe3+
Iron Homeostasis
Fe3+ Macrophage
Erythropoiesis Oxygen
_
Hepcidin
+
Body iron stores Inflammation/infection
Fe2+
Fe2+ Fe3+
Fe3+
RBC
Iron Absorption and Transport Figure 5. Iron metabolism
Iron Indices
• bonemarrowaspirate:goldstandardtestforassessmentofironstores(rarelydone) • serum ferritin: most important blood test for iron stores
■ decreased in iron deficiency anemia
■ elevated in infection, inflammation, malignancy, liver disease, hyperthyroidism, and iron overload • serumiron:measureofallnon-hemeironpresentinblood
■ varies significantly daily
■ virtually all serum iron is bound to transferrin, only a trace is free or complexed in ferritin • totalironbindingcapacity(TIBC):totalamountoftransferrinpresentinblood
■ normally, one third of TIBC is saturated with iron
■ high specificity for decreased iron, low sensitivity • saturation
■ serum Fe divided by TIBC, expressed as a proportion or a percentage • solubletransferrinreceptor(sTfR)
■ reflects the availability of iron at the tissue level
■ the transferrin receptor is expressed on the surface of erythroblasts and is responsible for iron
uptake – some is cleaved off and is present in circulation as sTfR
■ in iron deficient states more transferrin receptor is expressed on erythroblasts leading to an increase
in sTfR
■ low in reduced erythropoiesis and iron overload
■ useful in determining iron deficiency in the setting of chronic inflammatory disorders (see Iron
Deficiency Anemia, H15)
RBC precursors in bone marrow
LEGEND
Ferritin Hemosiderin Hepcidin Transferrin
© Cassandra Cetlin 2015, after Julie Man 2011
Fe3+-Hb