Page 566 - TNFlipTest
P. 566
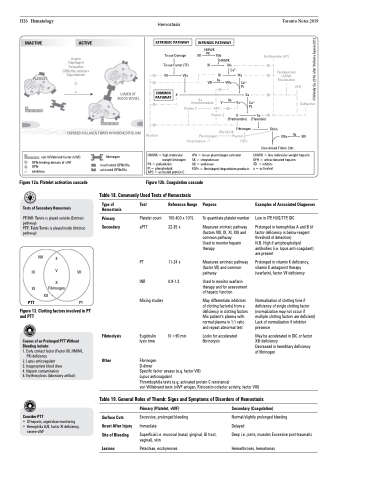
H26 Hematology INACTIVE
PLATELET
Hemostasis
Toronto Notes 2019
ACTIVE
Aspirin Clopidogrel Ticlopidine GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors Dipyridamole
Tissue Damage Tissue Factor (TF)
HMWK
XII PK XIIa
HMWK XI XIa
Antithrombin (AT)
Fondaparinux LMWH Rivaroxaban
EXTRINSIC PATHWAY
COMMON PATHWAY
VII
VIIa
IX VIII IIa
Ca2+
VIIIa
IXa
Ca2+ PL
INTRINSIC PATHWAY
LUMEN OF BLOOD VESSEL
X Xa
UFH Dabigatran
IIa XIII
IIa thrombomodulin
Protein C APC +
Protein S
IIa
V Va
Ca2+ PL
II
(Prothrombin) (Thrombin)
IIa
EXPOSED COLLAGEN FIBRES IN SUBENDOTHELIUM
tPA/SK/UK Fibrinogen Plasmin
FDPs
Fibrin
Warfarin
Plasminogen Tenecteplase
XIIIa Crosslinked Fribrin Clot
Figure 12a. Platelet activation cascade
Tests of Secondary Hemostasis
PT/INR: Tennis is played outside (Extrinsic
pathway)
PTT: Table Tennis is played inside (Intrinsic pathway)
Figure 12b. Coagulation cascade
HMWK = high molecular weight kininogen
PK = prekalikrein
Pl = phospholipid
APC = activated protein C
tPA = tissue plasminogen activator
SK = streptokinase
UK = urokinase
FDPs = fibrin(ogen) degradation products
LMWH = low molecular weight heparin UFH = unfractionated heparin
= inhibits a = activated
von Willebrand factor (vWf) GPIb-binding domain of vWf
GPIb
inhibition
fibrinogen
inactivated GPIIb/IIIa activated GPIIb/IIIa
Table 18. Commonly Used Tests of Hemostasis
XI PTT
XII
Fibrinogen
PT
Figure 13. Clotting factors involved in PT and PTT
Causes of an Prolonged PTT Without Bleeding include:
1. Early contact factor (Factor XII, HMWK,
PK) deficiency
2. Lupus anticoagulant
3. Inappropriate blood draw
4. Heparin contamination
5. Erythrocytosis (laboratory artifact)
Consider PTT
• IV heparin, argatroban monitoring
• Hemophilia A/B, factor XI deficiency,
severe vWF
Fibrinolysis
Other
Fibrinogen
D-dimer
Specific factor assays (e.g. factor VIII)
Lupus anticoagulant
Thrombophilia tests (e.g. activated protein C resistance)
von Willebrand tests (vWF antigen, Ristocetin cofactor activity, factor VIII)
Type of Hemostasis
Primary Secondary
Test
Platelet count aPTT
PT
INR
Mixing studies
Euglobulin lysis time
Reference Range
150-400 x 109/L 22-35 s
11-24 s 0.9-1.2
N >90 min
Purpose
Examples of Associated Diagnoses
Low in ITP, HUS/TTP, DIC
Prolonged in hemophilias A and B (if factor deficiency is below reagent threshold of detection)
N.B. High if antiphospholipid antibodies (i.e. lupus anti-coagulant) are present
Prolonged in vitamin K deficiency, vitamin K antagonist therapy (warfarin), factor VII deficiency
Normalization of clotting time if deficiency of single clotting factor (normalization may not occur if multiple clotting factors are deficient) Lack of normalization if inhibitor presence
May be accelerated in DIC or factor XIII deficiency
Decreased in hereditary deficiency of fibrinogen
VIII
IX V VII X
To quantitate platelet number
Measures intrinsic pathway (factors VIII, IX, XI, XII) and common pathway
Used to monitor heparin therapy
Measures extrinsic pathway (factor VII) and common pathway
Used to monitor warfarin therapy and for assessment of hepatic function
May differentiate inhibitors of clotting factor(s) from a deficiency in clotting factors Mix patient’s plasma with normal plasma in 1:1 ratio and repeat abnormal test
Looks for accelerated fibrinolysis
II
Table 19. General Rules of Thumb: Signs and Symptoms of Disorders of Hemostasis
Surface Cuts Onset After Injury Site of Bleeding
Primary (Platelet, vWF)
Excessive, prolonged bleeding Immediate
Superficial i.e. mucosal (nasal, gingival, GI tract, vaginal), skin
Petechiae, ecchymoses
Secondary (Coagulation)
Normal/slightly prolonged bleeding
Delayed
Deep i.e. joints, muscles Excessive post-traumatic
Lesions
Hemarthroses, hematomas
©Wendy Gu 2016 after Stefania Spano 2012