Page 588 - TNFlipTest
P. 588
H48 Hematology
Malignant Clonal Proliferations of Mature B-Cells Toronto Notes 2019
Malignant Clonal Proliferations of Mature B-Cells
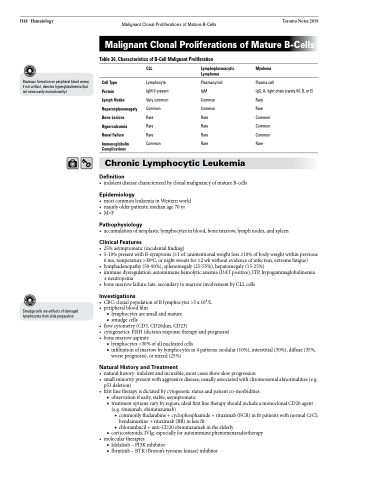
Table 36. Characteristics of B-Cell Malignant Proliferation
Rouleaux formation on peripheral blood smear, if not artifact, denotes hyperglobulinemia (but not necessarily monoclonality)
Cell Type
Protein
Lymph Nodes
Hepatosplenomegaly
Bone Lesions
Hypercalcemia
Renal Failure
Immunoglobulin Complications
CLL
Lymphocyte IgM if present Very common Common Rare
Rare Rare Common
Lymphoplasmacytic Myeloma Lymphoma
Plasmacytoid Plasma cell
IgM IgG, A, light chain (rarely M, D, or E) Common Rare
Common Rare
Rare Common
Rare Common
Rare Common
Rare Rare
Smudge cells are artifacts of damaged lymphocytes from slide preparation
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Definition
• indolentdiseasecharacterizedbyclonalmalignancyofmatureB-cells
Epidemiology
• mostcommonleukemiainWesternworld • mainlyolderpatients;medianage70yr
• M>F
Pathophysiology
• accumulationofneoplasticlymphocytesinblood,bonemarrow,lymphnodes,andspleen
Clinical Features
• 25%asymptomatic(incidentalfinding)
• 5-10%presentwithB-symptoms(≥1of:unintentionalweightloss≥10%ofbodyweightwithinprevious
6 mo, temperature >38oC, or night sweats for ≥2 wk without evidence of infection, extreme fatigue)
• lymphadenopathy(50-90%),splenomegaly(25-55%),hepatomegaly(15-25%)
• immunedysregulation:autoimmunehemolyticanemia(DATpositive),ITP,hypogammaglobulinemia
± neutropenia
• bonemarrowfailure:late,secondarytomarrowinvolvementbyCLLcells
Investigations
• CBC:clonalpopulationofBlymphocytes>5x109/L • peripheralbloodfilm
■ lymphocytes are small and mature
■ smudge cells
• flowcytometry(CD5,CD20dim,CD23)
• cytogenetics:FISH(dictatesresponsetherapyandprognosis) • bonemarrowaspirate
■ lymphocytes >30% of all nucleated cells
■ infiltration of marrow by lymphocytes in 4 patterns: nodular (10%), interstitial (30%), diffuse (35%,
worse prognosis), or mixed (25%)
Natural History and Treatment
• naturalhistory:indolentandincurable;mostcasesshowslowprogression
• smallminoritypresentwithaggressivedisease;usuallyassociatedwithchromosomalabnormalities(e.g.
p53 deletion)
• firstlinetherapyisdictatedbycytogeneticstatusandpatientco-morbidities
■ observation if early, stable, asymptomatic
■ treatment options vary by region; ideal first line therapy should include a monoclonal CD20 agent
(e.g. rituximab, obinutuzumab)
◆ commonly fludarabine + cyclophosphamide + rituximab (FCR) in fit patients with normal CrCl;
bendamustine + rituximab (BR) in less fit
◆ chlorambucil + anti-CD20 obinutuzumab in the elderly
■ corticosteroids, IVIg: especially for autoimmune phenomenaradiotherapy
• moleculartherapies
■ Idelalisib–PI3Kinhibitor
■ Ibrutinib – BTK (Bruton’s tyrosine kinase) inhibitor